Gain insights into attention bias, one of the cognitive biases that affect us all.
Introduction
In the vast realm of cognitive psychology, Attentional Bias stands as a significant concept, shedding light on how our perceptions and decisions are influenced by our focus. This cognitive bias, a systematic error in thinking that affects the decisions and judgments that people make, plays a critical role in our everyday lives, often without us even realizing it.
Attention Bias refers to how a person’s perception is affected by selective factors in their attention. It’s a fascinating phenomenon where our brain, instead of taking a balanced view of what’s around us, pays more attention to certain types of things while simultaneously ignoring others. This bias can manifest in various ways, influencing our behavior and decision-making processes in contexts as diverse as anxiety and depression, substance use disorder, law enforcement, and even our political beliefs.
In this comprehensive exploration of Attention Bias, we will delve into its implications in different areas of life and society, its evolutionary advantages, and the therapeutic approaches like Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) and mindfulness exercises that are used to mitigate its effects. We will also explore intriguing concepts like the Emotional Stroop (ES) Task and the role of selective attention in our daily lives.
Whether you’re a psychology enthusiast, a student, or a professional in the field, this blog aims to provide a definitive understanding of Attentional Bias, offering insights that are both academically rigorous and practically relevant.
We have written blog 125 most common biases and fallacies that impact our decision making. Read here
Defining Attention Bias
Attentional Bias is a psychological term that refers to the tendency of our perception to be influenced by our recurring thoughts. It is a type of cognitive bias that affects our attention, causing us to pay more heed to certain types of information while ignoring others.
In essence, Attention Bias is the uneven distribution of attention where certain emotions, stimuli, or thoughts take precedence over others. This bias can significantly impact our decision-making process and our interpretation of events and situations. It’s like wearing a pair of glasses that selectively magnifies certain aspects of our environment while minimizing others.
Attention bias is not inherently negative. It can help us focus on important tasks and make quick decisions when necessary. However, when it leads to an overemphasis on certain stimuli at the expense of others, it can distort our perception of reality and potentially lead to flawed decision-making.
Layman Example of Attention Bias
Let’s consider a simple, everyday example to understand Attention Bias. Imagine you’ve recently developed an interest in gardening. You’ve been reading about different plants, learning about gardening techniques, and even planning to start your own small garden. Suddenly, you start noticing plants everywhere. The small flower shop on your way to work, the new gardening show on TV, the beautiful garden in your neighbor’s yard – things that have always been there but never caught your attention before.
This doesn’t mean that there are suddenly more plants and gardening references around you. Rather, because of your newfound interest, your attention is now biased towards anything related to gardening. You’re more likely to notice plants, gardening tools, or anything related to this topic because it’s currently occupying a significant part of your thoughts. This is a classic example of Attentional Bias in action.
Academic Definitions of Attention Bias
In academic circles, Attention Bias is defined as the differential allocation of attentional resources towards certain types of information while simultaneously ignoring others. It is a cognitive bias that influences our perception, decision-making, and behavior.
According to cognitive psychology, Attentional Bias is a phenomenon that describes our tendency to pay more attention to certain types of stimuli, such as those that are emotionally significant or relevant to our current goals. It is a fundamental aspect of human cognition and is believed to be a result of the adaptive mechanisms that have evolved to enhance our survival.
In the context of clinical psychology, Attentional Bias is often discussed in relation to mental health disorders. For instance, individuals with anxiety disorders may exhibit an Attentional Bias towards threat-related stimuli, while those with substance use disorders may show a bias towards drug-related cues.
In the field of social psychology, Attentional Bias can refer to the tendency to focus more on certain social cues while ignoring others, which can influence our social interactions and judgments.
