What is Consumer Decision Making Process
The consumer decision-making process is a sequence of cognitive and emotional steps that a consumer goes through when identifying a need or want, gathering information, evaluating alternatives, making a purchase, and reflecting on their satisfaction with the product or service. This process is crucial in understanding consumer behavior and designing effective marketing strategies that cater to the needs and preferences of the target market.
There are several sources that define and explore the consumer decision-making process:
Engel, J. F., Blackwell, R. D., & Miniard, P. W. (1995). Consumer behavior. Fort Worth, TX: Dryden Press.
Engel, Blackwell, and Miniard’s widely cited book “Consumer Behavior” offers an in-depth analysis of the consumer decision-making process, along with other aspects of consumer behavior. The authors discuss various factors that influence each stage of the process and provide insights into how marketers can address these factors to create effective marketing campaigns.
Consumer Behavior by Engel, Blackwell, and Miniard’s
Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G. (2020). Principles of Marketing. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
In their book “Principles of Marketing,” Kotler and Armstrong provide a comprehensive overview of the consumer decision-making process and its implications for marketing strategies. The authors explain the five stages of the process and emphasize the importance of understanding the factors that influence consumers’ decisions to create targeted and impactful marketing efforts.
Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G. (2020)
Solomon, M. R. (2018). Consumer Behavior: Buying, Having, and Being. Boston, MA: Pearson.
Michael R. Solomon’s “Consumer Behavior: Buying, Having, and Being” is another well-regarded source that delves into the consumer decision-making process. The book provides a detailed analysis of the process and offers insights into the various factors that shape consumers’ choices, including psychological, social, and cultural influences.
Solomon, M. R. (2018). Consumer Behavior: Buying, Having, and Being. Boston
These sources offer a comprehensive understanding of the consumer decision-making process, emphasizing its importance in the field of marketing and consumer behavior. By studying these sources, marketers and businesses can better understand how consumers make their purchase decisions and develop marketing strategies that effectively address their needs and preferences.
Introduction to Consumer Decision Making Process
The consumer decision-making process plays a vital role in the success of any business. Understanding how consumers make their purchase decisions helps companies develop effective marketing strategies to target their potential customers and retain loyal ones. This comprehensive blog post delves into the stages of the consumer decision-making process, examining its different stages, and analyzing various factors that influence it. To provide an in-depth understanding, we will explore examples, case studies, relevant statistics, and research findings.
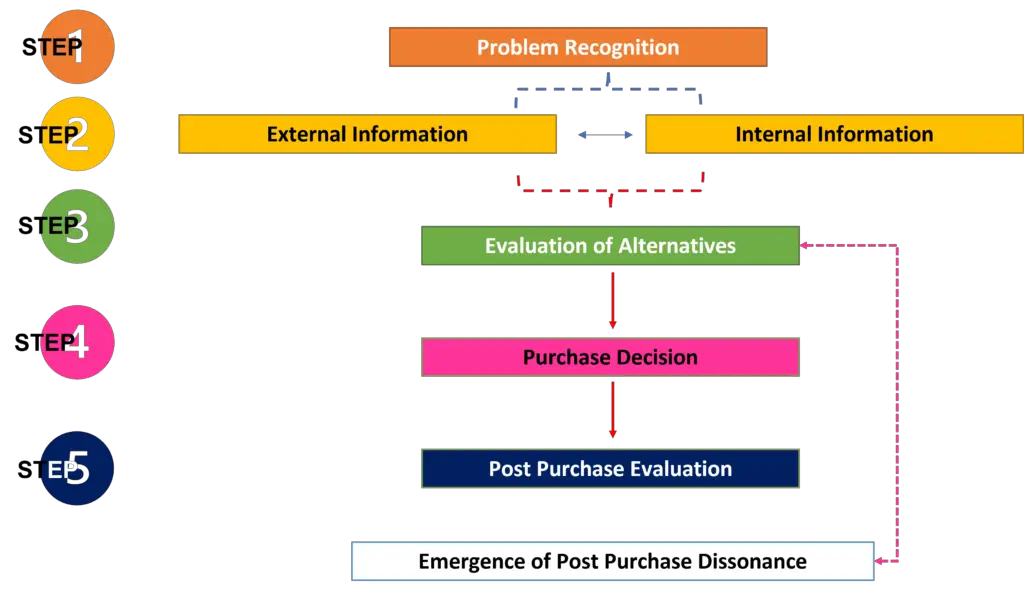
The Five Stages of the Consumer Decision-Making Process
The consumer decision-making process comprises five stages: problem recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase evaluation. Consumers tend to go through all these stages, albeit all the above stages, with varying degrees of intensity and involvement.
Problem Recognition
The consumer decision process begins with problem recognition, an internal or external stimulus that makes the consumer recognize a need or want. Internal stimuli might include personal experiences, feelings, or previous experiences, while external stimuli can come from marketing campaigns, personal sources gather information or brand ambassadors. The goal of marketers at this stage is to build brand awareness and trigger the consumer’s need for recognition.
