Master Product Classification: Unveil the Secrets of an Exceptional Marketing Strategy

Introduction
In the world of marketing, understanding the diverse range of products and their characteristics is crucial. Product classification plays a pivotal role in creating effective marketing strategies and targeting the right audience. This blog post delves into the concept of product classification, its importance, and the various types and classifications of different brands of products that marketers should be aware of. However, to understand a product classification we must first understand what a product is.
The core understanding will be reinforced by what are the levels of the product followed by the classification of the same. We will also understand why marketers use product classification to understand the demand for the product categories.
Definition of Product
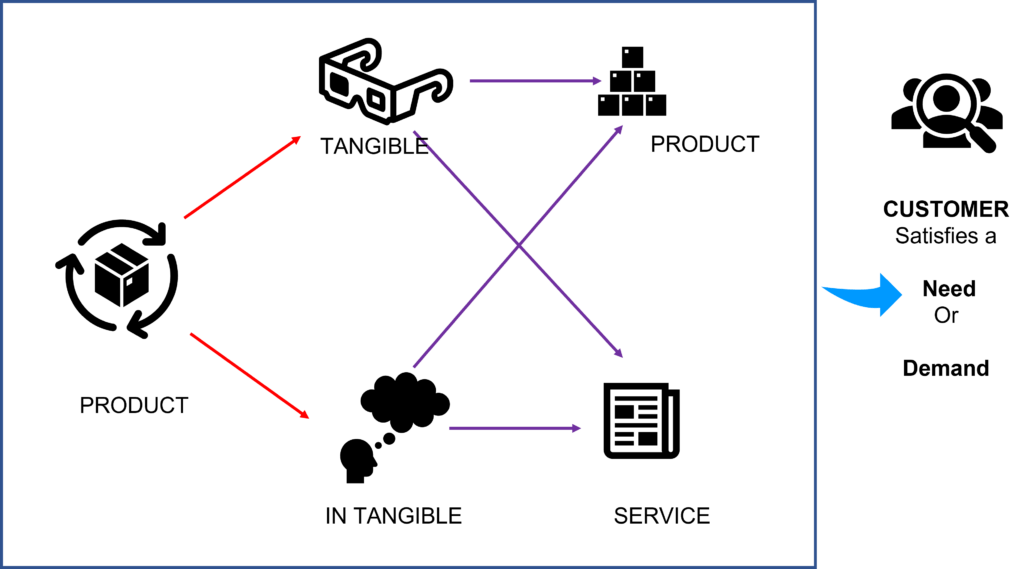
A product can be academically defined as a tangible or intangible item offered by a company or individual to satisfy a consumer’s need or want. Products can include goods, services, and ideas (Kotler & Keller, 2016).
According to Philip Kotler and Kevin Lane Keller, two leading marketing scholars, a product is “anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy a want or need, including physical goods, services shopping goods, experiences, events, persons, places, properties, organizations, information, and ideas” (Kotler & Keller, 2016)
Additionally, in their book “Marketing Management,” authors Roger J. Best and David W. Stewart state that “a product is a set of tangible and intangible attributes that a seller offers to potential buyers to satisfy their needs and wants” (Best & Stewart, 1990)
What is Product Classification in Marketing?
Product classification is the process of categorizing products into categories based either on their characteristics, purpose, or target market. These classifications help marketers develop tailored marketing strategies to reach consumers and create a competitive edge.
Importance of Product Classification
Marketing Strategies
Classifying products helps marketers design and implement appropriate marketing strategies for each product category. Different products require different marketing efforts, and understanding these classifications ensures that the marketing strategy aligns with the actual product type.
Target Market
Product classification helps marketers identify the target audience for each product category. Knowing the target market allows for better positioning and messaging, leading to increased sales and brand recognition.
Brand Recognition
Product classification aids marketers in building brand recognition by understanding which products are associated with specific consumer habits. This enables them to focus on promoting the products that are most likely to resonate with their target audience.
