The Media Dependency Theory, also known as the Dependency model or the Dependency theory, is a popular mass communication theory. This theory is grounded in classical sociological literature positing that media and their audiences should be studied in the context of larger social systems. Melvin DeFleur and Sandra Ball-Rokeach, two renowned sociologists, developed the theory in 1976.
The core idea of the theory is that the more dependent an individual is on the media for having his or her needs fulfilled, the more important media will be for that individual. People become dependent on mass media to understand certain aspects of the real world, especially those areas which they have little direct experience. The impact of media on individuals depends on the degree of their dependency on media content.
For instance, if a person relies heavily on the television for news then the television’s portrayal of the world becomes crucially important for the individual. If the person is not particularly dependent on the media for information (say he/she gets it from real-life experiences or other interpersonal communication), then the media’s potential influence on the individual is diminished.
Importance of Media Dependency Theory in Understanding Mass Communication
Media Dependency Theory plays a significant role in understanding mass communication and society’s interaction with media. It proposes that the more dependent an individual is on media, the more power these mediums of communication have over the individual’s behavior.
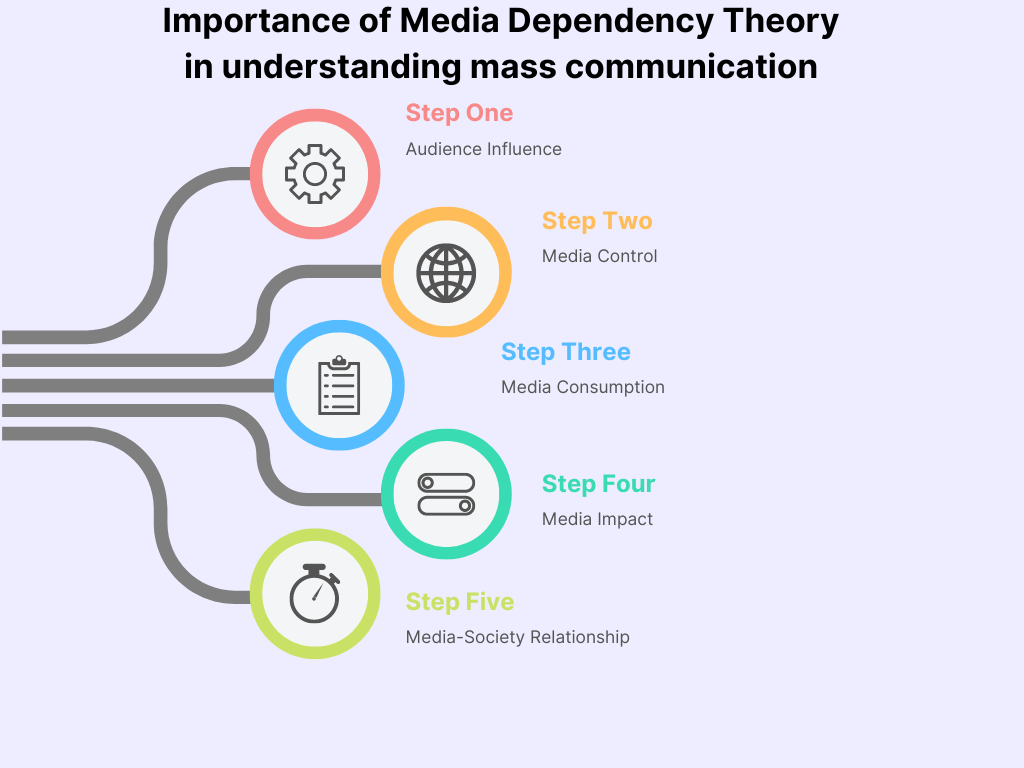
Audience Influence: It helps understand the influence of media on the audience. The more individuals rely on a media source for information, the more they may be affected by that source.
Media Control: The theory suggests that media can control the perceptions and behaviors of its audience. The viewers who are more dependent on a certain form of media are more likely to be influenced by it.
Media Consumption: It aids in understanding media consumption patterns. Individuals who are more dependent on media are likely to consume more of it.
Media Impact: The theory provides a framework to understand the impact of media on society’s attitudes and behaviors. For instance, it can help analyze how media coverage influences public opinion during elections or significant public events.
Media-Society Relationship: It offers insights into the relationship between society and media. It posits that media dependency increases during times of social change and conflict.
Explanation of the main principles of Media Dependency Theory
Media Dependency Relation: According to this theory, the degree of influence that the media can impart on an individual or group is directly proportional to the degree of dependency of the individual or group on the media. This is not a fixed relationship, but it fluctuates based on changes in society, the media, and individuals.
