Introduction
The Horizontal Marketing System: In today’s highly competitive business environment, traditional vertical marketing systems are gradually being replaced by more collaborative approaches. One such alternative is the horizontal marketing system, wherein companies form strategic alliances and partnerships to gain a competitive edge. This article will delve into the concept of a horizontal marketing system, its benefits, challenges, and real-life examples to illustrate its effectiveness in modern business.
Definition of Horizontal Marketing System
According to Kotler and Keller (2016), a horizontal marketing system is “a marketing system in which two or more unrelated companies put together resources or programs to exploit an emerging marketing opportunity.”
A horizontal marketing system refers to a collaborative approach in which companies within the same industry or complementary sectors form strategic alliances or partnerships to achieve common marketing objectives. Unlike the traditional vertical marketing system, wherein companies operate independently and compete with one another, a horizontal marketing system encourages cooperation and shared resources among participating firms.
This collaborative arrangement aims to leverage the collective strengths and capabilities of the involved companies to enhance market presence, increase competitive advantage, and achieve mutual growth and profitability. By pooling resources, sharing knowledge, and coordinating marketing efforts, companies within a horizontal marketing system seek to achieve synergistic outcomes that would not have been possible through individual efforts alone.
10 Features of a Horizontal Marketing System
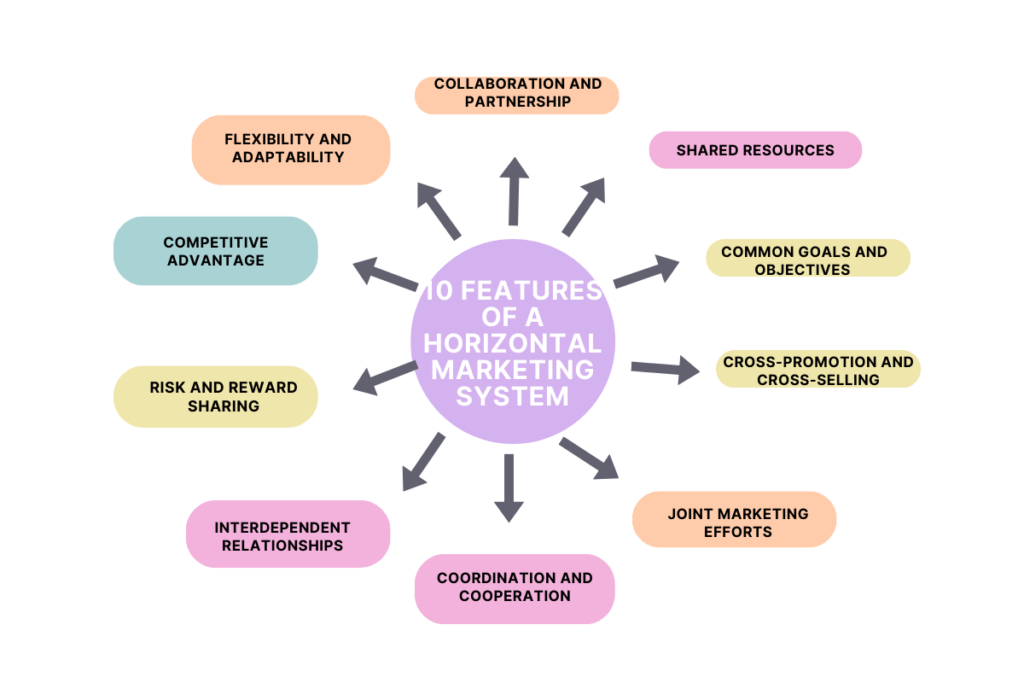
1. Collaboration and Partnership: A horizontal marketing system is characterized by collaboration and partnership between companies. It involves establishing alliances, joint ventures, or cooperative arrangements with other firms within the same industry or complementary sectors.
2. Shared Resources: Participating companies in a horizontal marketing system pool their resources, both financial and non-financial, to achieve common marketing objectives. This includes sharing distribution channels, marketing research, technology, and other relevant resources.
3. Common Goals and Objectives: Companies in a horizontal marketing system align their goals and objectives to create a unified marketing approach. They work together to enhance market presence, increase market share, improve customer satisfaction, or achieve other shared objectives.
4. Cross-promotion and Cross-selling: In a horizontal marketing system, companies engage in cross-promotion and cross-selling activities. They promote each other’s products or services to their customer bases and encourage customers to purchase complementary offerings from partner companies.
5. Joint Marketing Efforts: Companies within a horizontal marketing system collaborate on marketing activities to achieve greater effectiveness and efficiency. This may involve jointly developing marketing campaigns, conducting joint advertising or public relations efforts, or coordinating product launches.
