Introduction
Kelley’s Followership Model: In the realm of management, leaders often take center stage, receiving accolades and attention for their accomplishments. However, it is crucial to recognize the vital role that followers play in an organization’s success. Kelley’s Followership Model sheds light on the critical characteristics and behavior of followers, emphasizing their immense potential and impact. By dissecting this model, we can understand how effective followership can contribute to a collaborative and successful work environment.
The Foundation of Kelley’s Followership Model: 5 Types of Followers
At the core of Kelley’s Followership Model lie five key followership styles: the sheep, the yes-person, the alienated, the effective follower, and the exemplary follower. Each style reflects a unique combination of independent thinking, active participation, and relationship-building within the organization.
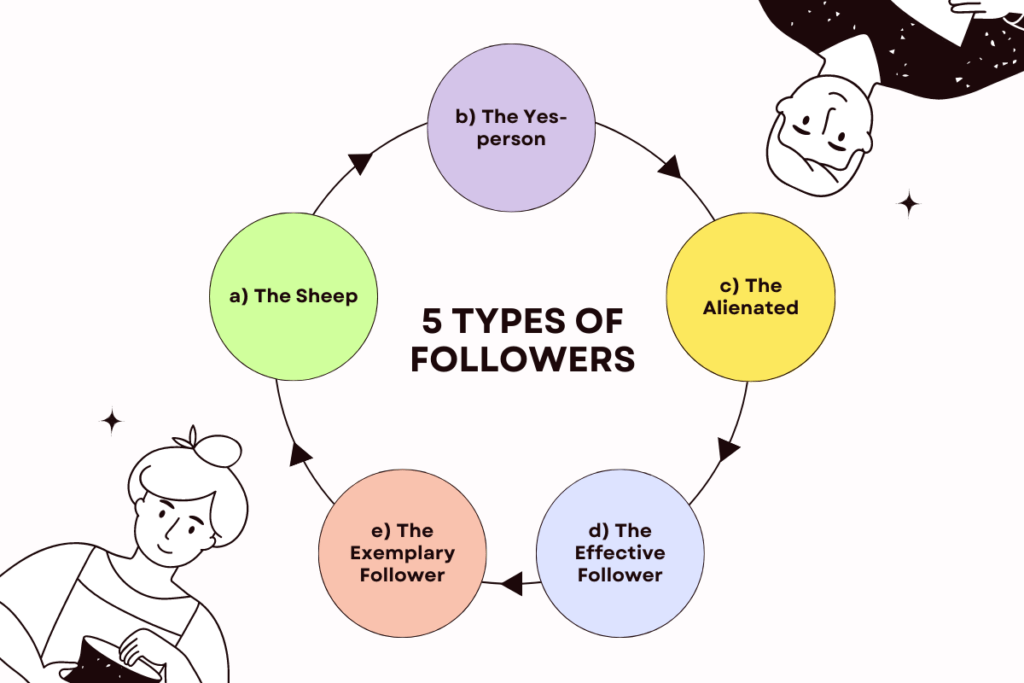
a) The Sheep
Sheep followers are highly dependent on their leaders. They lack initiative, rarely question decisions, and tend to accept orders without much thought or contribution. While these individuals may provide stability and obedience, they seldom bring innovative ideas or challenge the status quo.
b) The Yes-person:
Similar to sheep followers, yes-person followers demonstrate a high level of dependency on leaders. However, they tend to falsely agree with everything their leaders say or do, often resulting in groupthink. This conformity inhibits constructive criticism and stifles creativity, hindering the growth and progress of the organization.
c) The Alienated:
Alienated followers possess low levels of independent thinking and active participation. They are often critical, cynical, and disengaged with their work. Alienated followers tend to distance themselves from their leaders and the organization as a whole, leading to diminished productivity and increased turnover rates.
d) The Effective Follower:
Effective followers are valuable assets to any organization. They are self-reliant, critical thinkers, and actively engaged in their work. These followers display a healthy balance between independent thought and collaboration, and they embrace constructive feedback. Effective followers possess qualities that leaders seek, as they contribute to positive organizational outcomes, spur innovation, and drive growth.
e) The Exemplary Follower:
Exemplary followers embody the pinnacle of followership. They display exceptional initiative, strong critical thinking skills, and the ability to inspire others. These individuals possess a keen sense of self-awareness and are consistently reliable, proactive, and ethical in their actions. Exemplary followers not only support their leaders but also challenge them when necessary, helping the organization grow and adapt to changing environments.
