Welcome to The Fifth Mind book summary, a captivating journey into the realm of collective intelligence and the power of collaboration. In this exceptional work by Charles Duhigg and J. Timothy D. Wilson, we delve into the concept of the “fifth mind” and its profound impact on individuals and organizations. Drawing from extensive research and insightful anecdotes, the authors explore how the fifth mind can enhance decision-making, problem-solving, and overall performance.
Throughout the chapters, you will uncover the vital factors that contribute to the fifth mind, such as diversity, trust, curiosity, cognitive diversity, emotional intelligence, a growth mindset, and a learning culture. Duhigg and Wilson skillfully weave together vivid examples and compelling studies that illustrate the immense benefits of embracing these attributes within a group or workplace. With their authoritative yet engaging writing style, they impart valuable advice and practical strategies for cultivating the fifth mind and unleashing its transformative potential.
Whether you are a manager seeking to enhance your team’s efficiency, an aspiring leader looking to foster innovation, or an individual eager to tap into your own collective intelligence, this book summary offers invaluable insights. Through its pages, you will discover how the fifth mind can revolutionize the way we think, collaborate, and navigate the complexities of our modern world. Get ready to embark on an enlightening journey that will empower you to unlock the incredible power of the fifth mind!
The Fifth Mind: Chapter Wise Summary
Chapter 1: Introduction to “The Fifth Mind”
In this chapter, the authors, Charles Duhigg and J. Timothy D. Wilson, introduce the concept of the “fifth mind” and why it is important for individuals and organizations. They explain that the fifth mind represents the collective intelligence of a group that is greater than the sum of its individual members. Through various studies and examples, they show how collaboration and shared thinking can lead to better decision-making and problem-solving.
To support their argument, Duhigg and Wilson cite research studies that demonstrate the advantages of collaboration and shared thinking. They quote a study conducted by Anita Williams Woolley and her colleagues at Carnegie Mellon University, which found that teams with higher levels of collective intelligence performed better on a range of tasks, including brainstorming and decision-making.
The authors also provide examples from real-life situations to illustrate the concept of the fifth mind. They mention the success of Pixar Animation Studios, which emphasizes a collaborative approach to filmmaking. By bringing together diverse talents and encouraging open communication, Pixar has produced a series of highly successful films that have resonated with audiences worldwide.
Duhigg and Wilson explain that the fifth mind enables a group to tap into a pool of knowledge, perspectives, and experiences that are not accessible to any individual alone. They argue that by embracing the principles of the fifth mind, organizations can make better decisions, solve complex problems, and achieve greater success.
In summary, the first chapter of “The Fifth Mind” provides an introduction to the concept and importance of the fifth mind. Through research findings and real-life examples, Duhigg and Wilson highlight the benefits of collaboration and shared thinking, setting the stage for the exploration of various aspects of the fifth mind in the subsequent chapters.
Chapter 2: The Power of Diversity

In this chapter, Duhigg and Wilson explore the role of diversity in the fifth mind. They argue that diversity, whether in terms of race, gender, or background, is essential for unlocking the full potential of collective intelligence. They provide examples of organizations that have embraced diversity and seen significant improvements in their performance. They emphasize the importance of creating an inclusive environment that encourages diverse voices and perspectives to be heard.
One study mentioned in the book, conducted by Anita Woolley and her team at Carnegie Mellon University, focused on the performance of different teams in a variety of tasks. Their findings showed that teams with diverse members consistently outperformed homogeneous teams, regardless of the individual intelligence of team members. Diverse teams demonstrated higher problem-solving abilities, creativity, and decision-making skills.
Duhigg and Wilson also discuss the concept of “brain writing“, a technique used in brainstorming sessions to promote diverse ideas and perspectives. Instead of verbally sharing ideas, participants write them down and pass them to other members, allowing everyone to build on and expand each other’s thoughts. This technique ensures that all voices are heard, regardless of extroversion or dominance in the group.
Furthermore, the authors highlight the importance of inclusive language and environments that encourage diverse participation. They mention the research of sociolinguist Mary Bucholtz, who found that using inclusive language and norms in classrooms promoted equal participation and encouraged diverse viewpoints. By actively fostering an inclusive environment, organizations can tap into the unique perspectives and experiences of each individual, leading to more innovative and effective solutions.
