Introduction
Managers: In today’s rapidly changing business landscape, the ability to foster entrepreneurship within an organization is crucial for sustainable growth and competitive advantage. By encouraging and promoting entrepreneurial behavior, managers can transform their organization into a learning organization, where employees take risks, innovate, and continuously learn. This blog post will explore various strategies that managers can employ to create a culture of entrepreneurship that drives organizational learning. We will also provide relevant case studies and statistics to support these strategies. According to a survey by Gallup, organizations with high employee engagement are 21% more profitable.
How can managers encourage and promote entrepreneurship to create a learning organization?
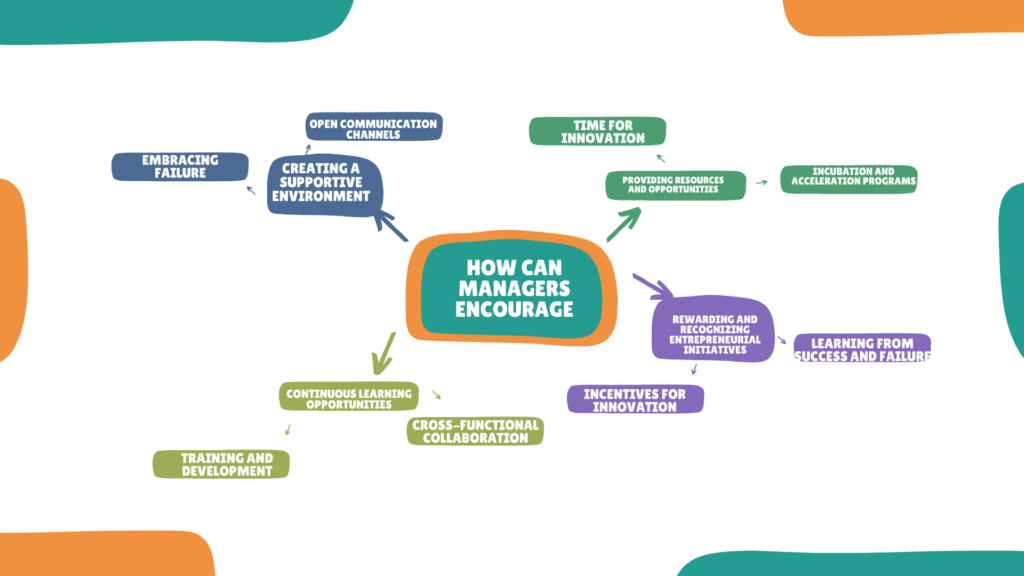
1. Creating a Supportive Environment:
Managers play a crucial role in creating an organizational climate that encourages risk-taking, experimentation, and learning. This entails:
a. Embracing Failure: Managers need to promote a positive attitude towards failure, viewing it as a learning opportunity rather than a setback. Encouraging employees to take calculated risks and learn from their mistakes can nurture entrepreneurial mindsets.
b. Open Communication Channels: Establishing open lines of communication that facilitate idea sharing and feedback can empower employees to express their entrepreneurial ideas and concerns. This creates an environment of trust and collaboration conducive to knowledge exchange.
2. Providing Resources and Opportunities:
Allocating adequate resources and opportunities that support entrepreneurial endeavors can ignite employees’ innovation and create a learning organization.
a. Time for Innovation: Allowing employees dedicated time to pursue innovative projects unrelated to their regular job responsibilities can unlock their entrepreneurial potential. This practice, known as “20% time” or “innovation time,” has been successfully implemented by companies like Google and Atlassian.
b. Incubation and Acceleration Programs: Managers can establish internal incubation or acceleration programs to provide mentorship, resources, and financial support to employees’ entrepreneurial initiatives. These programs foster a culture of experimentation and enable employees to bring their ideas to fruition.
3. Rewarding and Recognizing Entrepreneurial Initiatives:
To promote entrepreneurship within an organization, managers need to align the reward and recognition systems accordingly.
a. Incentives for Innovation: Introducing reward systems that recognize and appreciate entrepreneurial initiatives, such as bonuses, promotions, or public recognition, incentivizes employees to actively engage in creativity and entrepreneurship.
b. Learning from Success and Failure: Managers should foster a culture of sharing both successes and failures openly. Celebrating successful entrepreneurial ventures and discussing lessons learned from failed attempts reinforce a learning mindset and inspire further entrepreneurial engagement.
4. Continuous Learning Opportunities:
Managers should invest in continuous learning opportunities to equip employees with the necessary knowledge and skills for entrepreneurial success.
a. Training and Development: Providing training programs on entrepreneurship, innovation, and design thinking can enhance employees’ entrepreneurial capabilities and mindset. These programs can range from workshops to online courses or even partnering with external experts or universities.
b. Cross-Functional Collaboration: Promoting cross-functional collaboration allows employees to learn from diverse perspectives and expand their knowledge base. This enables them to build a holistic understanding of business operations and identify entrepreneurial opportunities.