We have written blog 125 most common biases and fallacies that impact our decision making. Read here
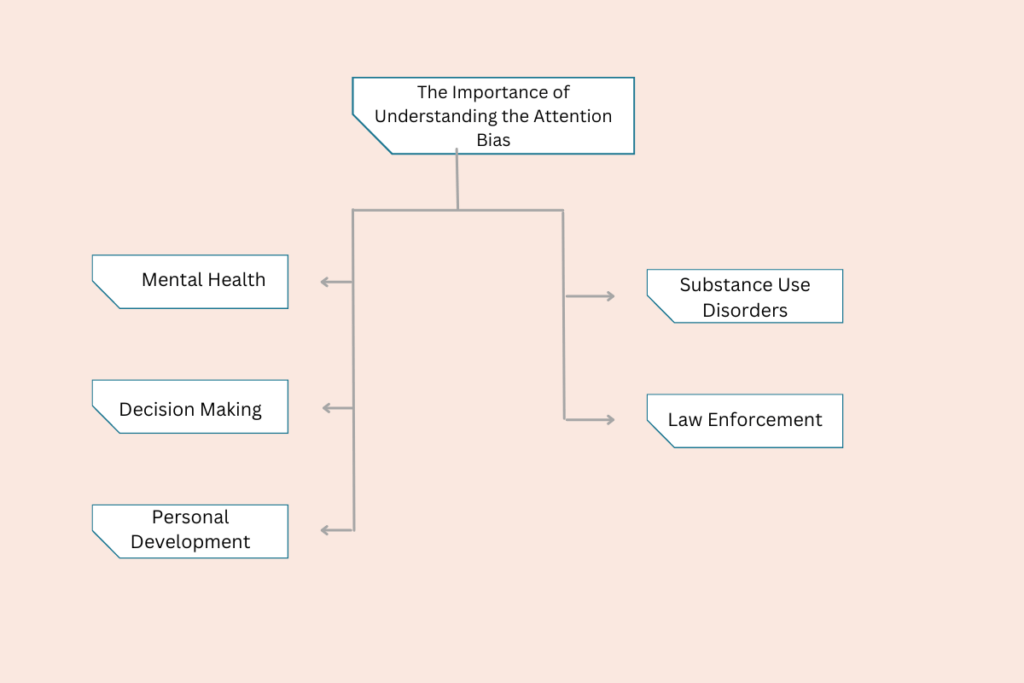
The Importance of Understanding the Attention Bias

Mental Health: Attention Bias plays a significant role in various mental health disorders. For instance, individuals with anxiety tend to focus more on threat-related stimuli, while those with depression often pay more attention to negative information. Understanding these biases can aid in the development of effective therapeutic interventions, such as Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT), which aims to challenge and change cognitive distortions and biases.
Substance Use Disorders: In the realm of addiction, individuals often exhibit an Attentional Bias towards drug-related cues. This can make the process of quitting more challenging, as these cues can trigger cravings and relapse. Recognizing this bias is a crucial step in the rehabilitation process.
Decision Making: Attentional Bias can significantly impact our decision-making process. By focusing on certain information and ignoring others, we may make decisions based on incomplete or skewed data. This understanding can help us make more informed and balanced decisions.
Law Enforcement: Attention Bias can also have implications in law enforcement, particularly in areas like racial profiling and prejudice in policing. Officers may unconsciously pay more attention to certain racial or ethnic groups due to societal biases, leading to unfair treatment.
Personal Development: On a personal level, understanding Attentional Bias can help us recognize our own biases and work towards mitigating their impact. Techniques like mindfulness exercises can help us manage our attention more effectively, reducing the influence of bias on our thoughts and actions.
We have written blog 125 most common biases and fallacies that impact our decision making. Read here
The Psychology behind Attention Bias
Attentional Bias is deeply rooted in our cognitive processes and is influenced by various psychological factors. It is a manifestation of our brain’s ability to selectively focus on certain stimuli while ignoring others. This selective attention is a fundamental aspect of human cognition, allowing us to navigate our complex environments without becoming overwhelmed by the sheer volume of sensory information we encounter every day.