Characteristics of 5 types of Kelley’s Followership Model with Real life Examples
1. The Sheep
– Display high dependency on leaders.
– Lack initiative, rarely questioning decisions.
– Accept orders without much thought or contribution.
Real-life example: In the infamous Stanford Prison Experiment, conducted by Dr. Philip Zimbardo, participants took on the role of guards and prisoners. Some of the participants who assumed the role of prisoners exhibited sheep followership characteristics by unquestioningly obeying the orders of the guards, despite the unethical treatment they were subjected to.
2. The Yes-person
– Exhibit high dependency on leaders.
– False agreement with everything leaders say or do.
– Conformity leading to groupthink.
Real-life example: During the Watergate scandal, many individuals working in the administration of President Richard Nixon demonstrated yes-person followership by blindly supporting and covering up illegal activities within the government, ultimately leading to their downfall.
3. The Alienated
– Show low levels of independent thinking and active participation.
– Critical, cynical, and disengaged with their work.
– Distance themselves from leaders and the organization.
Real-life example: At Enron, employees who began to question the unethical practices and financial mismanagement of the company were often marginalized and excluded from decision-making processes. These alienated followers felt disconnected from the organization and its leaders, ultimately contributing to Enron’s downfall.
4. The Effective Follower
– Exhibit self-reliance and critical thinking skills.
– Actively engaged in their work.
– Strike a balance between independent thought and collaboration.
Real-life example: Steve Jobs was known for fostering effective followership at Apple. He encouraged his team members to think outside the box, challenge ideas, and actively contribute to the development of innovative products. This culture of effective followership played a significant role in Apple’s success.
5. The Exemplary Follower:
– Display exceptional initiative and strong critical thinking skills.
– Inspire others through their actions.
– Exhibit self-awareness, reliability, proactivity, and ethical conduct.
Real-life example: Mahatma Gandhi exemplified exemplary followership during India’s independence movement. Through nonviolent protests, civil disobedience, and self-sacrifice, he inspired millions of followers, leading to significant social and political changes in India.
Remember, these examples are intended to demonstrate the general characteristics associated with each type of followership. In reality, individuals can exhibit a combination of followership styles depending on the context and their relationship with leaders.
Application of Kelley’s Followership Model
While Kelley’s model aims to analyze and classify followership styles, it also acknowledges that followership is not a fixed characteristic. Rather, individuals can display various styles depending on the context and their relationship with leaders. Here are some practical examples of how Kelley’s Followership Model can be applied:
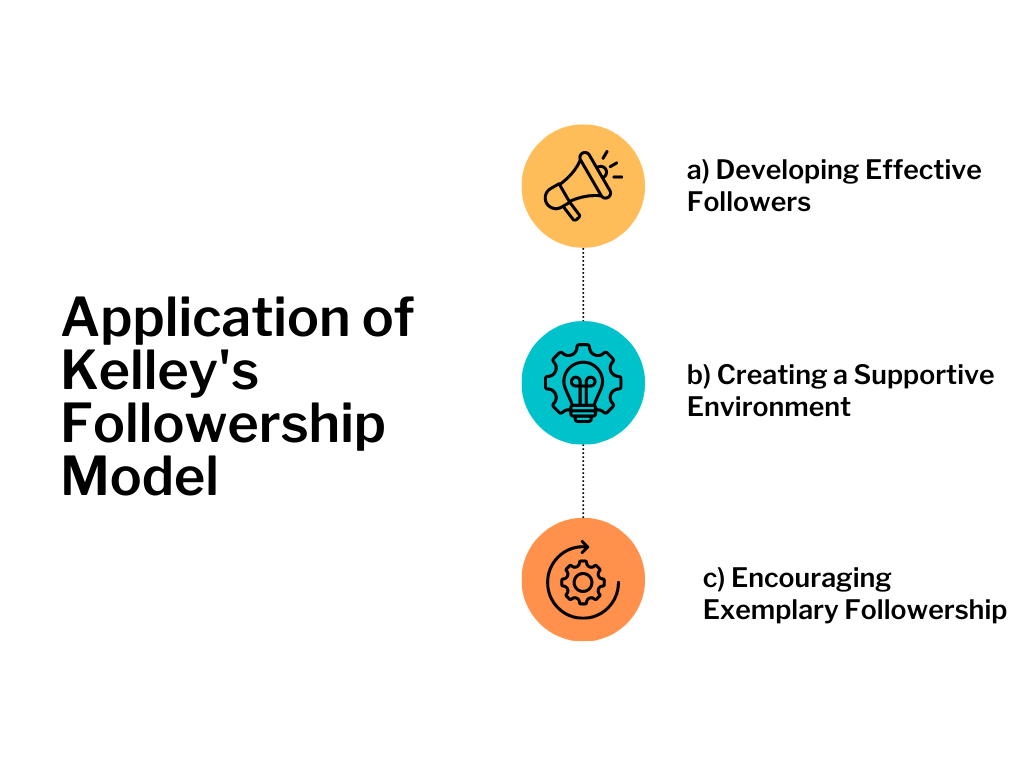
a) Developing Effective Followers:
Leaders can actively foster a culture of effective followership by encouraging autonomy and critical thinking among their team members. By promoting open communication channels, leaders empower their followers to voice their ideas, challenge norms, and actively participate in decision-making processes.