Societal Systems and Media: The theory states that societal systems (economic, political, cultural) and the media are interdependent. These systems rely on media to achieve their goals and objectives, while in turn, media needs these systems for their survival, functioning, and growth.
Effects of Media Dependency: The theory proposes that the effects of media dependency can be both micro and macro. At the micro-level, it can influence the cognition, affect, and behavior of individuals. At the macro level, it can bring about societal changes.
The role of media in society as per the theory
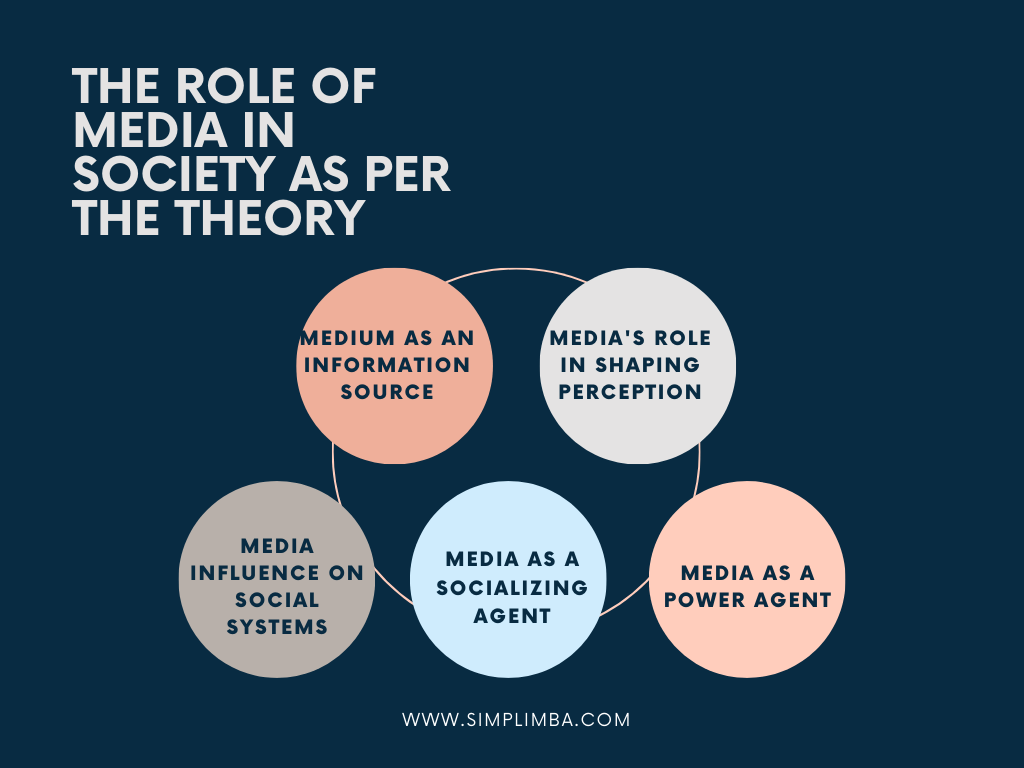
Medium as an Information Source: The theory asserts that the media functions as the primary source of information in modern societies. The more an individual depends on the media for obtaining information, the more significant the media’s influence on their attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors.
Media’s Role in Shaping Perception: According to Media Dependency Theory, media plays a crucial role in shaping our perceptions of reality. This is particularly true in situations where individuals have no direct experience or first-hand knowledge. In these cases, our perceptions, interpretations, and understanding of situations are largely shaped by how they are represented in the media.
Media Influence on Social Systems: On a larger scale, the media can influence various social systems such as political systems, economic systems, and cultural systems. It can shape public opinion, influence policies, drive consumer behavior, and play a role in cultural preservation or transformation.
Media as a Socializing Agent: The theory also postulates that media acts as a socializing agent. It imparts and propagates societal values, norms, and expectations, thus playing a role in social cohesion and order.
Media as a Power Agent: Lastly, Media Dependency Theory recognizes media as a power agent. By controlling the flow of information, media can exercise control and influence over individuals and societies. It can privilege certain knowledge, perspectives, and ideologies over others, thereby maintaining and reproducing power relations in society.
Origin and Development of the Media Dependency Theory
The Media Dependency Theory, also known as Media System Dependency Theory, originated during the 1970s. First proposed by Sandra Ball-Rokeach and Melvin Defleur, it posits that the more dependent an individual or society is on media for achieving goals, the more important media will be in a person’s life, and therefore, the more effects media use will have on individuals and society.
The development of this theory is a reflection of the dynamic relationship between the media, the audience, and the social system. It has evolved from a macroscopic perspective, focusing on the societal-level relationship between mass media and audiences, to incorporate more microscopic elements that consider the relationship on an individual level. This includes how individual motivations and goal-directed behavior play into media dependency.