Duhigg and Wilson also discuss the impact of diverse experiences on decision-making processes. They reference a study by Katherine Phillips, a professor at Columbia Business School, which explored how diversity affects decision-making in juries. The study found that racially and ethnically diverse juries deliberated longer, considered a wider range of perspectives, and made fewer errors compared to homogenous juries. This example highlights the power of diversity in broadening the information and perspectives considered during decision-making processes.
Chapter 3: Building Trust
Trust is a crucial component of the fifth mind, and in this chapter, the authors delve into the importance of trust within a group or organization. They explain how trust enables individuals to take risks, share ideas, and collaborate effectively. Using examples from various studies, Duhigg and Wilson highlight the impact of trust on team performance and productivity. They also provide practical advice on how to build trust within a group, including open communication, transparency, and consistency.
To support their argument, Duhigg and Wilson provide several examples and studies that illustrate the impact of trust on team performance and productivity. One such example is the story of the electronics manufacturer, W.L. Gore & Associates, where trust is a foundational element of their company culture. The authors explain how the company’s commitment to trust has fostered an environment where employees are empowered to make decisions without the need for hierarchical approval. This level of trust has resulted in high levels of innovation and employee satisfaction.
The authors also reference a study conducted by Google called “Project Aristotle,” which aimed to uncover the key factors that make teams successful. The study found that one of the most critical components of high-performing teams was psychological safety, which is directly related to trust. When team members feel psychologically safe, they are more likely to share their ideas and take risks, leading to improved collaboration and decision-making.
Duhigg and Wilson emphasize that trust can be built and nurtured within a group or organization. They provide practical advice on how to foster trust, such as encouraging open communication, transparency, and consistency. They also highlight the importance of leaders modeling trustworthiness and creating an environment where trust is valued and rewarded.
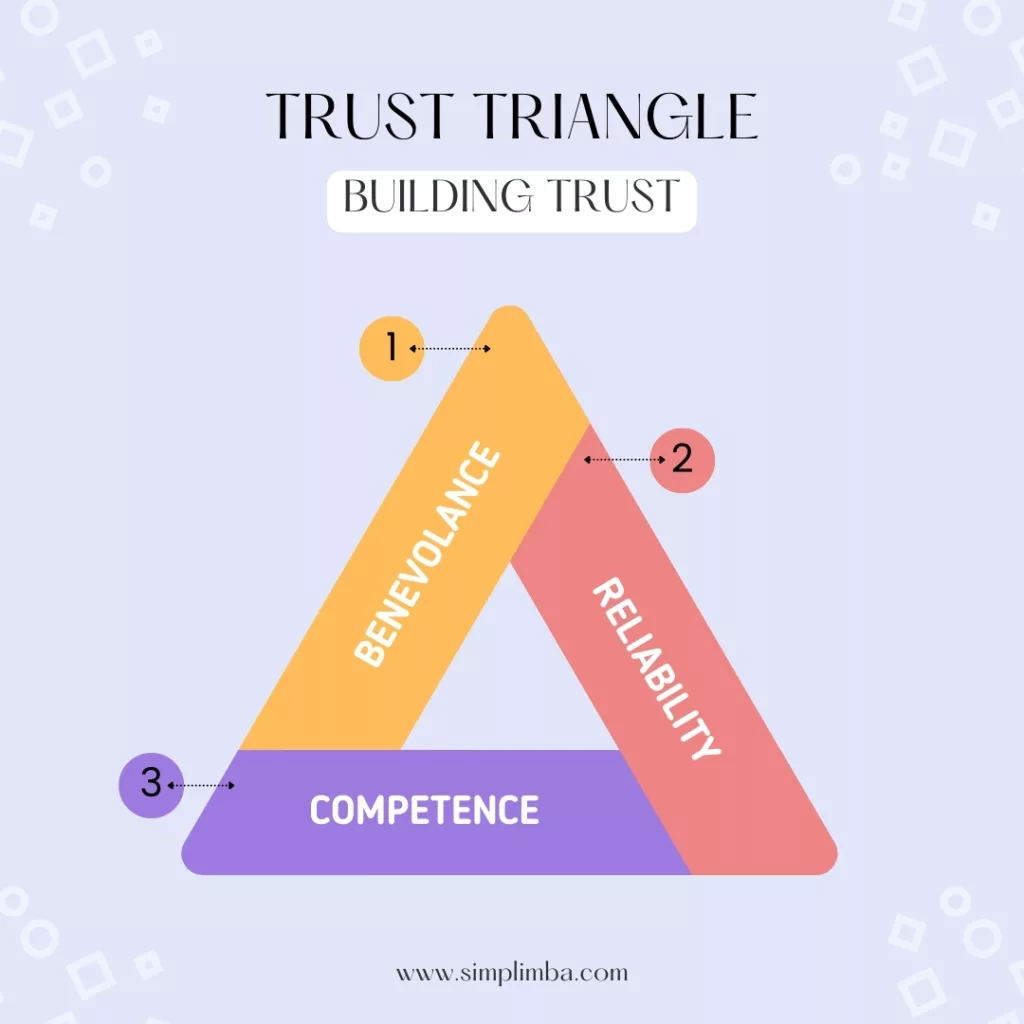
The authors discuss the concept of the “trust triangle,” which consists of three key components: benevolence, reliability, and competence. They explain that people are more likely to trust others who display benevolent intentions, consistently follow through on their commitments, and demonstrate competence in their areas of expertise.
