What would occur in the First step of management by objectives?
The first step in the management by objectives (MBO) process is to define clear and specific objectives. This involves setting goals that are measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
In this step, managers and employees work together to establish objectives that align with the organization’s overall vision and strategic goals. The objectives should be specific enough to provide clarity and direction, but also flexible enough to allow for adaptation and growth.
During this step, it is important to involve all relevant stakeholders in the goal-setting process to ensure buy-in and alignment. This includes managers, employees, and even customers and shareholders, depending on the nature of the objectives.
Additionally, it is crucial to consider the resources and support required to achieve the objectives. This includes allocating the necessary budget, manpower, and technology to ensure successful implementation.
By clearly defining objectives in the first step of Management By Objectives (MBO), organizations lay the foundation for a structured and goal-oriented approach to management. This helps to enhance productivity, focus efforts, and drive success.
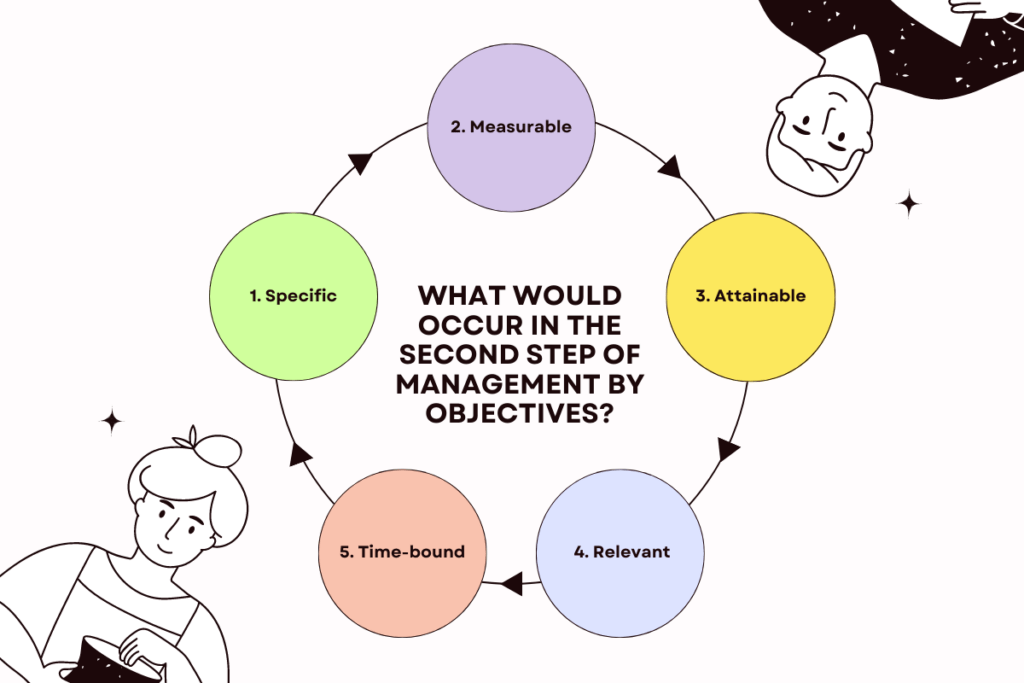
What would occur in the Second step of management by objectives?
In the second step of Management by Objectives (MBO), the focus is on setting clear objectives and SMART goals. This step is crucial as it lays the foundation for effective implementation of Management By Objectives (MBO) principles.
Setting specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals is essential for ensuring that objectives are well-defined and can be effectively measured and evaluated. Let’s delve into each element of SMART goals:

1. Specific: Objectives should be clear and specific to provide clarity and focus. Vague or ambiguous goals can lead to confusion and lack of direction. For example, instead of setting a generic goal like “increase sales,” a specific goal would be “increase sales by 10% in the next quarter.”