b) Creating a Supportive Environment:
Leaders should strive to create an environment where trust and collaboration are valued, allowing followers to feel safe in expressing their thoughts and opinions. Recognizing the unique strengths of each follower can enable leaders to assign appropriate responsibilities and further develop their followers’ skills and talents.
c) Encouraging Exemplary Followership:
Through their own behavior, leaders can inspire exemplary followership by consistently modeling integrity, accountability, and professionalism. When leaders demonstrate excellence in their role, followers are more likely to adopt similar qualities and strive for higher levels of performance.
Real-Life Examples of Kelley’s Followership Model
Kelley’s Followership Model finds its roots in numerous real-life examples that demonstrate the profound impact of effective followership:
a) Rosa Parks and the Civil Rights Movement:
Rosa Parks’ refusal to give up her seat on a bus in Montgomery, Alabama, sparked one of the most significant events in the Civil Rights Movement. Her act of defiance was a display of effective followership, as she challenged the prevailing unfair norms and inspired others to join her in the fight against racial segregation.
b) The Apollo 13 Mission:
During the Apollo 13 mission, NASA faced a critical situation when an oxygen tank exploded, jeopardizing the lives of the astronauts. Engineers on the ground and crew members in space demonstrated exemplary followership by working tirelessly to overcome challenges, support one another, and ultimately bring the astronauts safely home.
Relevance of Kelley’s Followership Model in Modern Corporate Setting
In the modern corporate setting, Kelley’s Followership Model holds great relevance as organizations increasingly recognize the importance of followers in achieving success. Here are some reasons why Kelley’s Followership Model remains valuable today:
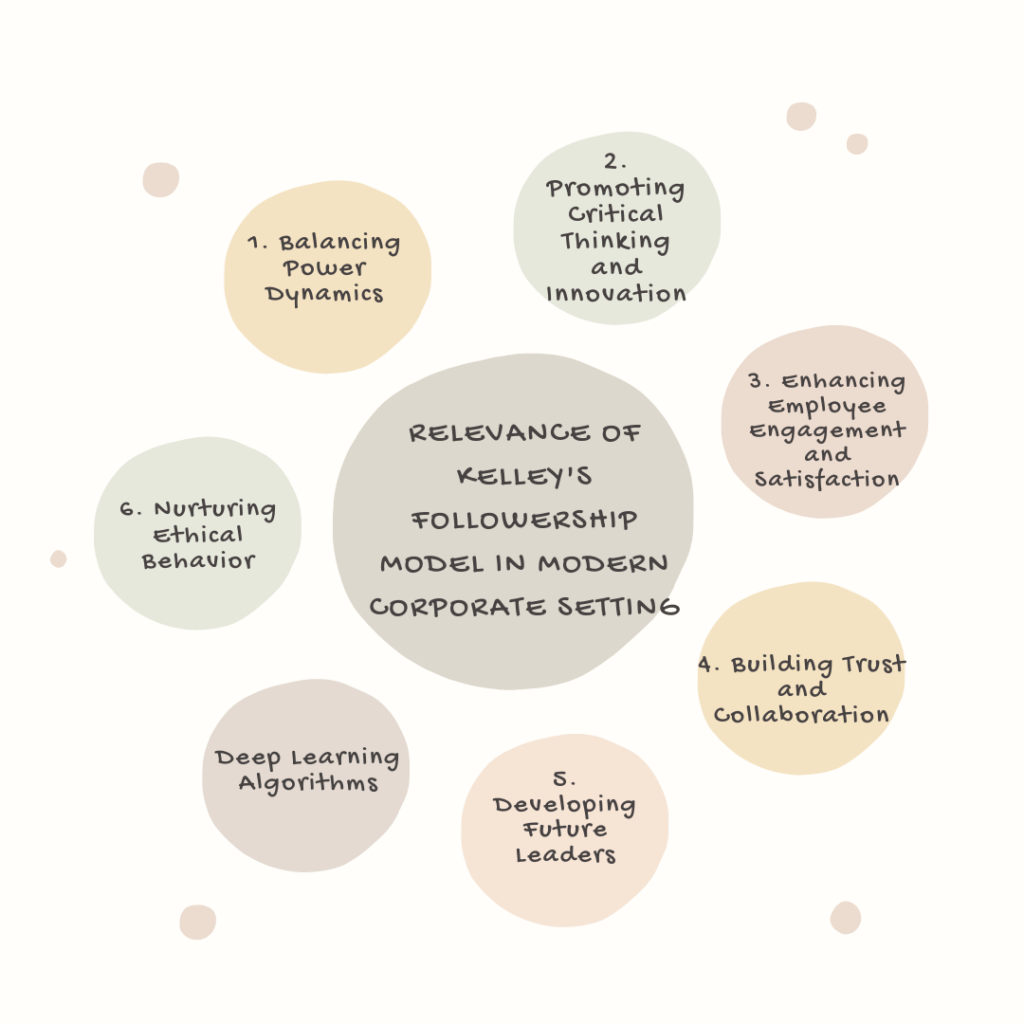
1. Balancing Power Dynamics:
Kelley’s Followership Model helps create a more balanced power dynamic between leaders and followers. It encourages leaders to view followers as active contributors rather than passive receivers of directives. By recognizing followers’ strengths and empowering them to voice their ideas and opinions, organizations can foster a culture of collaboration and shared decision-making.
2. Promoting Critical Thinking and Innovation:
