Introduction
Management by Objectives: In today’s competitive business landscape, effective management is essential for organizations to thrive. Management by Objectives (MBO), a strategic approach established by renowned management consultant Peter Drucker, has emerged as a powerful tool for achieving organizational goals and improving employee performance. In this blog post, we will delve into the essence of Management by Objectives (MBO), explore its implementation framework, and examine its impact on organizations through real-life case studies and statistical data.
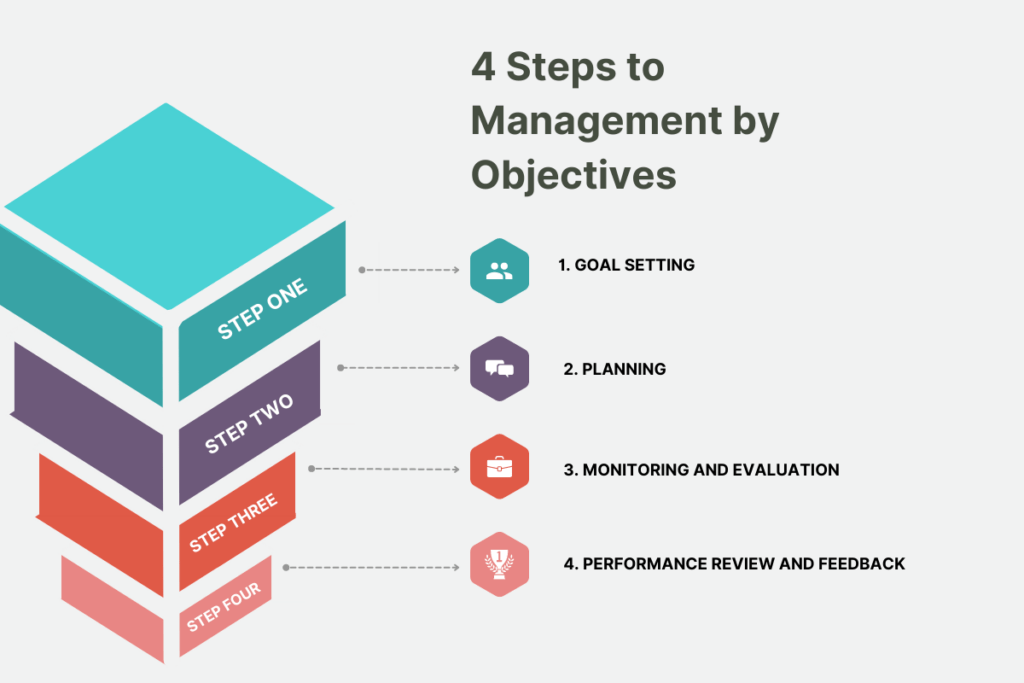
4 Steps to Management by Objectives
The four steps in Management by Objectives (MBO) are:

1. Goal Setting: This is the initial step in Management by Objectives (MBO), where specific and measurable objectives are set for individuals or teams. These goals should align with the overall organizational objectives and should be created in collaboration between managers and employees. The goals should be clear, concise, and challenging, yet attainable.
2. Planning: Once the goals are set, the next step is to develop action plans to achieve those objectives. Managers and employees need to identify the tasks, resources, and timeline required to accomplish the goals. This involves breaking down the goals into smaller, manageable tasks and creating a roadmap for their completion.
3. Monitoring and Evaluation: In this step, progress towards the objectives is tracked and measured regularly. Managers provide feedback and guidance to employees to help them stay on track and address any obstacles or challenges that arise. Regular check-ins and performance evaluations are conducted to assess the progress and make any necessary adjustments to the action plans.
4. Performance Review and Feedback: The final step in Management by Objectives (MBO) is the performance review where the achievements and results are evaluated against the set objectives. Managers provide feedback and discuss areas of improvement or success. This step is essential for recognizing employees’ efforts, rewarding their accomplishments, and identifying any areas where additional support or resources may be required. It also sets the foundation for setting new objectives for the next performance cycle.
Understanding the Essence of Management by Objectives
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a management philosophy that emphasizes goal setting, planning, execution, and performance evaluation. It enables organizations to align individual efforts with their overall objectives, fostering accountability, motivation, and continuous improvement. The core principles of MBO include:
a. Top-down goal alignment: Objectives are set by top-level management and then cascaded down to further levels, ensuring alignment and unity within the organization.
b. Participative goal setting: Employees actively participate in the goal-setting process, enabling greater commitment and ownership.
c. Clear communication: Effective communication ensures that goals and expectations are coherent and understood by all.
d. Results-oriented focus: The emphasis is on outcomes rather than tasks, encouraging employees to achieve measurable results.
e. Ongoing performance evaluation: Regular feedback and evaluation sessions help monitor progress and identify areas of improvement.
f. Motivation and rewards: MBO fosters a sense of achievement through recognition and rewards, enhancing employee motivation and commitment.
