Definition of Earned Media Value
Earned Media Value (EMV) is a metric used by marketing professionals to calculate the worth of media attention and goodwill generated through non-paid strategies, such as positive word-of-mouth, customer recommendations, or organic social media sharing. Unlike paid media, which involves direct payment for advertising, earned media comes as a result of excellent public relations, excellent customer service, or an outstanding product.
The EMV calculation differs across industries and companies, as it is largely subjective and depends on the specific goals of a business. However, a common approach is to equate the value of earned media with the cost of purchasing the same media exposure. For example, if a company receives a positive mention in a high-profile magazine, the EMV might be calculated as the cost of buying a full-page advertisement in the same magazine.
Importance of Earned Media Value in Business
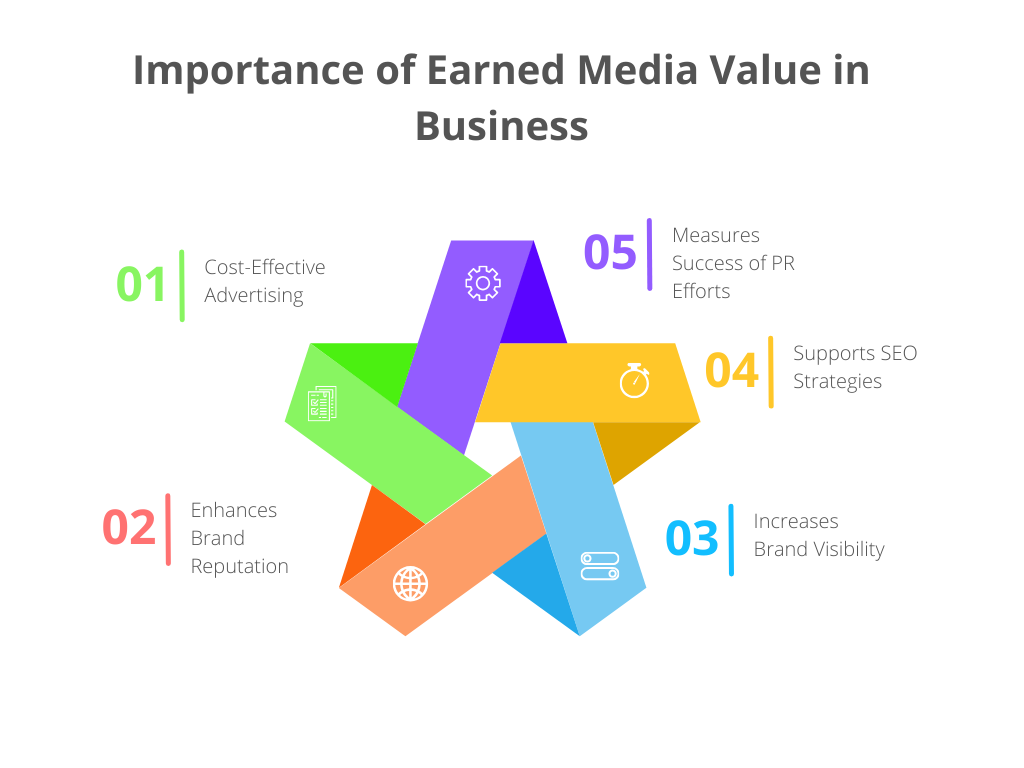
Cost-Effective Advertising: Earned media represents a cost-effective form of advertising. While there are costs associated with PR efforts to generate earned media, the costs are often significantly lower than purchasing equivalent advertising space. Additionally, earned media often tends to have a longer shelf life than paid advertising – a positive news article or a product review can continue to generate interest and sales long after its publication.
Enhances Brand Reputation: Earned media enhances the reputation of a brand. Positive mentions in media and recommendations from satisfied customers foster trust among potential customers. This is especially important in today’s digital era, where consumers often rely on reviews and recommendations before making a purchase.
Increases Brand Visibility: Earned media increases brand visibility. When customers, influencers, or news outlets share positive information about a brand, it expands the brand’s reach to a wider audience. This increased visibility often leads to higher brand recognition and potentially more sales.
Supports SEO Strategies: The role of earned media in Search Engine Optimization (SEO) cannot be overstated. Google and other search engines use mentions of a brand online as a factor in determining the brand’s relevance and authority. Consequently, the more positive mentions a brand has online, the higher its website will rank in search engine results, driving more organic traffic to the site.
Measures Success of PR Efforts: Finally, EMV is a valuable metric for businesses to measure the success of their PR efforts. By calculating the value of earned media, businesses can quantify the return on their PR investment and make informed decisions about future PR strategies.
The Evolution of Earned Media Value
Traditional Versus Modern Views
Traditional Views on Earned Media Value: The traditional perspective of earned media value primarily focuses on public relations and word-of-mouth referrals. The effectiveness of these methods was often measured by factors such as media coverage, audience reach and the frequency of mentions. However, this approach lacked precise quantification, and it was challenging to assess the actual return on investment (ROI).