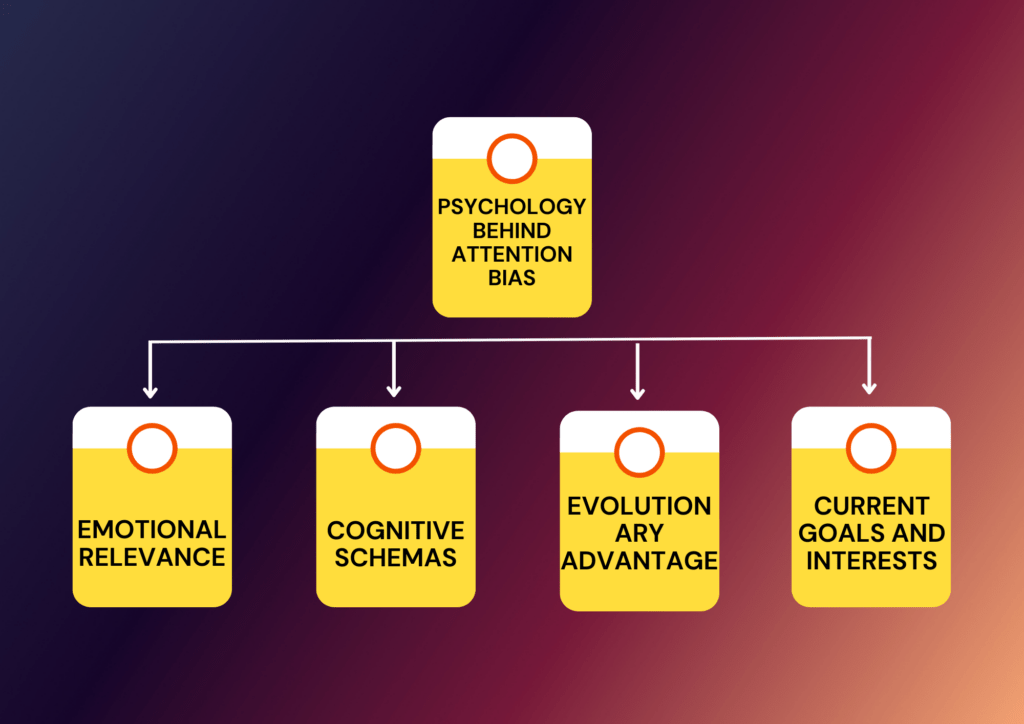
Emotional Relevance: One of the key factors that influence Attentional Bias is the emotional relevance of a stimulus. We are more likely to pay attention to things that evoke strong emotions. For instance, individuals with anxiety disorders often exhibit an Attentional Bias towards threat-related stimuli, as these stimuli evoke strong feelings of fear or worry.
Cognitive Schemas: Our cognitive schemas, or mental frameworks, also play a significant role in shaping our Attentional Biases. These schemas help us organize and interpret information, and we are more likely to focus on information that aligns with our existing schemas. For example, if we have a negative schema about ourselves, we may pay more attention to negative feedback while ignoring positive feedback.
Evolutionary Advantage: Some Attentional Biases may have evolutionary roots. For instance, our tendency to pay more attention to threatening stimuli could have been an adaptive response in our evolutionary past, helping us quickly identify and respond to potential dangers in our environment.
Current Goals and Interests: Our current goals and interests can also influence our Attentional Bias. If we are currently interested in a particular topic, we are more likely to notice related information in our environment.
We have written blog 125 most common biases and fallacies that impact our decision making. Read here
Historical Background
The concept of Attentional Bias has its roots in the broader field of cognitive psychology, which began to flourish in the mid-20th century. The term itself, however, started gaining traction in the late 1970s and early 1980s, as researchers began to explore the ways in which attention could be influenced by various factors, including emotional states and cognitive schemas.
Key Studies and Findings
One of the most influential studies in this field was conducted by American psychologist John Ridley Stroop in 1935. Known as the Stroop Task, this experiment demonstrated how our attention could be biased by conflicting information. Participants were asked to name the color of the ink in which a word was written, but the task was made difficult when the word itself was the name of a different color. This study laid the groundwork for understanding how our attention can be influenced by conflicting cognitive demands.
In the 1980s, a modified version of the Stroop Task, known as the Emotional Stroop Task, was used to demonstrate Attentional Bias in individuals with anxiety disorders. Participants were slower to name the color of threat-related words, suggesting that their attention was being drawn to the threatening content of the words.
More recent studies have explored Attentional Bias in the context of substance use disorders, with findings suggesting that individuals with these disorders show a bias towards drug-related cues. This has important implications for understanding the challenges faced by individuals attempting to quit substance use.