Historical context: Peter Drucker’s seminal work and its impact in Management By Objectives
Peter Drucker’s groundbreaking book, “The Practice of Management” (1954), introduced the concept of Management by Objectives (MBO) to the world. His insights revolutionized management practices, emphasizing the importance of aligning individual goals with organizational objectives. Drucker’s work laid the foundation for modern management principles and significantly impacted the way organizations operate today.
Management By Objectives: Setting Clear Objectives and SMART Goals
Clear and specific objectives are the foundation of Management by Objectives (MBO). SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-bound) ensure that objectives are well-defined, actionable, and aligned with the organization’s vision. Here are some illustrative examples from various industries:
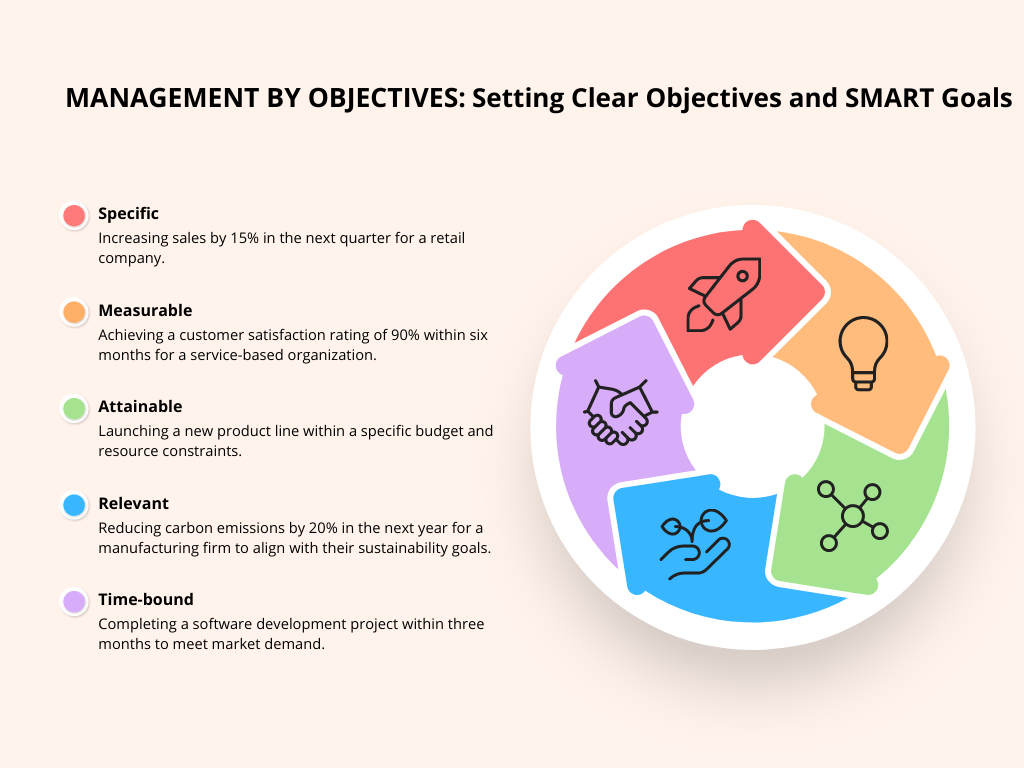
a. Specific: Increasing sales by 15% in the next quarter for a retail company.
b. Measurable: Achieving a customer satisfaction rating of 90% within six months for a service-based organization.
c. Attainable: Launching a new product line within a specific budget and resource constraints.
d. Relevant: Reducing carbon emissions by 20% in the next year for a manufacturing firm to align with their sustainability goals.
e. Time-bound: Completing a software development project within three months to meet market demand.
Crafting SMART objectives that align with organizational vision requires considering factors such as market conditions, competitive landscape, and internal capabilities. It is crucial to involve relevant stakeholders, communicate effectively, and continuously monitor and refine objectives.