Modern Views on Earned Media Value: The rise of digital media and online platforms has significantly transformed the concept of earned media value. Modern approaches consider likes, shares, mentions, comments, reviews, and ratings across various digital platforms as a part of earned media. With the help of analytics and tracking tools, it’s now possible to calculate the exact earned media value by analyzing user engagement, click-through rates, conversion rates, and other metrics. This approach provides a more accurate understanding of ROI in digital marketing.
| Aspect | Traditional Views | Modern Views |
| Focus | Public relations and word-of-mouth referrals | Digital media and online platforms |
| Metrics | Media coverage, audience reach, frequency | Likes, shares, mentions, comments, reviews, ratings |
| Quantification | Lacked precise quantification | Analyzing user engagement, click-through rates, conversion rates |
| Assessment of ROI | Challenging to assess ROI | More accurate understanding through analytics and tracking tools |
Challenges and Opportunities in Earned Media Value
Challenges in Measuring Earned Media Value: Despite the advancements in analytics, there are still challenges in measuring earned media value. These include the difficulty of attributing value to individual actions (like a like or share), lack of standardization in measurement practices, and the volatile nature of online platforms where a conversation can quickly change direction. Furthermore, the value of earned media can vary significantly between industries, making it challenging to create a one-size-fits-all measurement approach.
Opportunities in Earned Media Value: Despite the challenges, the evolution of earned media value offers exciting opportunities. The proliferation of digital platforms has made it easier for businesses to reach and engage with their target audience. Also, unlike paid media, earned media is often perceived as more credible and can significantly enhance a brand’s reputation. With the correct tools and strategies, businesses can maximize their earned media value, helping them stand out in today’s crowded digital landscape.
The Power of Influence: Understanding Earned Media Value
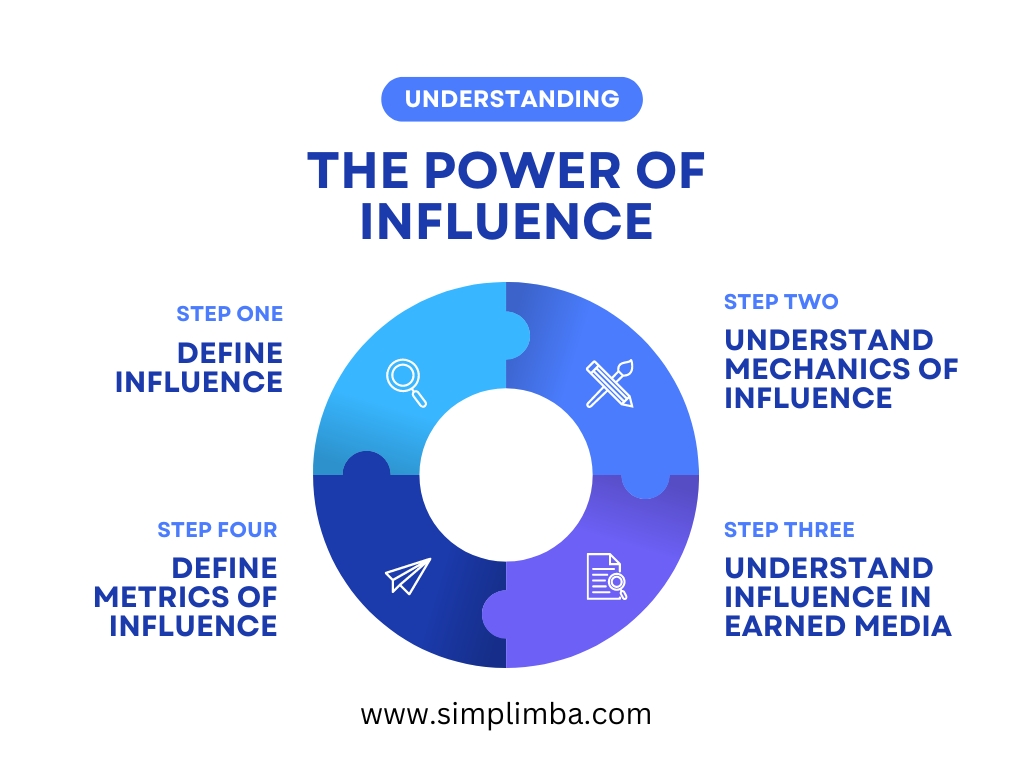
Defining Influence: Influence can be understood as the capacity to affect the character, development, or behavior of someone or something. In the context of earned media, influence is the ability of an individual, brand, or organization to shape public perception and drive actions or responses. It’s a critical component in driving word-of-mouth marketing and generating organic reach.
The Mechanics of Influence: Fundamentally, influence operates on principles of trust, credibility, and authority. When an influencer shares positive insights or opinions about a product or service, it can significantly sway public perception and behaviors. This accessibility to and control over the target audience’s trust and actions is what makes influencers an invaluable asset in earned media strategies.