Understanding the Concept of a Learning Organization
Definition and Importance
A learning organization is an organization that promotes continuous learning, growth, and development for its employees. It is a workplace where individuals are encouraged and supported to acquire new knowledge, skills, and competencies that will contribute to both personal and organizational success.
Learning organizations recognize that in today’s rapidly changing business environment, the ability to learn and adapt is crucial for survival and long-term competitiveness. They understand that employees are their most valuable assets and that investing in their development is essential for the organization’s overall success.
When organizations adopt a learning culture, they create a dynamic and innovative environment where employees are motivated to seek new challenges, take risks, and learn from their experiences. This encourages creativity, problem-solving, and continuous improvement, leading to increased productivity, higher employee satisfaction, and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
Characteristics of a Learning Organization
There are several characteristics that define a learning organization:
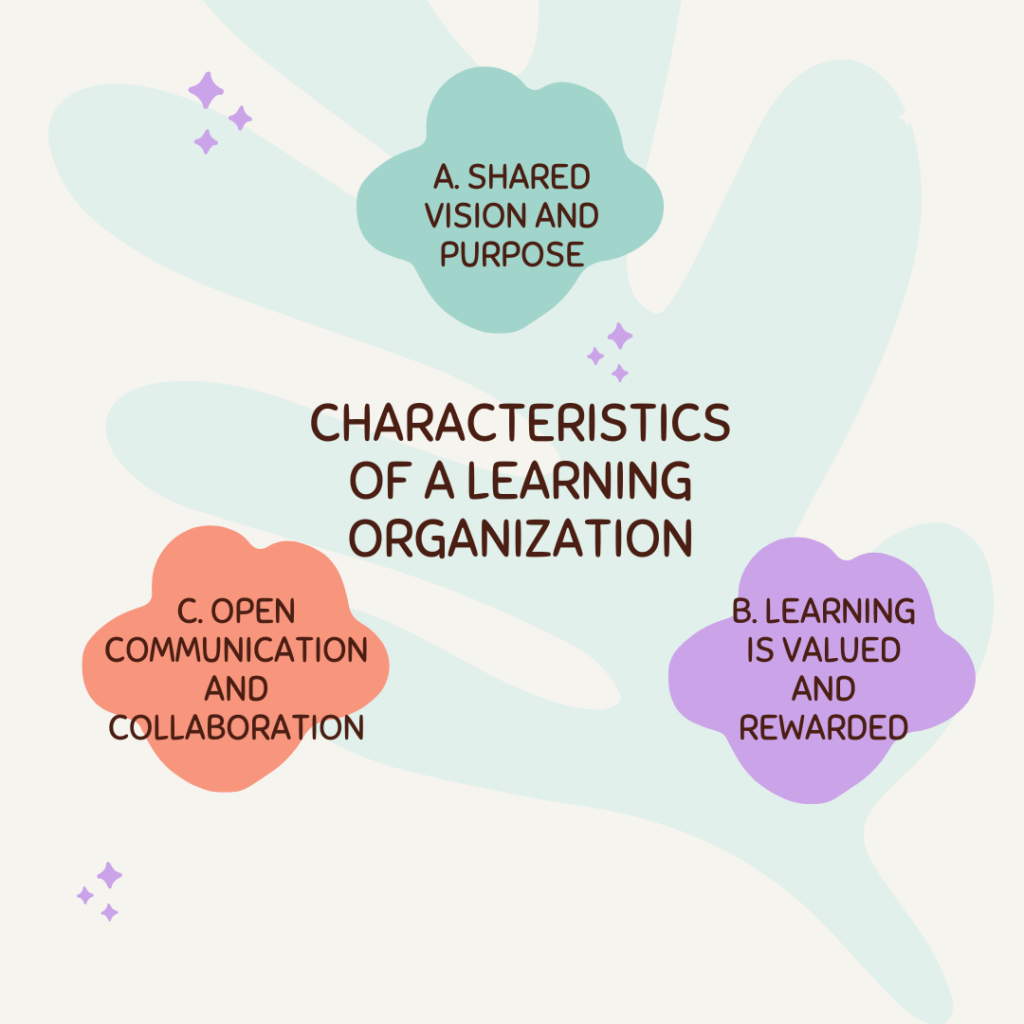
a. Shared vision and purpose: A learning organization has a clear and shared vision, which serves as a guiding principle for all its employees. This vision provides a sense of direction and purpose and helps align individual goals with organizational objectives.