Aligning Employee Goals with Organizational Targets
To achieve organizational success, it is vital to align individual objectives with broader organizational goals. Google is an exemplary case study in this regard. The company’s adoption of Management by Objectives (MBO) has fueled innovation and growth by aligning individual goals with organizational objectives. Google’s “OKRs” (Objectives and Key Results) framework sets ambitious, measurable goals at all levels, empowering employees to contribute to the company’s success while fostering collaboration.
To create seamless alignment, organizations should:
a. Clearly communicate organizational goals and objectives to all levels of the workforce.
b. Cascade and link objectives from top management to the individual employee level.
c. Provide training and resources to help employees understand how their work contributes to organizational targets.
d. Foster a culture of collaboration and knowledge-sharing to align efforts across teams and departments.
e. Encourage regular feedback and coaching to ensure alignment and facilitate course correction if needed.
Enhancing Performance through Regular Feedback and Evaluation
Feedback and evaluation play a crucial role in Management by Objectives (MBO), enabling organizations to track progress, identify strengths and weaknesses, and facilitate continuous improvement. Xerox Corporation’s successful turnaround story exemplifies the power of feedback and evaluation in Management by Objectives (MBO). In the early 2000s, Xerox implemented Management by Objectives (MBO), leveraging regular feedback and evaluation to transform their struggling business. By aligning individual performance goals with organizational objectives, Xerox achieved significant improvements in productivity, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.
Performance appraisal techniques such as 360-degree feedback, self-assessment, and objective metrics help assess progress accurately. Regular feedback sessions, performance reviews, and tailored coaching ensure that employees stay on track and receive guidance for improvement.
Motivating Employees through MBO
MBO, when effectively implemented, fosters a sense of ownership, engagement, and motivation among employees. Tata Motors’ transformation journey provides an excellent example of how Management by Objectives (MBO) can motivate employees to perform at their best. By aligning individual objectives with the company’s vision, Tata Motors empowered its workforce to take ownership of their roles, resulting in improved innovation, quality, and overall performance.
To motivate employees through MBO, organizations can:
a. Provide opportunities for skill development and career growth.
b. Recognize and reward outstanding performance.
c. Encourage a culture of open communication and transparency.
d. Promote shared accountability and teamwork.
e. Celebrate success and milestones, reinforcing a sense of achievement.
Overcoming Challenges in MBO Implementation
Implementing MBO may face certain challenges, ranging from resistance to change to lack of clear communication. By proactively addressing these obstacles, organizations can ensure successful Management by Objectives (MBO) adoption. Microsoft’s effective implementation provides a case study in overcoming challenges. Through focused communication, involving key stakeholders, and offering training and support, Microsoft successfully implemented MBO, enhancing productivity, employee engagement, and overall organizational performance.
To overcome obstacles in MBO implementation:
a. Provide comprehensive training and resources to help employees understand the MBO process.
b. Encourage open dialogue to address concerns and manage resistance to change.
c. Involve employees in the goal-setting process to enhance ownership and commitment.
d. Continuously communicate the benefits and objectives of MBO throughout the organization.
e. Monitor progress and make necessary adjustments as needed.
The Importance of Effective Communication in MBO
Communication plays a pivotal role in the success of MBO. Southwest Airlines excels in utilizing a communication strategy driven by MBO principles. By practicing open and transparent communication, Southwest Airlines ensures that employees understand the company’s goals, know their role in achieving them, and have the necessary information to make informed decisions. Regular updates, town hall meetings, and effective feedback mechanisms contribute to Southwest’s commitment to employee engagement and customer satisfaction.
To leverage effective communication in MBO:
a. Establish clear communication channels and platforms for sharing information.
b. Encourage two-way communication to facilitate feedback and open dialogue.
c. Provide regular updates on progress and outcomes.
d. Share success stories and recognize employee achievements.
e. Foster a culture of collaboration and knowledge-sharing.
Realizing the Benefits of MBO with Statistics and Examples
The benefits of MBO are well-documented and supported by statistics and examples. Organizations that implement MBO effectively experience:
a. Increased productivity and efficiency.
b. Enhanced employee engagement and motivation.
c. Improved communication and collaboration.
d. Higher customer satisfaction and quality of products/services.
e. Greater alignment of individual efforts with organizational objectives.