6. Coordination and Cooperation: Effective coordination and cooperation are key characteristics of a horizontal marketing system. Companies work closely together to synchronize their marketing strategies, messages, and tactics for a cohesive and integrated approach.
7. Interdependent Relationships: Companies in a horizontal marketing system rely on each other’s success and mutually benefit from the partnership. The success of one company positively impacts the overall performance and success of the entire system.
8. Risk and Reward Sharing: Companies within a horizontal marketing system share risks and rewards associated with their collaborative efforts. By spreading risks and pooling resources, they can minimize individual exposure and achieve shared benefits.
9. Competitive Advantage: The collaboration in a horizontal marketing system provides participating companies with a competitive advantage. Through shared resources, knowledge exchange, and combined strengths, they can differentiate themselves from competitors and create unique value propositions for customers.
10. Flexibility and Adaptability: Horizontal marketing systems are characterized by flexibility and adaptability to changing market conditions. Companies in the system are responsive to market trends, customer demands, and emerging opportunities, allowing them to quickly adjust their strategies and tactics accordingly.
5 Benefits of a Horizontal Marketing System
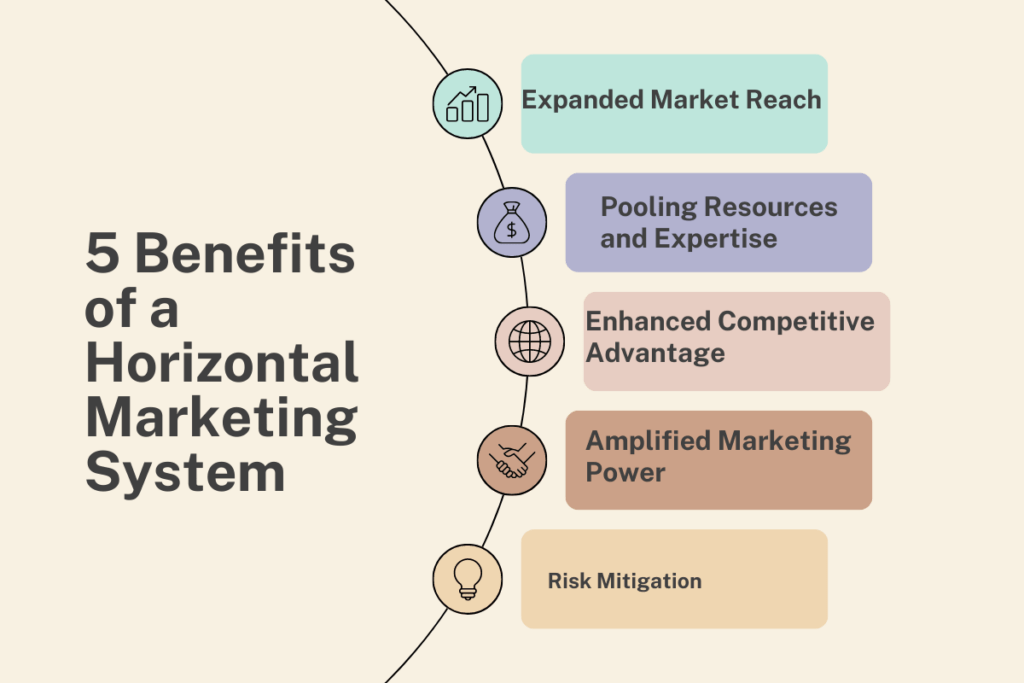
1. Expanded Market Reach: By joining forces with other companies, organizations can gain access to the customer bases of their partners. This expanded customer reach broadens their market coverage, improves brand visibility, and boosts sales potential.
2. Pooling Resources and Expertise: Collaboration among companies often involves pooling resources, both financial and human, allowing for better utilization of assets. This collective strength leads to cost savings, economies of scale, and improved access to diverse skill sets and expertise.
3. Enhanced Competitive Advantage: By partnering with complementary brands, a company can enhance its competitive advantage through shared knowledge, innovation, and improved product offerings. This collaboration can lead to accelerated growth, increased market share, and improved customer satisfaction.
4. Amplified Marketing Power: With multiple companies working together, marketing efforts can be combined, resulting in increased marketing power and effectiveness. This collaborative marketing approach ensures broader exposure and a stronger presence in the market.
5. Risk Mitigation: In a horizontal marketing system, companies can distribute risks among the partners. By diversifying their investments and expanding their product portfolios, companies can reduce the impact of market fluctuations or changes in consumer preferences.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Horizontal Marketing System
Advantages of Horizontal Marketing System
1. Expanded Market Reach: By forming strategic alliances and partnerships, companies in a horizontal marketing system can access new customer segments and expand their market reach. This leads to increased brand visibility, customer acquisition, and revenue potential.