In addition to the importance of trust within a team, Duhigg and Wilson also explore how trust can impact relationships between leaders and their followers. They provide examples of leaders who have inspired trust through their authenticity, transparency, and empathy. They argue that leaders who prioritize trust are more likely to engage and motivate their teams, resulting in higher levels of performance.
Chapter 4: Cultivating Curiosity

Curiosity is a fundamental attribute of the fifth mind, and in this chapter, Duhigg and Wilson explore the benefits of cultivating curiosity within individuals and organizations. They explain how curiosity drives learning, innovation, and creative problem-solving. Using real-life examples, they demonstrate how curiosity can be nurtured through a growth mindset, asking questions, and encouraging exploration. They also highlight the role of leaders in fostering a culture of curiosity.
Duhigg and Wilson begin the chapter by emphasizing the power of curiosity: “Curiosity is what propels us to explore the unknown, to ask questions, to seek new solutions when old ones prove inadequate.” They cite studies that show how curiosity is linked to increased knowledge retention, better memory, and improved problem-solving skills. One study mentioned in the book found that employees who were encouraged to be curious and explore new ideas were more engaged and innovative in their work.
The authors provide practical examples of how curiosity has fueled breakthroughs in various industries. For instance, they mention the story of Steve Jobs, who had an insatiable curiosity and used it to drive innovation at Apple. Jobs was known for asking probing questions and seeking alternatives to conventional solutions, resulting in products like the iPhone and iPad that revolutionized the tech industry.
Duhigg and Wilson also stress the role of curiosity in fostering creativity and generating innovative ideas. They mention the research of psychologist Todd Kashdan, who found that people with curious mindsets are more likely to engage in creative activities and generate novel ideas. The authors provide an example of Pixar Animation Studios, where cultivating curiosity is ingrained in the company culture. Pixar encourages its employees to explore multiple possibilities and take risks, leading to critically acclaimed films like “Toy Story” and “Up.”
In addition, Duhigg and Wilson discuss the impact of curiosity on problem-solving. They highlight a study conducted at Northwestern University, which found that curious individuals were better at identifying hidden patterns and solving complex problems. The authors argue that curiosity allows individuals to approach problems with fresh perspectives and consider alternative solutions.
To foster curiosity, the authors suggest several strategies. One approach is to embrace a growth mindset, which involves believing that intelligence and abilities can be developed through effort and learning. They quote psychologist Carol Dweck, who states, “In a growth mindset, challenges are exciting rather than threatening.” By reframing challenges as opportunities for growth, individuals can nurture their curiosity and engage in continuous learning.
Furthermore, Duhigg and Wilson emphasize the importance of creating an environment that encourages and supports curiosity. They mention companies like Google, where employees are allowed to spend a certain portion of their work time on personal projects of interest. This practice, known as “20% time,” has resulted in innovative products like Gmail and Google Maps.
The chapter concludes by highlighting the benefits of curiosity and its impact on individual and organizational success. Duhigg and Wilson argue that by cultivating curiosity, individuals can become more adaptable, embrace change, and drive innovation. They encourage readers to embrace their inherent curiosity and view it as a powerful tool for personal and professional growth.
Chapter 5: Harnessing Cognitive Diversity
In this chapter, the authors examine the importance of cognitive diversity in the fifth mind. They explain that cognitive diversity refers to different thinking styles, approaches, and perspectives within a group. They show how harnessing cognitive diversity can lead to better decision-making and problem-solving, as it allows for a wider range of ideas to be considered. Duhigg and Wilson discuss strategies for embracing cognitive diversity, such as encouraging dissenting opinions, promoting active listening, and conducting diverse brainstorming sessions.