Success stories from diverse industries, such as Apple, Starbucks, and Zappos, demonstrate how MBO has contributed to their remarkable achievements and sustainable growth.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Management by objectives (MBO)
Advantages of Management by Objectives (MBO)
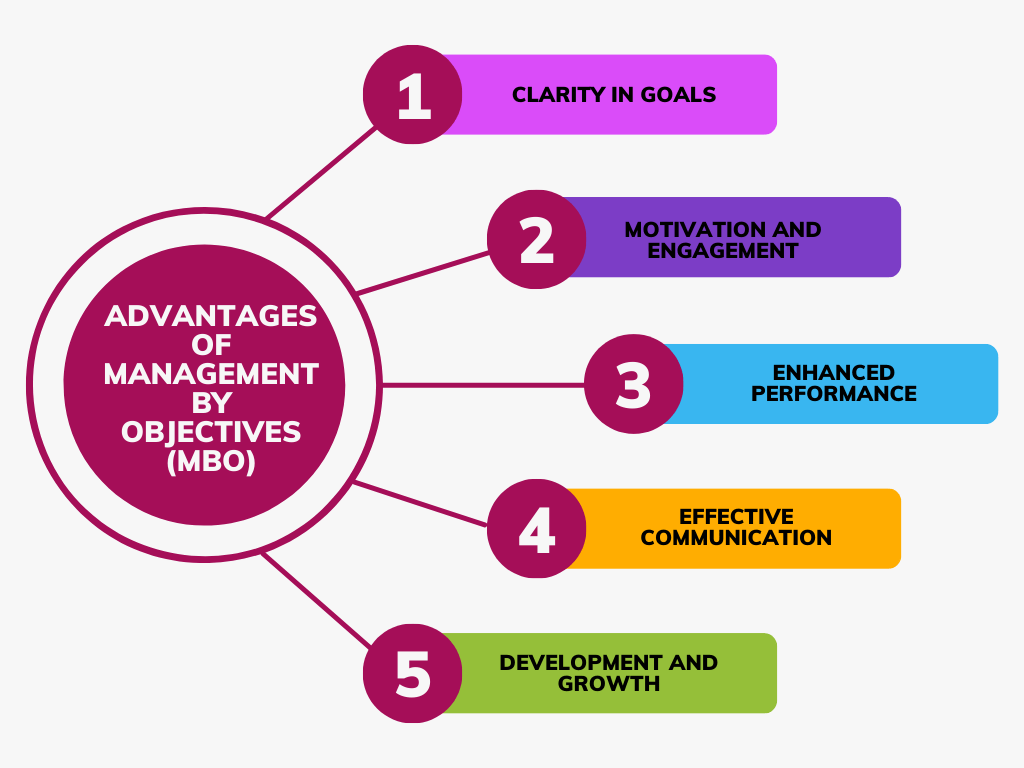
1. Clarity in Goals: MBO provides a clear understanding of organizational goals and individual objectives, ensuring alignment and focus across all levels of the organization.
2. Motivation and Engagement: Setting challenging yet attainable goals and involving employees in the goal-setting process helps foster a sense of ownership, motivation, and commitment to achieving organizational targets.
3. Enhanced Performance: MBO emphasizes regular feedback and performance evaluation, promoting a culture of continuous improvement and increased productivity.
4. Effective Communication: MBO encourages open and transparent communication between managers and employees, fostering better collaboration, cooperation, and problem-solving.
5. Development and Growth: MBO provides opportunities for employee development through goal attainment and performance evaluation, leading to personal and professional growth.