b. Learning is valued and rewarded: In a learning organization, learning is not only encouraged but also rewarded. Employees are given opportunities to learn through training programs, workshops, conferences, and other development activities. Their learning is also recognized and appreciated, motivating them to further enhance their skills and knowledge.
c. Open communication and collaboration: A learning organization fosters a culture of open communication and collaboration, where ideas and feedback are freely exchanged. Employees are encouraged to share their knowledge and expertise, which leads to higher levels of creativity and innovation.
d. Continuous improvement: Learning organizations are committed to continuous improvement. They regularly review their processes, systems, and practices to identify areas for improvement and make necessary changes. They learn from their mistakes and use feedback to enhance their performance.
e. Empowered employees: In a learning organization, employees are empowered to take ownership of their own learning and development. They are provided with the autonomy and resources they need to acquire new skills and apply them in their work.
Benefits of Becoming a Learning Organization
Becoming a learning organization offers several benefits:
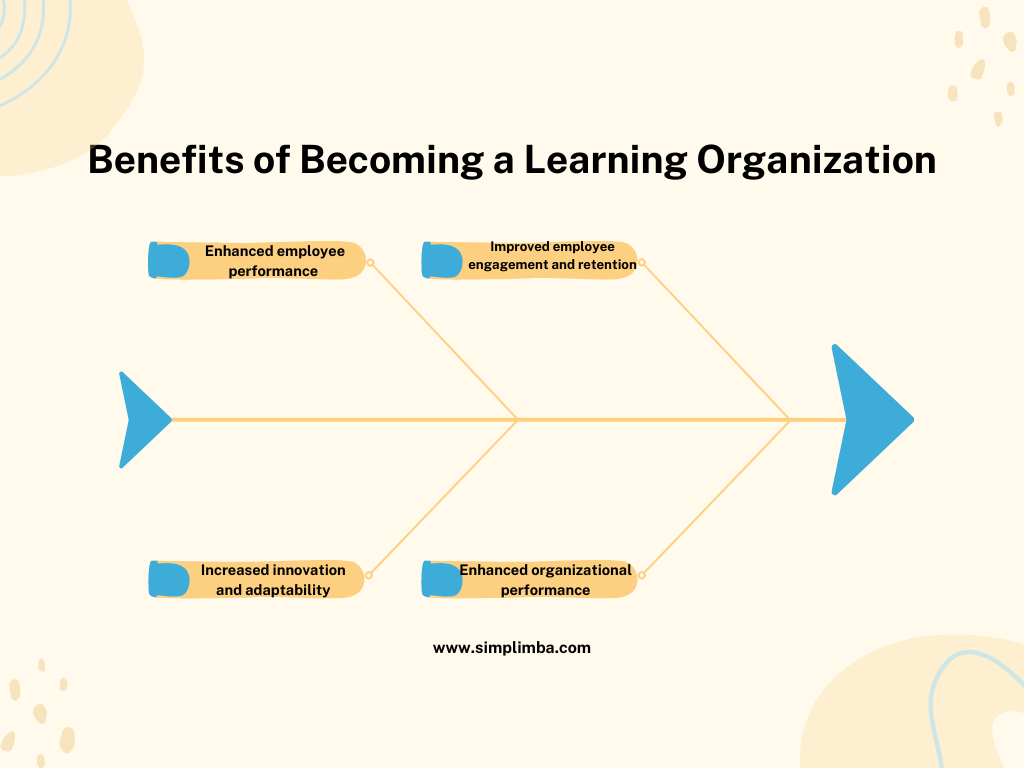
a. Enhanced employee performance: When employees are provided with learning opportunities, they develop new skills and knowledge that enable them to perform better in their roles. This leads to increased productivity, improved quality of work, and higher customer satisfaction.
b. Increased innovation and adaptability: Learning organizations encourage employees to think outside the box and be innovative in their approach. This fosters a culture of creativity and allows the organization to adapt to changing business environments and customer demands.
c. Improved employee engagement and retention: When employees feel valued and supported in their learning and development, they are more engaged and committed to the organization. This reduces turnover rates and increases employee retention.
d. Enhanced organizational performance: Learning organizations are better equipped to respond to market changes, seize new opportunities, and overcome challenges. This ultimately leads to improved organizational performance and sustained competitive advantage.
Why does an organization need an entrepreneurship spirit?
The entrepreneurship spirit is crucial for the success and growth of any organization. A study by HBR found that companies with a strong learning culture enjoy a 37% higher employee productivity rate and a 92% higher innovation rate. Here are several reasons why an organization needs this spirit:

1. Innovation and Adaptability: Entrepreneurship spirit fosters a culture of innovation and encourages employees to think outside the box. In today’s rapidly changing business environment, organizations need to continuously adapt and find new ways to provide value to their customers. By encouraging entrepreneurial thinking, organizations can identify new opportunities, develop innovative products or services, and stay competitive in the market.