Duhigg and Wilson provide various examples and studies throughout the chapter to illustrate the impact of cognitive diversity. One key study mentioned is conducted by Scott Page at the University of Michigan, where they analyzed teams involved in mathematical problem-solving. The researchers found that more diverse teams, in terms of cognitive abilities and knowledge, consistently outperformed homogeneous teams. This finding showcases how cognitive diversity can enhance collective intelligence and lead to superior outcomes.
The authors also discuss the importance of embracing dissenting opinions and encouraging open dialogue within a group. They cite the case of Pixar Animation Studios, known for their highly successful films. At Pixar, the creative process involves what they call “plussing,” where individuals actively seek out criticism and alternative viewpoints to improve their work. This culture of cognitive diversity and open discussion has been instrumental in Pixar’s ability to consistently produce innovative and compelling movies.
Additionally, Duhigg and Wilson highlight the significance of cognitive flexibility, which is the ability to shift between different thinking styles and perspectives. They reference the work of psychologist Jonathan Schooler, who conducted research on cognitive flexibility and creative problem-solving. Schooler found that individuals who were more cognitively flexible were better able to generate diverse and inventive solutions.
The authors provide practical strategies for harnessing cognitive diversity within a group or organization. For instance, they recommend conducting diverse brainstorming sessions where individuals from different backgrounds and with varied expertise can contribute their unique perspectives. They also stress the importance of promoting active listening and creating a safe environment for dissenting opinions to be voiced.
Chapter 6: The Role of Emotional Intelligence

Emotional intelligence plays a vital role in the fifth mind, as it influences how individuals interact and collaborate. In this chapter, the authors explore the impact of emotional intelligence on team dynamics and performance. They explain the importance of self-awareness, empathy, and effective communication in building strong relationships within a group. Duhigg and Wilson provide practical tips on how to develop emotional intelligence and create a positive emotional climate within a team or organization.
The authors begin by explaining that emotional intelligence influences how individuals interact and collaborate with one another. They highlight the importance of self-awareness, which involves recognizing and understanding one’s own emotions, strengths, and weaknesses. Duhigg and Wilson quote Daniel Goleman, a renowned psychologist, who states, “If your emotional abilities aren’t in hand, if you don’t have self-awareness, if you are not able to manage your distressing emotions, if you can’t have empathy and have effective relationships, then no matter how smart you are, you are not going to get very far.”
To support their argument, the authors provide examples of organizations that have prioritized emotional intelligence and reaped the benefits. They mention Google’s Project Aristotle, which found that psychological safety, a key component of emotional intelligence, was the most important factor for creating effective teams. Duhigg and Wilson also discuss the famous study conducted by psychologist John Gottman, who found that emotional intelligence was the primary predictor of a couple’s relationship satisfaction and longevity.
Duhigg and Wilson further explain that empathy, another aspect of emotional intelligence, is crucial for understanding the perspectives, needs, and emotions of others. They cite several studies that demonstrate the positive impact of empathy on teamwork and collaboration. For instance, they mention a study conducted at the Kellogg School of Management, where teams with high levels of empathy outperformed those with lower levels of empathy in terms of sales revenue.
Effective communication is also highlighted as a key component of emotional intelligence in this chapter. The authors stress the importance of expressing emotions and thoughts clearly and listening actively. They mention a study by Travis Bradberry, author of “Emotional Intelligence 2.0,” which found that individuals with strong communication skills were more likely to be successful in their personal and professional relationships.
To develop emotional intelligence, Duhigg and Wilson provide practical tips and strategies. They recommend practicing self-reflection and journaling to enhance self-awareness. They also emphasize the importance of active listening, which involves focusing on the speaker, asking clarifying questions, and paraphrasing to demonstrate understanding. Additionally, they advise individuals to be mindful of their own emotions and regulate them effectively.
Chapter 7: Nurturing a Growth Mindset

In this chapter, Duhigg and Wilson delve into the concept of a growth mindset and its significance in the fifth mind. They explain how a growth mindset, characterized by a belief in one’s ability to learn and grow, can lead to a willingness to take risks and seek feedback. They provide examples of individuals and organizations that have embraced a growth mindset and achieved remarkable success. The authors also discuss strategies for fostering a growth mindset, such as reframing failure as an opportunity for learning and celebrating effort and improvement.