Disadvantages of Management by Objectives (MBO)
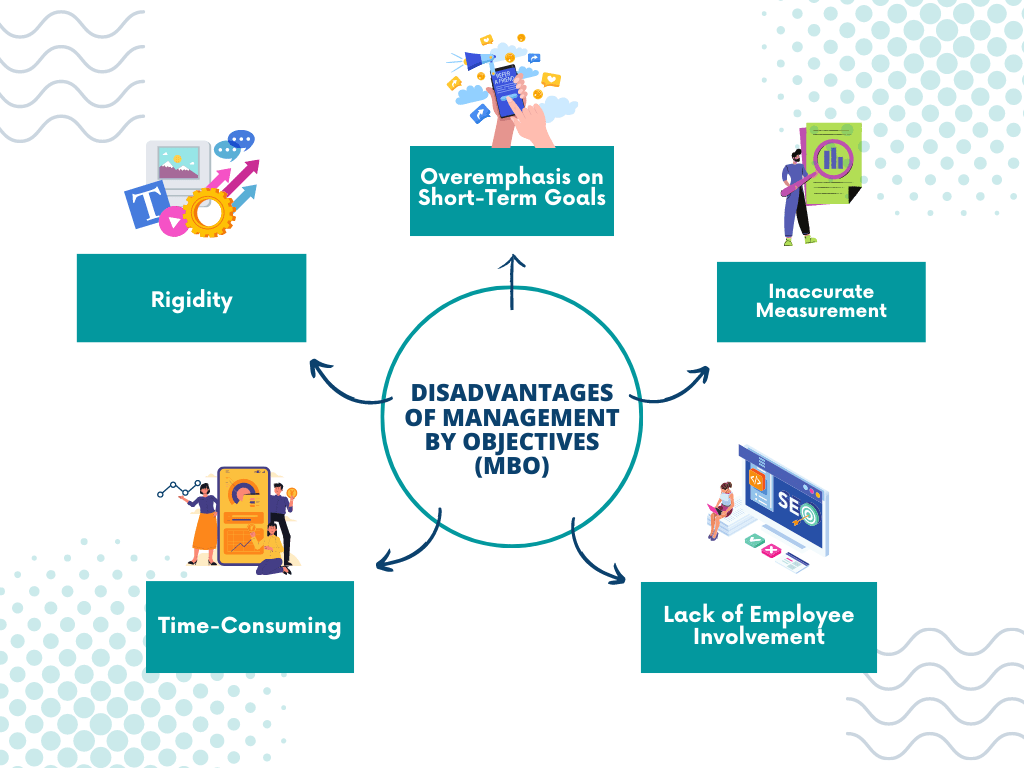
1. Time-Consuming: The MBO process can be time-consuming, particularly in large organizations that have numerous employees and complex goal-setting structures.
2. Rigidity: The rigid nature of MBO can limit flexibility and adaptability in dynamic and uncertain business environments. It may not be suitable for rapidly changing industries or projects that require creative thinking and innovation.
3. Overemphasis on Short-Term Goals: MBO may encourage a focus on short-term objectives, potentially sacrificing long-term strategic planning and innovation.
4. Inaccurate Measurement: Setting measurable goals can be challenging, especially in areas where the outcomes are qualitative or subjective, making it difficult to assess employee performance accurately.
5. Lack of Employee Involvement: In some cases, the top-down nature of goal setting in MBO can lead to a lack of employee involvement and buy-in, resulting in reduced motivation and commitment.
It is important to note that the disadvantages can be mitigated through effective implementation and regular assessment of the MBO process. Each organization should carefully consider its unique context and organizational culture before adopting MBO as a management approach.
Management By Objectives Case Studies
Case Study 1: Apple Inc.
Apple Inc. is a globally renowned technology company known for its innovative products and high-performance culture. The company’s success can be attributed, in part, to its effective implementation of Management by Objectives (MBO).
MBO at Apple is centered around the concept of setting clear objectives that align with the organization’s vision and goals. By establishing specific targets for each department and individual employee, Apple ensures that everyone is working towards a common objective.
For example, Apple’s retail division sets objectives to increase customer satisfaction, sales growth, and operational efficiency. These objectives are then broken down into SMART goals for each employee, such as achieving a specific sales target or improving customer service ratings.
Through regular feedback and evaluation, Apple monitors employees’ progress and provides continuous support to help them achieve their goals. The company emphasizes open communication and encourages managers to have ongoing conversations with their teams to address any challenges and improve performance.
Apple’s MBO approach also fosters a culture of innovation and creativity. By setting ambitious goals, Apple encourages employees to think outside the box and push boundaries. This approach has resulted in groundbreaking products like the iPhone, iPad, and Mac, which have revolutionized the technology industry.
Case Study 2: Starbucks Corporation
Starbucks Corporation, the global coffeehouse chain, has implemented Management by Objectives (MBO) as a key driver for its success. Through a well-defined MBO framework, Starbucks aligns individual objectives with the company’s broader goals, creating a cohesive and focused workforce.
At Starbucks, every employee, from baristas to store managers, is encouraged to set SMART goals that support the company’s mission of providing a unique coffee experience. These goals may include improving customer satisfaction, increasing sales, or introducing new products.
To ensure alignment, Starbucks’ leadership team communicates the company’s objectives and vision to employees through regular meetings and cascading goal-setting sessions. By involving employees in the goal-setting process, Starbucks promotes a sense of ownership and engagement, encouraging them to go above and beyond to achieve their targets.
Feedback and evaluation play a crucial role in the MBO process at Starbucks. The company conducts regular performance reviews, providing constructive feedback and recognition to employees who have demonstrated exceptional performance. This continuous feedback loop helps employees stay motivated and continuously improve their performance.