A great example of this is Google’s “20% time” policy, which allows employees to spend 20% of their work time on projects or ideas that are not in their job description. This policy has led to the development of successful products like Gmail and Google Maps, showcasing the power of fostering entrepreneurship within an organization.
2. Risk-taking and Resilience: Entrepreneurs are known for their willingness to take risks and their ability to bounce back from failures. In a rapidly changing business landscape, organizations that encourage their employees to take calculated risks are more likely to seize new opportunities and achieve long-term success.
For instance, Amazon is known for its risk-taking culture. The company has taken bold moves like entering new markets, such as cloud computing with Amazon Web Services, and investing in original content through Amazon Studios. These strategic risks have paid off and contributed to Amazon’s growth and dominance in various industries.
3. Employee Engagement and Retention: Empowering employees with an entrepreneurial mindset can significantly increase their engagement and job satisfaction. When employees feel a sense of ownership over their work and are encouraged to take initiative, they become more motivated and committed to achieving the organization’s goals.
Research has shown that entrepreneurial organizations have higher levels of employee satisfaction, productivity, and retention. For example, a study by Nanyang Technological University found that organizations that foster entrepreneurship saw lower turnover rates and higher job performance among their employees. Deloitte’s 2021 Global Human Capital Trends report states that organizations that prioritize learning are three times more likely to be more agile and resilient.
4. Competitive Advantage: Organizations that embrace the entrepreneurship spirit gain a valuable competitive edge. By encouraging employees to think and act like entrepreneurs, organizations can differentiate themselves from their competitors and create unique value propositions.
Consider the case of Airbnb, a company that disrupted the hospitality industry by allowing individuals to rent out their homes to travelers. By encouraging entrepreneurship among its hosts, Airbnb has been able to rapidly expand its network and offer a more diverse and personalized range of accommodations compared to traditional hotels.
Case Study: The PayPal Mafia
Promoting entrepreneurship within an organization can significantly contribute to the development of a learning organization. Embracing entrepreneurial principles encourages innovation, risk-taking, and a relentless pursuit of improvement. One remarkable example of a group of entrepreneurs who went on to create a successful learning organization is the PayPal Mafia. This influential group demonstrates how managers can nurture entrepreneurial spirit and foster a culture of continuous learning within an organization.
1. Encourage and Support Risk-Taking:
To promote entrepreneurship, managers should encourage employees to take calculated risks. PayPal’s co-founders, known as the PayPal Mafia, took bold risks by extending the company’s services to new markets and challenging traditional banking systems. Managers should create an environment that allows employees to experiment without fear of failure. Encouraging autonomy and supporting innovative ideas can stimulate entrepreneurial thinking.
Case Study: Elon Musk, one of the leading members of the PayPal Mafia, took the risk of investing heavily in SpaceX, Tesla, and SolarCity. Despite initial skepticism, these ventures have not only thrived but revolutionized their respective industries.
2. Provide Resources and Opportunities:
Managers play a crucial role in empowering employees by providing the necessary resources and opportunities to explore entrepreneurial endeavors. PayPal’s co-founders offered early PayPal employees a unique opportunity to be part of their new ventures, even if they were unrelated to PayPal’s core business. This approach allowed them to cultivate an environment of continuous learning and entrepreneurial growth.
Case Study: Many PayPal employees went on to become successful entrepreneurs and industry leaders. Notable examples include Peter Thiel (Palantir), Max Levchin (Affirm), and Reid Hoffman (LinkedIn).
3. Foster Collaboration and Cross-Pollination:
Managers must facilitate collaboration among employees from diverse backgrounds to encourage entrepreneurship. PayPal’s success can be attributed, in part, to the diverse skill sets and perspectives brought by its team members. This cross-pollination of ideas led to creative solutions and disruptive innovations.
Case Study: PayPal’s co-founders regularly held intensive debates and brainstorming sessions, encouraging constructive criticism and feedback, which enabled the company to challenge conventional norms and drive innovation.
4. Promote a Culture of Learning:
To create a learning organization, managers need to promote a culture of continuous learning and personal development. Leaders should instill a growth mindset that values learning from both successes and failures. PayPal’s co-founders embraced continuous learning, constantly seeking ways to improve their offerings and pivot when necessary.
Case Study: After PayPal’s merger with eBay, some members of the PayPal Mafia founded companies such as YouTube, Yelp, and Yammer. These successful ventures demonstrate how an entrepreneurial mindset and a focus on learning can lead to new innovations and market disruptions
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page