2. Resource Sharing: Participating companies can pool their resources, such as expertise, technology, distribution channels, and financial capabilities. This collaboration allows for cost-sharing, economies of scale, and efficient utilization of resources.
3. Enhanced Competitive Advantage: Collaboration among companies within a horizontal marketing system can lead to a competitive advantage. By leveraging each other’s strengths, companies can create unique value propositions, differentiate themselves from competitors, and offer innovative solutions to customers.
4. Shared Risk and Cost Reduction: In a horizontal marketing system, companies can distribute risks among partners, reducing individual exposure. This sharing of risk also extends to costs, as companies can divide the expenses related to marketing, research and development, and other activities.
5. Knowledge and Learning Opportunities: Collaboration with other firms provides opportunities for knowledge exchange, learning, and skill development. Companies can tap into the expertise and experiences of their partners, leading to enhanced knowledge transfer and innovation.
Disadvantages of Horizontal Marketing System
1. Lack of Control: Companies in a horizontal marketing system might have to relinquish some control over their operations and decision-making processes. This can result in conflicts, disagreements, or differences in strategic direction among the partner firms.
2. Dependency on Partners: Companies become dependent on the performance and actions of their partners. If one partner fails to uphold its commitments or underperforms, it can negatively impact the entire system.
3. Complex Coordination: Coordinating activities, strategies, and communication among multiple firms can be challenging. It requires effective communication channels, coordination mechanisms, and constant collaboration to ensure alignment and harmony within the horizontal marketing system.
4. Potential for Conflict: Collaboration among competitors or companies with different cultures and objectives can lead to conflicts of interest. Disagreements over decision-making, resource allocation, or market positioning can arise and hinder effective collaboration.
5. Limited Autonomy: Companies within a horizontal marketing system may have to make compromises and align their activities with the collective goals of the system. This can limit individual autonomy and flexibility in decision-making.
6. Trust and Relationship Building: Forming and sustaining trust among partners is crucial for the success of a horizontal marketing system. It can take time to develop strong working relationships and establish a foundation of trust, which can be challenging for companies new to collaboration.
7 Types of Horizontal Marketing System
1. Strategic Alliances: Strategic alliances involve companies joining forces to achieve specific strategic objectives. These alliances can be formed between companies in the same industry or complementary sectors. Strategic alliances may involve sharing resources, technology, distribution channels, or engaging in joint marketing activities to achieve competitive advantage and mutual growth.
2. Joint Ventures: Joint ventures occur when two or more companies establish a separate legal entity to pursue a specific business opportunity. This entity is jointly owned and managed by the participating companies, allowing them to pool their resources, share risks and rewards, and collaborate on various aspects of business operations such as production, marketing, and distribution.
3. Cross-Licensing: Cross-licensing agreements occur when companies agree to share intellectual property rights, including patents, trademarks, or copyrights, with each other. This allows companies to leverage each other’s technologies, products, or brand names. Cross-licensing promotes innovation, fosters collaboration, and can lead to the development of new products or services.
4. Franchising: Franchising is a horizontal marketing system where a franchisor grants rights to independent business owners (franchisees) to operate under its established brand and business model. Franchisees benefit from the brand recognition, support systems, and marketing strategies provided by the franchisor, while the franchisor expands its reach and market presence through the franchise network.
5. Consortia: Consortia consist of multiple companies joining together to pursue common goals or business opportunities. These may be formed to address specific industry challenges, develop industry standards, or engage in joint research and development. Consortia facilitate cooperation, knowledge sharing, and resource pooling among participating companies.
6. Co-opetition: Co-opetition is a term used to describe a situation where companies simultaneously cooperate and compete with each other. In a co-opetitive relationship, companies seek mutual benefits by collaborating on certain aspects of their business while competing in other areas. This allows companies to leverage the strengths of their competitors to achieve shared market goals.
7. Industry Associations: Industry associations are formed by companies within the same industry to collaborate on various issues such as market research, lobbying for common interests, standardization efforts, or joint promotional activities. Industry associations foster cooperation, networking, and knowledge sharing among member companies.
Challenges of Implementing a Horizontal Marketing System
While the benefits are compelling, implementing a successful horizontal marketing system is not without its challenges:
1. Trust and Coordination: Building trust among competitors and aligning goals and strategies can be a daunting task. It requires open communication, shared objectives, and effective coordination between partners.
2. Compatibility and Alignment: Ensuring compatibility between partnering companies’ cultures, values, and business models is crucial for seamless integration. Misalignment can hinder collaborative efforts and lead to conflicts.