Influence in Earned Media: Earned media refers to any publicity gained through promotional efforts other than advertising. This includes mentions in news outlets, word-of-mouth, and social media shares, among others. Influence plays a key role in earned media as influencers can help amplify the reach of such unpaid publicity, propel positive public relations, and enhance brand image.
Metrics for Evaluating Influence: The impact of influence in earned media can be determined using metrics such as overall reach (number of people exposed to the message), engagement rates (how many people interacted with the content), sentiment analysis (positive, negative, or neutral perceptions), and conversion rates (how many people took the desired action after exposure to the message).
Case Studies of Successful Use of Influence in Earned Media
Case Study 1: Dove’s Real Beauty Sketches Campaign: Dove leveraged the influence of ordinary women to drive their campaign message about real beauty. The campaign video quickly became viral, gaining vast amounts of earned media through shares, likes, comments, and organic mentions in press and blogs. The success of the campaign underscores the power of relatable influencers in driving engagement and positive brand sentiment.
Case Study 2: ALS Ice Bucket Challenge: This campaign demonstrated the power of influence in driving viral participatory content. The challenge involved influencers and celebrities pouring a bucket of ice water over their heads to raise awareness for ALS. As influencers and ordinary people alike joined the campaign, it generated immense amounts of earned media, leading to significant increases in donations for ALS research.
Case Study 3: Tesla and Elon Musk: Tesla’s earned media success can be significantly attributed to the influence of its CEO, Elon Musk. Musk’s active and engaging social media presence has helped generate extensive press coverage and social media buzz around Tesla’s products and projects. This case demonstrates the role of executive influence in driving earned media.
Case Study 4: Nike’s Colin Kaepernick Ad: Nike’s bold decision to feature controversial figure Colin Kaepernick in its ad campaign was a calculated risk that paid off. Despite initial backlash, the campaign gained extensive media coverage and conversation, largely driven by the influence of Kaepernick. This case illustrates how influence can be leveraged to drive conversation and publicity even amidst controversy.
10 Key Metrics to Measure Earned Media Value

Social media engagement is a measure of the number of interactions a user has with your content on platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, etc. This includes likes, shares, comments, and retweets. High engagement rates generally indicate that your content is resonating with your audience and sparking conversation. For calculating the engagement rate, you can use the formula (Total Engagement / Total Followers) * 100% to get a percentage.
Website Traffic: Page Views, Unique Visitors
Website traffic is the measure of the number of people who visit your website. Page views are the total number of pages viewed, while unique visitors are the number of distinct individuals who have viewed your site during a specific period. High website traffic generally indicates high interest in your brand or products.
Lead Generation: Conversion Rates, New Leads
Lead generation refers to the process of attracting potential customers (leads) and converting them into people who have an interest in your company’s product or service. Conversion rates are the percentage of visitors who complete a desired action (like filling out a form), and new leads are the number of people who have shown interest for the first time during a specific period.
SEO Impact: Organic Rankings, Backlink Quality
SEO impact refers to how well your website is optimized for search engines. Organic rankings refer to where your website appears in search engine results for certain keywords, while backlink quality refers to the number and relevance of other sites linking to your site. High organic rankings and quality backlinks generally mean your website is trusted by search engines, which can lead to increased visibility and traffic.
Brand Sentiment: Positive Mentions, Brand Advocacy
Brand sentiment is the perception of your brand by the public. Positive mentions are the number of times your brand is mentioned in a positive context, while brand advocacy refers to customers who actively promote your brand to others. High positive sentiment and brand advocacy usually indicate high customer satisfaction.
Customer Retention: Repeat Business, Customer Loyalty
Customer retention refers to the ability of a company to retain its customers over a specific period. Repeat business is the number of customers who make repeat purchases, while customer loyalty refers to customers who consistently choose your brand over competitors. High customer retention generally indicates a high level of customer satisfaction.
Media Coverage: Press Mentions, Interviews
Media coverage refers to the amount of exposure your brand gets in the media. This can include press mentions, interviews, articles, etc. The more media coverage you get, the higher your brand visibility and awareness.
Content Creation: User-Generated Content, Viral Content
Content creation refers to the creation of content by your brand or by your users. User-generated content is content created by your users, while viral content is content that becomes popular very quickly. Both types contribute to increasing your brand visibility and engagement.
Audience Growth: Follower Count, Subscriber Count
Audience growth refers to the increase in the number of people who follow your brand on various platforms. Follower count is the number of people who follow your brand on social media, while subscriber count is the number of people who subscribe to your newsletters or other subscriptions. The higher these numbers, the larger your potential customer base.
Sales Impact: Incremental Sales, Revenue Increase
Sales impact refers to the effect of your marketing efforts on sales. Incremental sales are the number of additional sales made due to a specific campaign, while revenue increase is the increase in revenue due to these additional sales. High sales impact generally indicates a successful marketing campaign.
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page