Starbucks’ MBO-driven approach has contributed to its remarkable growth and market leadership in the coffee industry. By aligning individual goals with the company’s strategic objectives, Starbucks has cultivated a motivated and customer-centric workforce, resulting in consistently exceptional customer experiences across its global network of stores.
Case Study 3: Nike Inc.
Nike Inc., the renowned sports apparel and footwear company, has effectively implemented Management by Objectives (MBO) to drive performance, innovation, and brand success. Through its MBO framework, Nike aligns employee goals with the organization’s overall objectives, fostering a culture of excellence and continuous improvement.
Nike’s MBO process emphasizes setting specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. For instance, a product development team might have goals to increase sales revenue by a certain percentage, design innovative products that meet specific customer needs, or improve manufacturing efficiency.
To ensure alignment, Nike employs a top-down approach, where organizational objectives are cascaded down to teams and individuals. This creates a clear line of sight between employees’ roles and the company’s overall goals.
Regular feedback and evaluation are critical to Nike’s MBO process. The company holds performance reviews to assess employees’ progress, provide constructive feedback, and recognize outstanding achievements. This performance-driven culture motivates employees to continually strive for excellence.
Nike’s MBO approach has led to groundbreaking innovations such as the Flyknit technology and the Nike FuelBand. By empowering employees to take ownership of their goals and providing the necessary resources and support, Nike has established itself as a market leader in the sports apparel industry.
Case Study 4: Nestlé SA
Nestlé, a multinational food and beverage company, has successfully implemented Management by Objectives (MBO) to drive organizational performance and growth. By aligning individual objectives with broader company goals, Nestlé creates a results-oriented culture and ensures the entire workforce is working towards common objectives.
Nestlé’s MBO framework follows a five-step process: goal-setting, action planning, performance reviews, feedback, and rewards. Through goal-setting, employees define specific, measurable targets that contribute to Nestlé’s strategic priorities, such as increasing market share, improving product quality, or enhancing sustainability efforts.
To enhance alignment, Nestlé promotes cross-functional collaboration and communication. Employees across different departments and regions work together to achieve shared goals and leverage their collective expertise for success.
Regular performance reviews and feedback sessions ensure employees receive timely guidance and recognition for their contributions. Nestlé believes in a coaching-based feedback culture, where managers act as mentors, supporting their teams’ professional development and fostering a sense of accountability.
Nestlé’s MBO approach has helped the company achieve sustainable growth and strengthen its position as a leader in the food and beverage industry. By aligning individual aspirations with the company’s strategic priorities, Nestlé empowers its workforce to drive innovation, improve operational efficiency, and deliver exceptional value to its customers.
Case Study 5: Zappos
Zappos, an online shoe and clothing retailer, has embraced Management by Objectives (MBO) as a core management philosophy to create a strong and motivated workforce. Zappos’ customer-centric approach to MBO has contributed to its reputation for exceptional customer service and high employee satisfaction.
Zappos’ MBO process centers around aligning employee goals with the company’s core values and customer service objectives. Employees are encouraged to set goals that contribute to creating a positive shopping experience and exceeding customer expectations.
To ensure alignment, Zappos provides transparency and clear communication channels throughout the organization. Employees have access to company-wide goals and progress updates, enabling them to see how their individual objectives connect to the bigger picture.
Zappos also emphasizes the importance of regular feedback and evaluation. Managers conduct regular check-ins to provide guidance and support, offer constructive feedback, and recognize employees’ contributions. This feedback-driven culture promotes continuous improvement and motivates employees to excel in their roles.
Through its MBO-driven approach, Zappos has built a loyal customer base and achieved remarkable business growth. The company has become synonymous with exceptional customer service, as employees are motivated to go above and beyond to exceed customer expectations.
These case studies highlight how companies across different industries have successfully implemented Management by Objectives (MBO) to drive performance, align individual and organizational goals, foster innovation, and create a motivated and engaged workforce. By following the principles and steps of MBO, organizations can set clear objectives, align employee goals with corporate targets, provide regular feedback and evaluation, and realize long-term benefits in terms of improved performance and growth.
Conclusion:
Management by Objectives (MBO) provides a strategic framework for organizations to align individual efforts with overall objectives, leading to improved performance, innovation, and growth. By setting clear objectives and SMART goals, aligning employee goals with organizational targets, providing regular feedback and evaluation, motivating employees, and fostering effective communication, organizations can maximize the benefits of MBO. With case studies, statistics, and examples validating its effectiveness, MBO remains a powerful management tool essential for achieving sustainable organizational success.
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page