The 5 Levels of Products
The concept of the 5 levels of a product, also known as the “Five Product Levels Model,” was introduced by marketing expert Philip Kotler. The model helps marketers and businesses understand the various components of a product offering, enabling them to differentiate their products from competitors and create added value for customers. The 5 levels of a product are as follows:
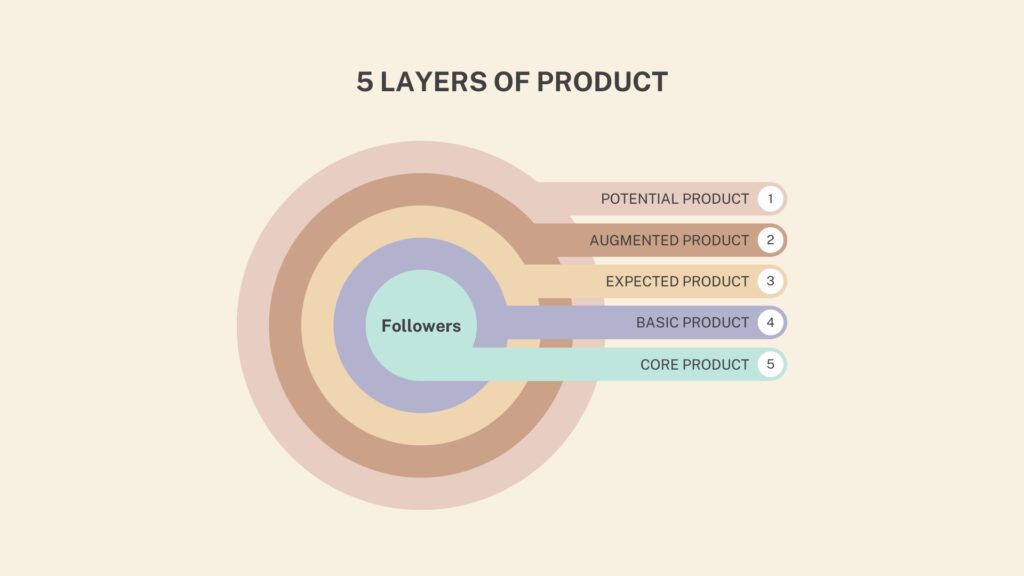
Core Benefit: The core benefit is the fundamental reason a customer buys a product. It represents the primary value or problem-solving capability that the product provides to the customer. For example, the core benefit of a smartphone is communication.
Basic Product: The basic product is the most basic version of a product that contains only the essential features necessary to provide the core benefit. For instance, a basic smartphone would include basic features such as calling, texting, and a simple camera.
Expected Product: The expected product consists of the attributes and features that customers typically expect from a product in a given category. These features go beyond the basic product and align with customer expectations based on market standards. In the case of a smartphone, the expected features might include a high-resolution display, decent battery life, and a selection of pre-installed apps.
Augmented Product: The augmented product refers to additional features, services, or benefits that enhance the product offering and differentiate it from competitors. These added-value components often create a competitive advantage for the product. For a smartphone, augmented features could include extended warranties, free software updates, or a unique design.
Potential Product: The potential product represents all the possible improvements, innovations, and future developments that a product could undergo. It envisions the product’s full potential and the value it could deliver to customers in the long term. For a smartphone, potential product elements might include foldable screens, advanced artificial intelligence capabilities, or seamless integration with other devices.
By considering each of these 5 levels, marketers can better understand their own product line’s value proposition, identify opportunities for innovation, and create a more compelling and competitive offering for their customers.