3. Regulatory and Legal Considerations: Forming alliances or partnerships may require navigating through complex legal and regulatory frameworks. Thorough research and expert advice are essential to ensure compliance and protect all parties involved.
4. Internal Resistance: Introducing change within a company may be met with resistance from employees or stakeholders who may perceive strategic alliances as threats rather than opportunities. Effective change management is crucial to overcome such resistance.
Real-Life Examples of Horizontal Marketing Systems
1. Starbucks and Barnes & Noble Partnership: Starbucks, a renowned coffee chain, formed a partnership with Barnes & Noble, a leading bookstore chain, to open Starbucks cafes within Barnes & Noble bookstores. This collaboration allows customers to enjoy coffee while browsing books, creating a mutually beneficial experience for both companies and attracting customers to their establishments.
2. Nike and Apple Collaboration: Nike and Apple collaborated on the development of Nike+ technology, which allows users to track their fitness activities through Nike+ running shoes and devices connected to iPods and iPhones. This partnership combines Nike’s athletic expertise with Apple’s technology, creating a unique and integrated fitness experience for users.
3. McDonald’s and Coca-Cola Alliance: McDonald’s and Coca-Cola have had a longstanding alliance where Coca-Cola is the exclusive soft drink provider for McDonald’s fast-food restaurants worldwide. This collaboration allows both companies to leverage their strong brand presence and cross-promote their products, benefiting from the synergies between the two renowned brands.
4. GoPro and Red Bull Partnership: Action camera manufacturer GoPro partnered with Red Bull, an energy drink company, to create and promote extreme sports content. This collaboration involves GoPro cameras being used to capture high-energy activities sponsored by Red Bull, enabling both companies to enhance their brand image and reach a specific target audience interested in adventure sports.
5. Microsoft and Intel Alliance: Microsoft and Intel have a strategic alliance aimed at integrating Microsoft software with Intel processors to create compatible and optimized technology products. This collaboration ensures that Microsoft’s operating systems and Intel’s hardware work seamlessly together, providing customers with a reliable and efficient computing experience.
5 Examples of Horizontal Marketing System from India
1. Flipkart-Walmart Partnership: In 2018, U.S. retail giant Walmart acquired a majority stake in Flipkart, one of India’s largest e-commerce companies. This strategic partnership allowed Flipkart to leverage Walmart’s global expertise in supply chain management and retail operations while providing Walmart with access to India’s expanding e-commerce market. Through this collaboration, both companies aimed to enhance their market presence and compete more effectively against competitors like Amazon.
2. Ola-Uber Collaboration: Ride-sharing platforms Ola and Uber have formed a collaborative partnership in various cities across India. The partnership allows passengers to book rides using either platform, promoting convenience and flexibility for users. By collaborating, Ola and Uber aim to leverage each other’s resources and enhance their market coverage while providing a seamless experience for customers.
3. Paytm-ICICI Bank Alliances: Paytm, a digital payment platform, has formed strategic alliances with ICICI Bank, one of India’s largest private sector banks. Through these partnerships, Paytm users can link their digital wallets with their ICICI Bank accounts, enabling seamless transactions and fund transfers. This collaboration helps both companies expand their customer base, enhance payment services, and tap into the growing digital payment market in India.
4. Amul-Dunkin’ Donuts Tie-up: Amul, India’s leading dairy cooperative, collaborated with the international chain Dunkin’ Donuts to offer Amul ice cream and dairy products at Dunkin’ Donuts outlets across the country. This collaboration allowed Dunkin’ Donuts to offer a wider range of dessert options to its customers, while Amul gained access to a new distribution channel and expanded its market presence in the fast-food segment.
5. SpiceJet-Etihad Airways Codeshare Agreement: Indian budget airline SpiceJet entered into a codeshare agreement with Etihad Airways, the national airline of the United Arab Emirates. Through this partnership, passengers can book seamless flights and connect between the two airlines, expanding connectivity options and enhancing travel convenience. The collaboration helps SpiceJet improve its international reach, while Etihad Airways benefits from increased access to domestic Indian routes.
Conclusion
The evolution from traditional vertical marketing systems to horizontal marketing systems is a testament to the changing dynamics of the business world. Horizontal marketing systems provide numerous benefits, including expanded market reach, resource sharing, enhanced competitive advantage, amplified marketing power, and risk mitigation. Despite the challenges faced, successful implementation of a horizontal marketing system has been achieved in various industries, leading to mutually beneficial growth and innovation. As businesses continue to adapt and collaborate, horizontal marketing systems are poised to shape the future of strategic alliances in the marketplace.
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page