Example: A consumer might feel thirsty on a hot day, prompting them to look for a refreshing beverage (internal stimulus), or they might see an advertisement for a new smartphone, sparking their interest in upgrading their old device (external stimulus).
Factors influencing Problem Recognition
Problem recognition is the first step in the decision-making process, where a consumer identifies a need or want. Factors influencing problem recognition include:
Internal stimuli: Personal experiences, emotions, or physiological states (e.g., hunger, thirst, or tiredness) can trigger problem recognition.
External stimuli: Marketing efforts, social influences, and environmental factors can prompt consumers to recognize a need or want.
Life events: Changes in personal circumstances, such as moving to a new city, getting married, or having a baby, can create new needs and wants.
Information Search
The information search stage is the next step in the consumer buying process. Once a need is recognized, the consumer gathers information to find solutions to their problem. Consumers might use search engines, personal sources, or previous customers’ reviews to collect data on potential products or services. Marketing efforts, such as targeted advertisements or content marketing, can assist consumers in this information stage.
Example: When searching for a new smartphone, a consumer might read online reviews, compare prices, and ask friends for their opinions.
Factors Influencing Information Search:
After recognizing a problem, consumers seek information about potential products or services to address their needs. Factors influencing consumer feelings during the information search stage include:
Perceived risk: The higher the perceived risk associated with a purchase (e.g., financial, functional, or social), the more extensive the information search is likely to be.
Prior knowledge: Consumers with prior knowledge or experience with a product or service may require less information search.
Personal characteristics: Individual differences, such as motivation, involvement, and cognitive style, can influence the extent of information search.
Available sources: The accessibility and credibility of information sources (e.g., online reviews, personal recommendations, or advertising) can affect the information search process.
Evaluation of Alternatives
After gathering information, the consumer evaluates alternatives based on various criteria, such as product price, features, quality, and brand reputation. Marketing campaigns aimed at highlighting a brand’s unique selling points can influence the consumer’s evaluation process. Consumers tend to evaluate alternatives by comparing their options to their internal criteria for evaluating alternatives and weighing the pros and cons of each.
Example: A consumer might compare prices of smartphones based on battery life, camera quality, processing power, and style options.
Factors Influencing Evaluation of Alternatives:
In this stage of customer journey, consumers compare and evaluate the gathered information to choose the best alternative. Factors influencing the evaluation of alternatives include:
Decision criteria: Consumers use various criteria, such as price, quality, features, and brand reputation, to evaluate alternatives.
Individual preferences: Personal preferences and values can influence the importance placed on different decision criteria.
Cognitive processes: Consumers may use different cognitive processes, such as heuristics or mental shortcuts, to simplify the evaluation of alternatives.
Social influences: Opinions and recommendations from friends, family, or influencers can impact the evaluation process.
Purchase Decision
The consumer recognizes actual purchase decision is the penultimate stage in the decision-making process. The consumer makes their choice and buys the product or service. Factors such as product availability, delivery time, and the buying experience can affect the purchasing decision. Companies should focus on delivering a smooth, hassle-free buying process to convert potential customers into actual buyers.
Example: A consumer might decide to buy a smartphone from an online retailer that offers a competitively priced product with fast delivery.
Factors Influencing Purchase Decision
The purchase decision is the step where consumers make their final choice and buy the product or service. Factors influencing the consumer makes purchase decision include:
Availability: Limited availability or stock can create a sense of urgency and influence the purchase decision.
Buying experience: A smooth and hassle-free buying process can positively impact the purchase decision.
Sales promotions: Discounts, special offers, or incentives can make a product or service more attractive and influence the decision to buy.
External factors: Unforeseen circumstances or changes in personal situations can affect the purchase decision.
Post-Purchase Evaluation
The final stage in the consumer decision-making process is post-purchase evaluation. After the actual purchase itself, the consumer evaluates the product or service based on their personal experiences, comparing it to their initial expectations. A positive post-purchase evaluation can lead to customer satisfaction and loyalty, while a negative evaluation can result in buyer’s remorse, product returns, or negative word-of-mouth.
Example: A satisfied consumer might recommend the smartphone they purchased to a friend, becoming a brand ambassador and contributing to the company’s customer base.
Influencing Factors in the Consumer Decision-Making Process
Factors influencing Post Purchase Evaluation
Product performance: The actual performance of the product or service influences consumer satisfaction and future purchasing behavior.
Cognitive dissonance: Consumers may experience cognitive dissonance if the product or service does not meet their expectations, leading to dissatisfaction or regret.
Word-of-mouth: Positive or negative feedback from others can influence consumers’ post-purchase evaluation and their perception of the product or service.
After-sales support: Effective customer service, warranties, and return policies can impact consumer satisfaction and loyalty during the post-purchase evaluation stage.