The theory has also developed to reflect the changing media landscape. With the rise of digital media, the theory has been updated to incorporate the internet and social media platforms, reflecting how these new mediums have influenced our dependency on media.
Key figures and their contributions to the Media Dependency Theory
Sandra Ball-Rokeach: A professor of communication and sociology at the University of Southern California, Ball-Rokeach was instrumental in the development of the Media Dependency Theory. Her work mainly focused on the relationship between media structures and audience characteristics, demonstrating how these relationships influence dependency relations.
Melvin Defleur: A former professor of mass communication at Boston University, Defleur worked closely with Ball-Rokeach in the development of the Media Dependency Theory. He contributed to the theory with his research on mass communication and its effects on social behavior, emphasizing the importance of media in shaping public opinion.
Other contributors: Over the years, numerous scholars have contributed to the development and refinement of the Media Dependency Theory. These include Robert M. Entman, who has explored media framing and its influence on political communication, and Sherry Turkle, who has delved into the impact of digital media and technology on individual and societal dependency on media.
The Impact of Media Dependency on Society
Analyses of Real-Life Scenarios:
Media Exposure and Perception: In real-life scenarios, the mass media has a significant impact on shaping individual and public perceptions. For instance, extensive media coverage on issues like crime, terrorism, and health crises can create a heightened sense of fear and urgency. This is often referred to as the Mean World Syndrome in media studies, suggesting that individuals who consume large amounts of media, particularly violent media, tend to perceive the world as more dangerous than it is.
Media and Political Orientation: The media also plays a significant role in shaping political opinions. People often form opinions based on what they see, read, or hear in the media, which can greatly influence their political orientation. For instance, a study by DellaVigna and Kaplan (2007) found that the introduction of Fox News had a small but statistically significant effect on the vote share in Presidential elections in favor of the Republican party in the United States.
The Influence of Media Dependency on Public Opinion and Behavior
Media Dependency Theory: This theory posits that the more dependent an individual or society is on the media for having its needs fulfilled, the more important the media will be to that person or society. It suggests that media dependency can influence public opinion and behavior in significant ways. For example, a study by Ball-Rokeach and DeFleur (1976) found that individuals who were more dependent on television for information were also more likely to be influenced by televised messages.
Impact on Consumer Behavior: The media, particularly advertising, greatly affects consumer behavior. It influences public opinion about a product or service and can shape purchasing decisions. For instance, a study by Chatterjee (2011) showed that media exposure significantly influenced consumer preferences for branded goods.
Media and Social Change: Media dependency can also lead to social change. The media can bring awareness to certain issues and garner public support, leading to policy changes or shifts in societal attitudes. For instance, the media played a crucial role in the Civil Rights Movement in the U.S. by bringing attention to the systemic discrimination faced by African Americans.
Media Literacy and Critical Thinking: On the flip side, over-dependence on media can lead to a lack of critical thinking if consumers take all information at face value. This underlines the importance of media literacy which promotes critical thinking, enabling consumers to analyze and evaluate media messages.
Strengths of Media Dependency Theory
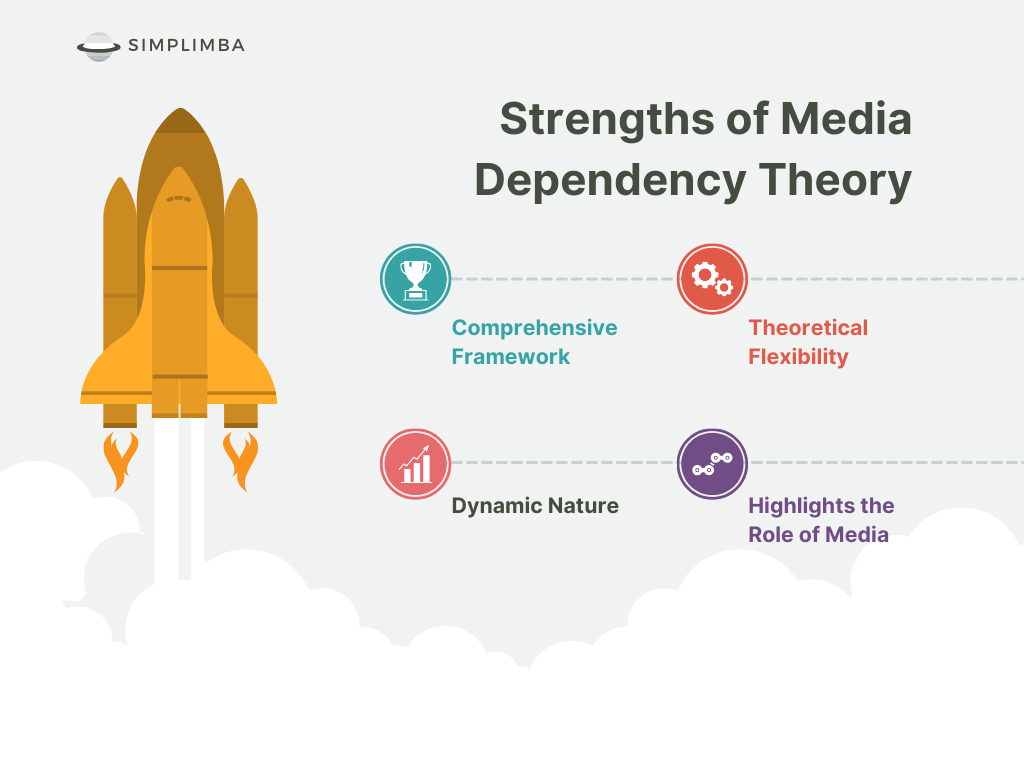
Comprehensive Framework: One of the key strengths of the Media Dependency Theory is that it provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the relationship between the media and its audience. This theory goes beyond simple media effects and takes into account the broader social and psychological contexts in which media consumption occurs.