The Four Classifications of Products
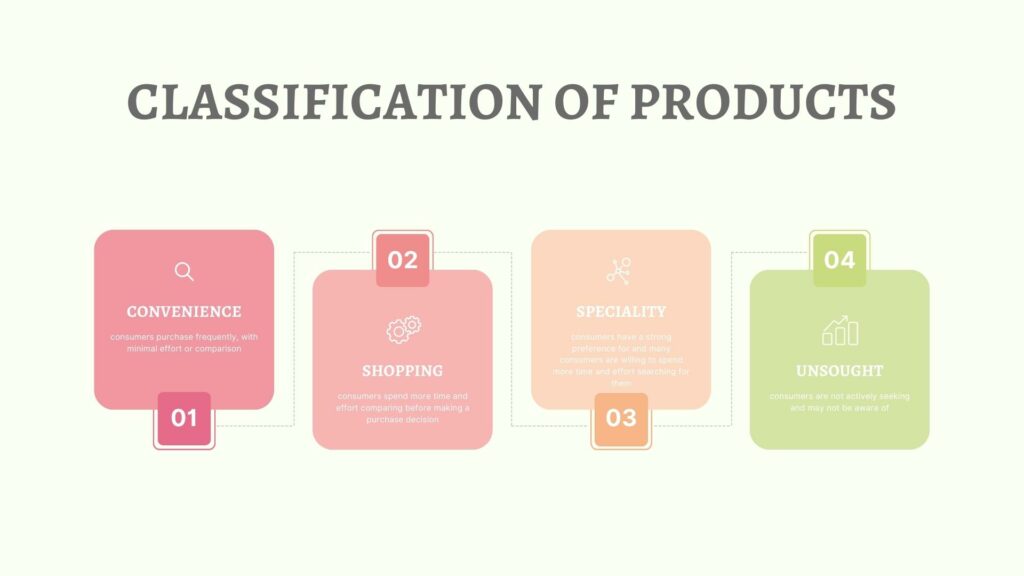
Convenience Products
Convenience products are those that consumers purchase frequently, with minimal effort or comparison. Examples of convenience products include snacks, toothpaste, and newspapers. These products are often low-cost, and marketing efforts should focus on their convenience good making them easily accessible to consumers.
Shopping Products
Shopping products are items that consumers spend more time and effort comparing before making a purchase decision. Examples of shopping products include clothing, appliances, and electronics. Marketing strategies for shopping for products should emphasize product quality and differentiation, as consumers often compare products with competing brands.
Specialty Products
Specialty products or specialty items are items that consumers have a strong preference for and many consumers are willing to spend more time and effort searching for them. Examples of specialty products include luxury cars, high-end electronics, and designer clothing. Marketers should focus on creating brand loyalty and personal selling for these products.
Unsought Products
Unsought products are those that consumers are not actively seeking and may not be aware of. Examples of the unsought products include life insurance and funeral services. Marketing efforts for unsought products should focus on wide-scale promotion and reminding consumers of their existence and potential benefits.
The Seven Types of Products
Consumer Goods
Consumer goods are products intended for personal consumption by the end user. Examples of consumer products include food, clothing, and household items. Marketing strategies for consumer goods should focus on engaging with the consumer product target audience and building brand recognition.
Industrial Products
Industrial products are items used in the production of other goods or services. Examples of consumer products include machinery, equipment, and raw materials. Marketing efforts for industrial products should target businesses and consumers approach emphasize product efficiency and reliability.
Raw Materials
Raw materials are the basic components used in the production of other goods. Examples include wood, metals, and agricultural products. Marketing strategies for raw materials marketing specialty goods should focus on quality, availability, and price.
Durable Goods
Durable goods are products that have a long life span and are not consumed or destroyed during their use. Examples include cars, furniture, and appliances. Marketing efforts for durable goods should emphasize product quality, durability, and after-sales support.
Non-Durable Goods
Non-durable goods are products that have a short life span and are consumed or destroyed during their use. Examples include food, beverages, and disposable items. Marketing strategies for non-durable goods should focus on convenience, price, and consumer habits.
Services
Services are intangible offerings provided by individuals or businesses to satisfy consumer needs. Examples include haircuts, car repairs, and legal advice. Marketing efforts for services should focus on the expertise, quality, and value provided by the service provider.
Ideas
Ideas are concepts or intellectual property that can be marketed and sold, such as patents, trademarks, or copyrights. Marketing strategies for ideas should focus on the benefits, uniqueness, and potential applications of the idea.