Influencing Factors in the Consumer Decision-Making Process
Information Availability
The availability of information can significantly impact the consumer buying decision process. Consumers tend to make purchase decisions based on all the facts they can gather. Easy access to information, such as online reviews, makes it easier for potential customers to evaluate alternatives and make informed buying decisions.
Example: A consumer looking for a new pair of headphones might find numerous reviews and comparisons on various websites, helping them make a well-informed purchasing decision.
Social Influence
Personal sources, such as friends and family, can influence the consumer decision-making process. Consumers tend to trust the opinions of their close ones and often rely on their recommendations when making purchase decisions.
Example: A potential customer might decide to buy a particular brand of headphones because their friend recommended it, based on their positive experience.
Risk Management
Perceived risks, including financial, functional, psychological, and social risks, can influence the consumer buying process. Companies can address these risks by offering guarantees, warranties, or return policies, making potential customers more comfortable with their purchasing decision.
Example: A customer might feel more confident in buying an expensive product if the company offers a one-year warranty and a 30-day return policy.
Marketing Efforts
Marketing efforts, such as advertising, promotional offers, and public relations, can significantly impact the consumer decision process. Effective marketing campaigns can build brand awareness, create a positive brand image, and persuade potential customers to choose a specific product or service.
Example: A well-executed marketing campaign might convince a consumer to buy a new pair of sneakers from a specific brand, even if they had initially considered other alternatives.
Case Study: The Power of Influencer Marketing
In recent years, influencer marketing has become a powerful tool in shaping consumers’ buying decisions. By collaborating with social media influencers who have a strong following and credibility, brands can reach their customer and target market more effectively and persuasively.
A notable example is the collaboration between beauty brand Glossier and a wide range of influencers. Glossier’s influencer marketing efforts have been highly successful in creating a loyal customer base loyal customers, driving sales, and generating positive word-of-mouth.
In this case, influencers play a crucial role in the information search stage of the consumer decision-making process, as potential customers rely on their reviews and recommendations. Moreover, influencers can impact the customer searches and evaluation of alternatives, as their endorsements might persuade consumers to choose Glossier over competitors.

Psychological, social, and cultural influences play a significant role in shaping the consumer decision-making process. These factors can impact the way consumers perceive, process information, evaluate different alternatives together, and make purchase decisions.
Psychological influences:
Perception: Consumers’ perception of a product or service is shaped by their sensory experiences and cognitive interpretation. This perception influences how they process information, evaluate alternatives, and make purchase decisions.
Motivation: The level of motivation or personal interest in a product or service can impact the extent of information search, evaluation, and decision-making. Highly motivated consumers are more likely to engage in a thorough decision-making process.
Learning: Past experiences and learning can impact consumers’ preferences, attitudes, and expectations, influencing their decision-making process. Consumers may rely on their previous experiences to evaluate and choose products or services.
Attitudes: Consumers’ attitudes towards a product, brand, or service can significantly impact their decision-making process. Positive attitudes may lead to favorable evaluations and purchase decisions, while negative attitudes can result in the opposite.
Social influences:
Family: Family members can influence consumers’ preferences, needs, and decision-making processes, as they often share similar values, experiences, and consumption habits.
Reference groups: Reference groups, such as friends, colleagues, or social media influencers, can impact consumers’ decision-making process through recommendations, opinions, or shared experiences. Consumers may be more likely to choose a product or service that has been endorsed by their reference groups.
Social roles and status: Consumers’ social roles and status can affect their decision-making process, as they may seek products or services that align with their position in society or their desired image.
Cultural influences:
Culture: Culture shapes consumers’ values, beliefs, and preferences, which in turn influence their decision-making process. Consumers from different cultural backgrounds may have distinct preferences, evaluation criteria, and decision-making styles.
Subculture: Subcultural groups within a society, such as ethnic or religious groups, can also influence consumers’ decision-making processes. Members of a particular subculture may share specific preferences, values, or consumption habits that impact their purchase decisions.
Social class: Social class can impact consumers’ decision-making processes, as individuals from different social classes may have varying levels of resources, needs, and preferences. Consumers from higher social classes may prioritize luxury, quality, or exclusivity, while those from lower social classes may focus more on affordability and functionality.
Conclusion
Understanding the consumer decision-making process is crucial for businesses looking to attract and retain customers. This in-depth analysis of the buyer decision process, along with relevant examples, case studies, and research findings, provides valuable insights for companies aiming to develop effective marketing strategies.
By acknowledging the five stages of the consumer decision-making process – problem recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, the purchase decision, and post-purchase evaluation – businesses can tailor their marketing efforts to address the unique needs of consumers at each stage. Additionally, considering factors such as information availability, social influence, risk management, and marketing efforts to previous customers, companies can create a comprehensive approach to target their desired market and ensure customer satisfaction.
In the ever-evolving landscape of consumer behavior, staying informed and adaptable is essential for businesses to succeed. By leveraging the insights provided in this blog post, companies can create informed marketing stra
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page