Theoretical Flexibility: The theory is flexible in that it can be applied to various forms of media – from newspapers and television to social media platforms. This adaptability allows for a broader understanding of the influence of media on individuals and society.
Dynamic Nature: The theory considers the relationship between media and audience as dynamic and reciprocal. It posits that the dependence of individuals on media increases during times of social change and crisis, which in turn enhances the media’s potential effects.
Highlights the Role of Media: Media Dependency Theory highlights the significant role that media plays in shaping our perceptions of reality. It underscores the power of media in influencing attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, especially when individuals have no first-hand experience or alternative sources of information.
Weaknesses of Media Dependency Theory
Lack of Empirical Evidence: One major criticism of Media Dependency Theory is the lack of substantial empirical evidence to support its claims. While the theory provides a comprehensive framework for understanding media-audience relations, it has been difficult to test these relationships methodically and empirically.
Overemphasis on Media Power: Critics argue that the theory over-emphasizes the power of the media while underestimating the ability of audiences to critically analyze and interpret media messages. This might not consider the active role of the audience in decoding the media content.
Neglects Individual Differences: The theory tends to neglect individual differences in media consumption. It assumes a homogeneous audience with similar media dependencies, which is not always the case. Differences like age, education, gender, and cultural background can significantly affect media use and interpretation.
Limited Scope: Although the theory acknowledges the role of social systems and individual needs in determining media dependency, it does not adequately address how these factors interact and influence each other. Therefore, it offers a somewhat limited view of the complex dynamics between media and its audience.
Media Dependency Theory in the Digital Age
Application of the theory in modern, digitized media landscapes
Digitization and Media Dependency: The shift from traditional to digital media has resulted in a new understanding of media dependency theory. The digital age has reshaped how individuals consume and interact with media. Digitization has allowed for the proliferation of multiple media outlets, significantly increasing the amount of information available to consumers. This abundance of information has, in turn, intensified the dependency of individuals on media for their understanding of the world.
Media as a Primary Source of Information: In the digital age, media has become a primary source of information for most individuals. According to a study by the Pew Research Center in 2018, 64% of adults in the United States stated that they received news from digital sources, surpassing television and print outlets. This demonstrates the increasing reliance on digital media for knowledge and news.
Dependency and Credibility: The dependency on digital media also leads to questions about the credibility of information. With the rise of “fake news” and misinformation, the need for independent verification and fact-checking has increased. Thus, while dependency has increased, so has the scrutiny of information sources.
The Relationship between Social Media and Media Dependency
Social Media as a Form of Media: Social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram are now considered significant forms of media. They are not just tools for communication but also sources of information, thus contributing to media dependency.
Social Media Use and Dependency: According to a study by Statista in 2020, there were 3.6 billion social media users worldwide, a number predicted to increase to almost 4.41 billion in 2025. This points to an increasing dependency on social media. It’s also important to note that the extent of dependency may vary depending on the individual’s purpose of using social media – whether for news, communication, entertainment, or a combination of these.
Influence of Social Media: Given the rise in social media use, its influence on public opinion and behavior cannot be underestimated. Social media can amplify certain perspectives and mute others, shaping public discourse in significant ways. This amplifying effect can deepen dependency on social media for information and social connection.
The Role of Algorithms: Algorithmic recommendation systems employed by social media platforms also contribute to media dependency. These algorithms can create echo chambers or filter bubbles, where users are exposed primarily to content that aligns with their existing views, thus reinforcing their beliefs and further increasing their dependency on the platform.
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page