Understanding Product Classifications
Convenience Goods
Impulse Purchases
Impulse purchases are items that consumers buy on a whim, without prior planning. Examples include candy bars, magazines, and small toys. Marketing efforts for impulse purchases should focus on attractive packaging, strategic product placement one brand name, and promotions to encourage impulse buys.
Checkout Line Products
Checkout line products are items placed near the cash register to encourage last-minute purchases. Examples of such products include gum, mints, and small personal care items. Marketing strategies for checkout line products should focus on visibility, convenience, and lower price.
Shopping Goods
Homogeneous Shopping Products
Homogeneous shopping products are items consumers perceive as similar and are willing to substitute with other brands based on price and availability. Examples include gasoline, bottled water, and basic clothing items. Marketing efforts for homogeneous shopping goods products should focus on competitive pricing, promotions, and distribution.
Heterogeneous Shopping Products
Heterogeneous shopping products are items that consumers perceive as distinct, and they often compare features’ lowest price, quality, and brand reputation before making a final purchase decision. Examples include smartphones, computers, and appliances. Marketing strategies for heterogeneous products should emphasize product differentiation, quality, and brand reputation.
Specialty Goods
Brand Loyalty
Brand loyalty is the strong preference most consumers have for a specific brand, often resulting from positive experiences or emotional connections. Marketing efforts for specialty products should focus on building and maintaining brand loyalty through exceptional customer experiences, quality products, and targeted marketing campaigns.
Personal Selling
Personal selling involves direct interaction between a salesperson and a consumer to persuade the consumer to purchase a product. Specialty products often require personal selling to educate consumers about why product exists and the unique features, benefits, and value of the product.
Unsought Goods
Wide Scale Promotion
Wide-scale promotion involves using various marketing channels to reach a large audience and create awareness about a product or service. Unsought products often require wide-scale promotion to inform consumers about their existence, benefits, and potential uses.
Reminding Consumers purchase
Reminding consumers is a marketing tactic used to keep a product or service in the minds of consumers, even if they are not actively seeking it. For unsought products, marketers should focus on creating memorable advertisements and promotions to remind consumers of the product’s existence and potential benefits.
Marketing Strategies for Different Product Classifications

Convenience Products
Marketing strategies for convenience products should focus on making the products easily accessible, with wide distribution in convenience stores and competitive pricing. In-store promotions, eye-catching packaging, and strategic product placement in different stores can help drive impulse purchases and increase sales.
Shopping Products
For shopping products, marketing strategies should emphasize product differentiation, quality, and value. Providing detailed product information, offering comparisons with competing brands and other examples only the product itself, and creating engaging advertising campaigns can help consumers make informed purchase decisions.
Specialty Products
Marketing strategies for specialty products should focus on building brand loyalty and creating a strong emotional connection with consumers. Personal selling, targeted marketing campaigns, and exceptional customer experiences with specialty products can help establish a strong preference for the brand.
Unsought Products
For unsought products, marketing efforts should focus on wide-scale promotion and reminding consumers of the product’s existence and potential benefits. Informative advertisements, public relations campaigns, and educational marketing materials can help raise awareness and generate interest in these products.
Why is a differentiated marketing strategy required for various products classification?