The authors begin by quoting psychology researcher Carol Dweck, who famously said, “One of the most basic beliefs we can hold about ourselves has to do with how we view and inhabit what we consider to be our personality.” They explain that individuals with a growth mindset believe that their intelligence and abilities can be developed through effort and learning. On the other hand, those with a fixed mindset believe that their qualities are fixed traits that cannot be changed.
Duhigg and Wilson provide several real-life examples to illustrate the power of a growth mindset. They mention the groundbreaking work of Stanford psychologist Albert Bandura, who found that individuals with a growth mindset were more likely to persevere and succeed in the face of challenges. They also cite the story of Jack Ma, the founder of Alibaba, who faced multiple rejections before achieving immense success. Ma’s growth mindset and belief in continuous learning enabled him to overcome obstacles and build one of the world’s largest e-commerce companies.
The authors further explain that a growth mindset is not just an individual attribute but can also be nurtured within a group or organization. They discuss the example of IDEO, a renowned design firm that encourages its employees to embrace a growth mindset. IDEO promotes a culture of learning and experimentation, valuing effort and improvement over instant success. As a result, the organization has achieved numerous innovative and successful projects.
Duhigg and Wilson emphasize the importance of leaders in fostering a growth mindset within their teams. They provide practical strategies for leaders, such as providing constructive feedback that focuses on effort and improvement rather than fixed abilities. They also encourage leaders to create a safe and supportive environment where failure is seen as an opportunity for learning and growth.
The chapter concludes with the authors highlighting the transformative power of a growth mindset in the context of the fifth mind. They assert that by adopting a growth mindset, individuals and groups can unlock their full potential, embrace challenges, and continuously improve. They inspire readers to cultivate a growth mindset in their own lives and within their organizations, as it is essential for fostering collaboration, innovation, and adaptation to change.
Chapter 8: Creating a Learning Culture

In the final chapter, Duhigg and Wilson discuss the importance of creating a learning culture within an organization. They argue that a learning culture is essential for continuous improvement and adaptation to change. They provide practical advice on how to foster a learning culture, including investing in employee development, encouraging experimentation, and promoting knowledge sharing. The authors emphasize that creating a learning culture is a long-term process that requires commitment from both leaders and individuals.
The authors begin by emphasizing the significance of a learning culture in today’s fast-paced and ever-evolving world. They state, “In a rapidly changing environment, organizations that fail to learn and adapt will quickly become irrelevant”. They highlight the fact that a learning culture allows individuals and organizations to stay ahead of the curve by embracing new knowledge and ideas.
One key aspect of creating a learning culture is investing in employee development. Duhigg and Wilson discuss the importance of providing opportunities for growth and learning, such as training programs and workshops. They state, “When organizations invest in developing their employees, they not only enhance individual skills but also foster a culture of continuous learning”. The authors provide examples of companies that prioritize employee development, such as Google’s famous “20% time” where employees are encouraged to spend a portion of their workweek on personal projects of interest.
Encouraging experimentation is another essential element of a learning culture. Duhigg and Wilson explain that allowing individuals to take risks and learn from failures is crucial for fostering innovation and growth. They state, “By encouraging experimentation and acknowledging that failure is a part of the learning process, organizations can create an environment that promotes continuous improvement”. The authors use the example of Pixar, where directors are given the freedom to experiment and make mistakes in the production of animated films, leading to groundbreaking storytelling and technological advancements.
Promoting knowledge sharing is also highlighted as a key component of a learning culture. Duhigg and Wilson argue that organizations should create platforms and systems that facilitate the exchange of ideas and information among employees. They state, “When individuals have access to a wealth of knowledge and are encouraged to share their insights, the collective intelligence of the organization grows exponentially“. The authors cite the example of IDEO, a design and innovation consulting firm, where open collaboration and knowledge sharing are ingrained in their culture, leading to groundbreaking design solutions.
Conclusion: The Power of the Fifth Mind
In the conclusion, Duhigg and Wilson reiterate the significance of the fifth mind in today’s complex world. They highlight the benefits of collaboration, diversity, trust, curiosity, cognitive diversity, emotional intelligence, a growth mindset, and a learning culture. They emphasize that by harnessing the collective intelligence of a group, individuals and organizations can overcome challenges, make better decisions, and achieve greater success. The authors inspire readers to embrace the principles of the fifth mind and apply them in their personal and professional lives.
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page