Factors Influencing Attention Bias
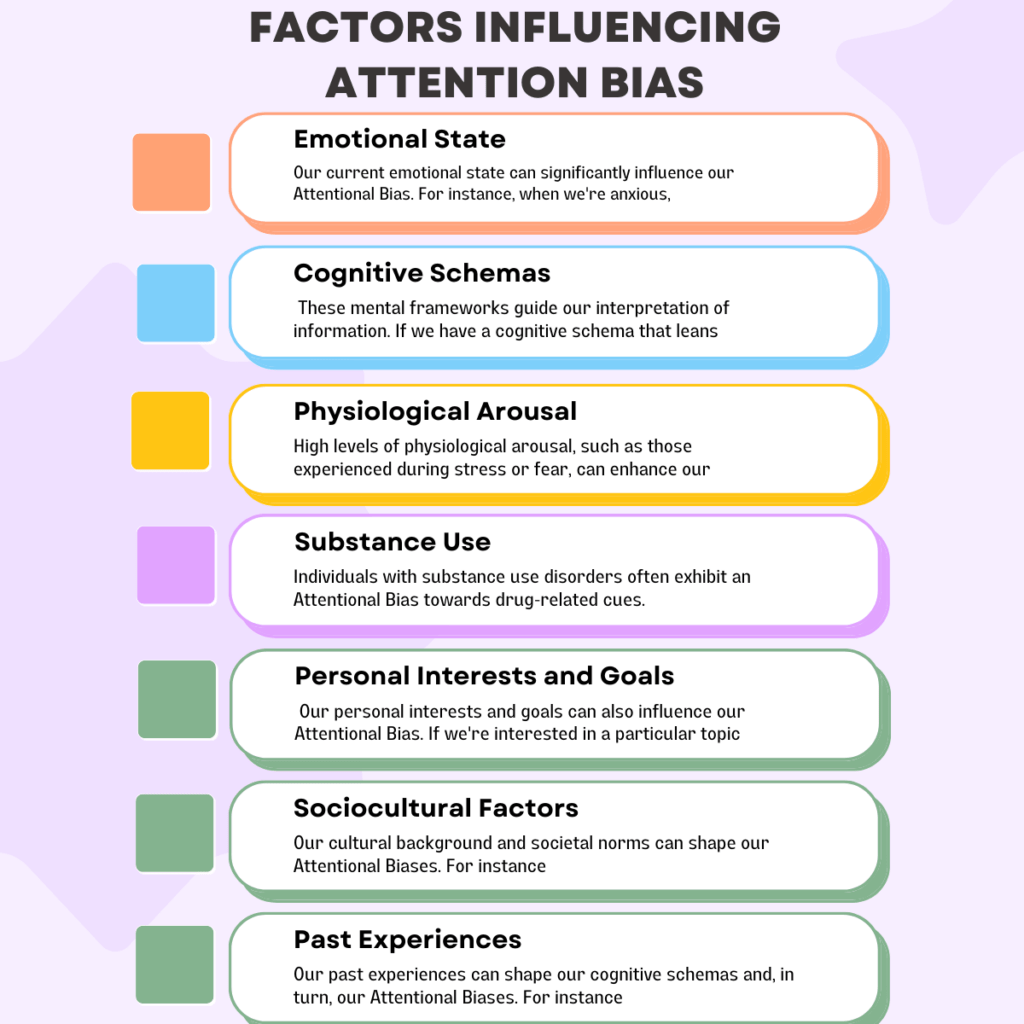
Emotional State: Our current emotional state can significantly influence our Attentional Bias. For instance, when we’re anxious, we’re more likely to focus on threat-related stimuli. Similarly, individuals experiencing depression may pay more attention to negative information.
Cognitive Schemas: These mental frameworks guide our interpretation of information. If we have a cognitive schema that leans towards negativity, we may exhibit an Attentional Bias towards negative stimuli.
Physiological Arousal: High levels of physiological arousal, such as those experienced during stress or fear, can enhance our Attentional Bias towards threat-related stimuli.
Substance Use: Individuals with substance use disorders often exhibit an Attentional Bias towards drug-related cues. This can make the process of quitting more challenging, as these cues can trigger cravings.
Personal Interests and Goals: Our personal interests and goals can also influence our Attentional Bias. If we’re interested in a particular topic, we’re more likely to notice related information in our environment.
Sociocultural Factors: Our cultural background and societal norms can shape our Attentional Biases. For instance, societal stereotypes can lead to biases in how we perceive and interpret information about different social groups.
Past Experiences: Our past experiences can shape our cognitive schemas and, in turn, our Attentional Biases. For instance, if we’ve had negative experiences with dogs in the past, we may exhibit an Attentional Bias towards dogs in the future.