2. Measurable: Objectives should be measurable to track progress and determine the level of success. Measurable goals are quantifiable and allow for the assessment of performance and achievement. For instance, instead of setting a broad goal of “improve customer satisfaction,” a measurable goal would be “increase customer satisfaction ratings by 15%.”
3. Attainable: Objectives should be achievable and realistic within the given resources and constraints. Setting unattainable or unrealistic goals can demotivate employees and hinder progress. It is important to consider the available resources, capabilities, and external factors when setting goals.
4. Relevant: Objectives should be relevant and aligned with the organization’s overall strategy and priorities. Setting goals that are directly tied to the organization’s mission and vision ensures that efforts are focused on what truly matters. Each goal should contribute to the broader objectives of the organization.
5. Time-bound: Objectives should have a specific timeframe or deadline for completion. Setting deadlines creates a sense of urgency and helps prioritize tasks. It also allows for tracking progress and holding individuals accountable. For example, instead of setting a goal of “improve employee training,” a time-bound goal would be “implement a new employee training program by the end of the quarter.”
By incorporating the SMART approach, organizations can ensure that their objectives are well-defined, achievable, and aligned with the overall vision. This clarity and specificity lead to increased motivation, focus, and ultimately, improved performance.
What would occur in the Third step of management by objectives?
The third step in the management by objectives (MBO) process is to align employee goals with organizational targets. This step is crucial for ensuring that individual objectives are in line with the broader goals of the organization.
By aligning employee goals with organizational targets, companies can create a seamless connection between individual and organizational objectives, fostering a sense of unity and purpose among employees.
One notable case study in this regard is the implementation of Management By Objectives (MBO) at Google. Google adopted MBO as a key management tool to foster innovation and drive growth. By aligning individual goals with the company’s broader objective of organizing the world’s information and making it universally accessible and useful, Google created an environment that encouraged employees to think creatively and take risks.
To achieve effective alignment, organizations can employ several strategies. First, it is important to clearly communicate the organization’s vision and mission to employees so they understand the bigger picture and how their individual goals contribute to it. Regular communication and transparency are crucial in fostering this understanding.
Second, organizations can set up regular check-ins or performance reviews to ensure that employees’ objectives are aligned with organizational targets and to provide guidance as needed. This helps employees stay on track and make any necessary adjustments to their goals.
Additionally, organizations can encourage collaboration and cross-functional projects to promote a better understanding of the different roles and departments within the organization. This allows employees to see how their individual objectives fit within the larger organizational framework, leading to better coordination and alignment.
Finally, it is important to provide the necessary resources and support for employees to achieve their goals. This can include training, mentoring, and providing access to tools and technologies that enable employees to perform at their best.
By aligning employee goals with organizational targets, companies can create a culture of shared accountability and collective success. This not only leads to improved performance and productivity but also enhances employee satisfaction and engagement.
What would occur in the Fourth step of management by objectives?
In the fourth step of Management by Objectives (MBO), the focus is on enhancing performance through regular feedback and evaluation. This step involves regularly assessing employee progress towards their objectives and providing feedback on their performance.
During this step, managers and employees collaborate to review the employee’s progress and discuss any challenges or barriers they may be facing. The manager provides constructive feedback on areas where the employee is excelling and areas where they can improve.
The purpose of regular feedback and evaluation is to keep employees engaged and motivated, and to ensure that they are on track to meet their objectives. It also provides an opportunity for managers to recognize and reward employees for their accomplishments.
The feedback and evaluation process in Management By Objectives (MBO) is typically based on specific criteria and metrics that were established during the goal-setting phase. This allows for an objective evaluation of performance and provides a clear standard against which employees can be measured.
In addition to providing feedback, this step also involves discussing and addressing any issues or challenges that may be hindering employee performance. It may also involve identifying opportunities for further development or training to help employees improve and achieve their objectives.
Overall, the fourth step of Management By Objectives (MBO) is crucial for enhancing performance and ensuring that employees are continuously improving and growing within their roles. By providing regular feedback and evaluation, organizations can foster a culture of accountability and drive employee performance.