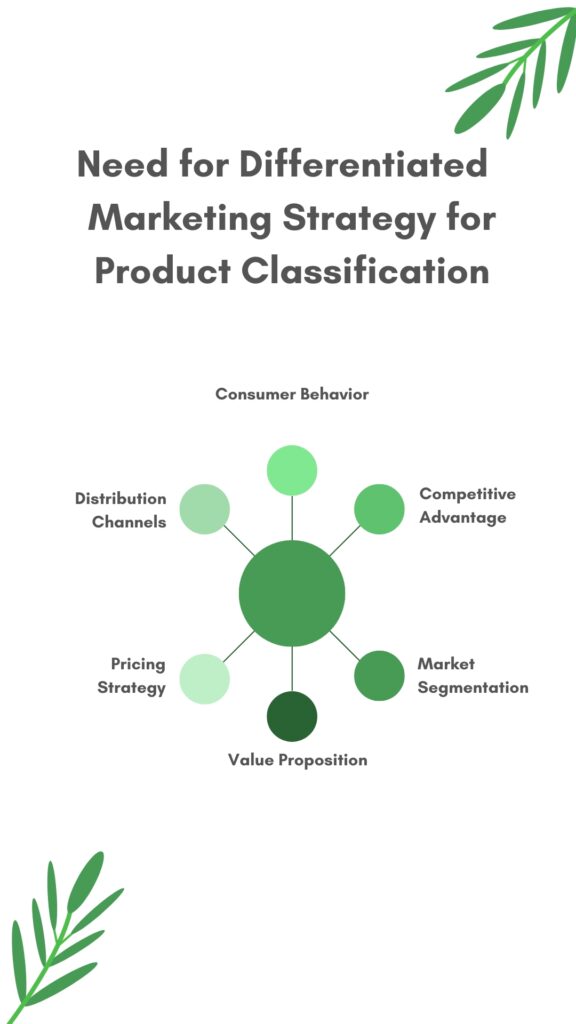
Consumer Behavior: Different product classifications have varying levels of consumer involvement, purchase frequency, and decision-making processes. A differentiated marketing strategy enables businesses to address these varying consumer behaviors by tailoring their marketing mix (product, price, place, and promotion) to meet the unique needs of each product category.
Competitive Advantage: Employing a differentiated marketing strategy allows businesses to create a competitive advantage by offering unique products and services that cater to specific market segments. By targeting niche markets and delivering tailored value propositions, businesses can establish a strong market position and distinguish themselves from competitors.
Market Segmentation: A differentiated marketing strategy allows businesses to effectively segment their target market based on demographics, psychographics, geographic, and behavioral factors. By identifying and focusing on specific market segments, businesses can allocate their resources more efficiently, design targeted marketing campaigns, and create tailored products and services that meet the unique needs of each segment.
Value Proposition: Different product classifications demand unique value propositions. A differentiated marketing strategy enables businesses to develop compelling value propositions for each product category, emphasizing the specific benefits and features that appeal to their target audience. This approach increases the likelihood of customer satisfaction, loyalty, and repeat purchases.
Pricing Strategy: Different product classifications require diverse pricing strategies based on factors such as cost structure, competitive landscape, and consumer price sensitivity. A differentiated marketing strategy allows businesses to implement pricing strategies that align with the specific characteristics of each product category, maximizing profitability and perceived value.
Distribution Channels: Different product classifications may require distinct distribution channels based on factors such as the product’s nature, target market, and logistical requirements. A differentiated marketing strategy enables businesses to choose the most appropriate distribution channels for each product category, ensuring efficient delivery and accessibility for their customers.
Conclusion
Product classification is a crucial aspect of marketing, as it helps marketers understand the diverse range of products, their characteristics, and their target markets. By categorizing products into various types and classifications, marketers can develop tailored marketing strategies to reach consumers effectively and create a competitive edge. Understanding product characteristics, categories and classification is essential for developing effective marketing strategies, targeting the right audience, and building brand recognition.
FAQs
What is product classification in marketing? Product classification is the process of categorizing products based on their characteristics, purpose, or target market. It helps marketers develop tailored marketing strategies and target the right audience.
What are the four classifications of products? The four classifications of products are convenience products, shopping products, specialty products, and unsought products.
What are the seven types of products? The seven types of products are consumer goods, industrial products, raw materials, durable goods, non-durable goods, services, and ideas.
Why is product classification important? Product classification is important because it helps marketers design and implement appropriate marketing strategies for each product category, identify the target market, and build brand recognition.
How do marketing strategies differ for various product classifications? Marketing strategies differ for various product classifications based on factors such as the level of consumer involvement, the frequency of purchase, and the degree of differentiation among products. Different strategies are required for convenience products, shopping products, specialty products, and unsought products to effectively reach and engage consumers.
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page