We have written blog 125 most common biases and fallacies that impact our decision making. Read here
Real-World Implications of Attention Bias
How to overcome Attention Bias
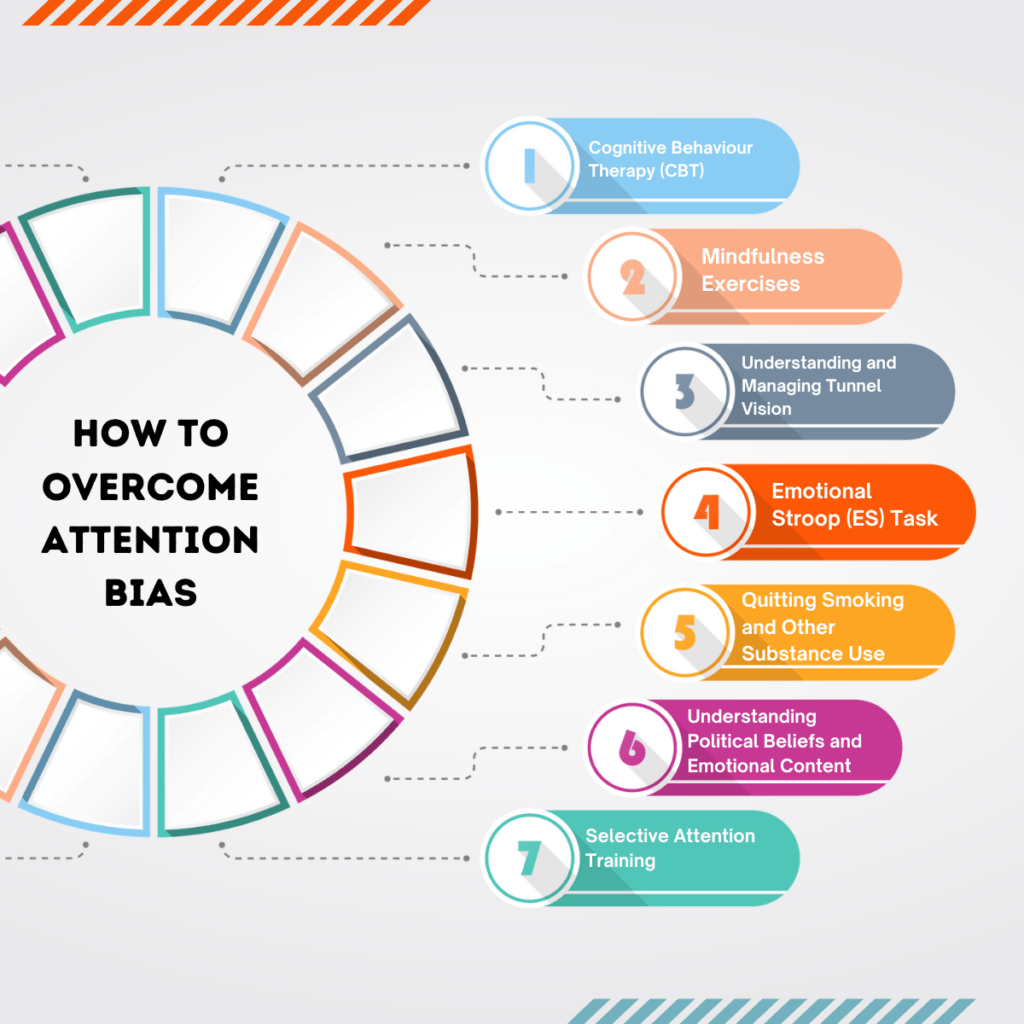
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT): CBT is a type of psychotherapy that can help individuals recognize and change distorted thought patterns that lead to problematic behaviors and emotions. In the context of Attention Bias, CBT can help individuals identify their biases and develop strategies to manage them effectively.
Mindfulness Exercises: Mindfulness involves paying full attention to the present moment without judgment. Regular mindfulness exercises can help individuals become more aware of their Attentional Biases and learn to direct their attention in a more balanced way.
Understanding and Managing Tunnel Vision: Tunnel vision, a term often used to describe a narrow focus that excludes peripheral information, can be a manifestation of Attentional Bias. By recognizing when we’re experiencing tunnel vision, we can take steps to broaden our focus and consider a wider range of information.
Emotional Stroop (ES) Task: The ES task is a tool used in psychological research to measure Attentional Bias. By participating in such tasks, individuals can become more aware of their biases. This awareness is the first step towards managing these biases effectively.
Quitting Smoking and Other Substance Use: As substance use can enhance Attentional Bias towards drug-related cues, quitting substance use can help reduce this bias. Support from healthcare professionals and use of appropriate therapeutic interventions can aid this process.
Understanding Political Beliefs and Emotional Content: Our political beliefs and emotions can influence our Attentional Bias. By understanding this, we can strive to ensure that our attention is not unduly influenced by these factors.
Selective Attention Training: This involves training individuals to direct their attention away from negative stimuli and towards positive or neutral stimuli. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with anxiety disorders, who often exhibit an Attentional Bias towards threat-related stimuli.
Appreciating Evolutionary Advantages: Understanding that some aspects of Attentional Bias may have evolutionary roots can help us appreciate why we have these biases. For instance, our tendency to pay more attention to threatening stimuli could have been an adaptive response in our evolutionary past, helping us quickly identify and respond to potential dangers in our environment.
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page