Effective followers are critical thinkers who actively engage in their work. They are not afraid to challenge the status quo and offer new solutions to problems. Embracing the principles of Kelley’s Followership Model helps organizations tap into the collective intelligence of their teams, unlocking innovation, and driving continuous improvement.
3. Enhancing Employee Engagement and Satisfaction:
When followers feel valued and empowered, their engagement and satisfaction levels rise. Organizations that implement the principles of Kelley’s Followership Model cultivate an environment where followers can contribute meaningfully, fostering a sense of purpose and fulfillment in their work. This, in turn, enhances employee retention and productivity.
4. Building Trust and Collaboration:
Kelley’s Followership Model emphasizes the importance of trust and collaboration between leaders and followers. By embracing effective followership, leaders demonstrate their trust in their teams, leading to increased loyalty and dedication. Effective followers, on the other hand, actively support their leaders and promote a positive team dynamic built on trust and mutual respect.
5. Developing Future Leaders:
The model acknowledges that followership is not a one-way street but rather a continuum where individuals can transition between different styles. This recognition allows organizations to identify potential future leaders among their followers. By fostering effective and exemplary followership, organizations can develop a pipeline of individuals who possess the necessary qualities and skills to step into leadership roles.
6. Nurturing Ethical Behavior:
Kelley’s model emphasizes the importance of ethics and integrity in followership. Effective and exemplary followers not only challenge their leaders but also hold themselves accountable for their actions. This commitment to ethical behavior helps organizations maintain a strong moral compass, fostering a culture of honesty and transparency.
Conclusion
Kelley’s Followership Model highlights the importance of followers and their potential to drive organizational success. By understanding the various followership styles and cultivating an environment that promotes effective and exemplary followership, leaders can tap into the immense capabilities of their team members. Recognizing followers as valuable contributors and empowering them to voice their ideas and challenge existing norms fosters a dynamic, innovative, and collaborative work culture. Ultimately, embracing the power of effective followership leads to stronger teams, improved outcomes, and increased organizational resilience
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page