Which theorist created “management by objectives” in US businesses?
Peter Drucker, often referred to as the father of modern management, introduced the concept of Management By Objectives (MBO) in his 1954 book, “The Practice of Management.” This book revolutionized the field of management by emphasizing the importance of setting clear objectives and aligning them with individual and organizational goals.
Drucker believed that traditional management styles were becoming obsolete in the rapidly changing business world. He proposed a more results-oriented approach that focused on collaboration, accountability, and continuous improvement. This approach eventually came to be known as “management by objectives.”
MBO is based on the principle that employees perform better when they have a clear understanding of what is expected of them and are involved in the goal-setting process. It involves a systematic approach that includes setting objectives, monitoring progress, providing regular feedback, and evaluating performance.
What is a reason why management by objectives (mbo) efforts can sometimes fail?
One reason why management by objectives (MBO) efforts can sometimes fail is due to a lack of clear communication and understanding of the objectives and goals. If employees are not properly informed and involved in the goal-setting process, they may not fully understand what is expected of them and how their work aligns with the larger organizational objectives. This can lead to confusion, lack of motivation, and ultimately, failure to achieve the desired outcomes.
Additionally, if the objectives and goals set during the Management By Objectives (MBO) process are unrealistic or not aligned with the resources and capabilities of the organization, it can lead to failure. Setting overly ambitious or unattainable goals can breed frustration and demotivation among employees, as they may feel overwhelmed or unsupported in their efforts to achieve them.
Another reason for MBO failure is a lack of accountability and follow-up. It is not enough to simply set objectives and goals; there needs to be a system in place for regular monitoring, feedback, and evaluation of progress. If there is no mechanism to track and measure performance against the established objectives, it becomes easy for employees to lose focus and for the MBO process to lose effectiveness.
Resistance to change can also pose a significant challenge in the implementation of MBO. Some employees may be resistant to adopting a new management approach, especially if they are accustomed to a more traditional “command and control” style of management. Overcoming this resistance requires effective change management strategies, clear communication of the benefits of MBO, and perhaps even training and support to help employees understand and embrace the new approach.
Ultimately, the success of MBO depends on various factors, including clear communication, achievable objectives, regular monitoring and evaluation, and effective change management. By addressing these potential pitfalls and proactively managing the implementation process, organizations can increase their chances of successfully implementing MBO and reaping its benefits.
A central characteristic of management by objectives is that?
it promotes open and effective communication within an organization. One company that exemplifies this is Southwest Airlines, which has successfully implemented MBO and used it to drive their communication strategy.
Southwest Airlines is known for its strong company culture and customer-centric approach. The airline industry is highly competitive, and Southwest has set itself apart by focusing on employee engagement and satisfaction. They realized that in order to achieve their goals and deliver exceptional customer service, they needed to align their employees’ objectives with the company’s objectives.
To do this, Southwest Airlines implemented a comprehensive system of goal-setting and communication. They established clear and specific objectives for each department and employee, ensuring that everyone understood their role in the company’s success. These objectives were aligned with the overall organizational goals, such as improving customer satisfaction and increasing operational efficiency.
Southwest also emphasized the importance of regular feedback and evaluation. They implemented a performance management system that allowed employees to track their progress towards their objectives and receive feedback from their managers. This created a culture of continuous improvement and allowed employees to make adjustments to their goals and performance as needed.
In terms of communication, Southwest Airlines made sure that their employees were well-informed about the company’s goals and objectives. They held regular town hall meetings, where senior leaders would communicate updates on the company’s progress and share success stories. They also created an interactive intranet platform, where employees could access information about their objectives, track their progress, and collaborate with their colleagues.
Additionally, Southwest Airlines emphasized the importance of two-way communication. They encouraged their employees to provide feedback and suggestions on how the company could improve. This not only fostered a sense of ownership and engagement among employees but also allowed the company to identify and address any issues or challenges that arose.
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page