What is Centralization in an organization?
Centralization in an organization refers to the concentration of decision-making power at the top levels of management. This means that the top management makes most of the important decisions and controls the operations of the organization, while the lower levels of management and employees have limited decision-making authority.
There are various degrees of centralization, ranging from highly centralized to decentralized. In a highly centralized organization, the top management has complete control over the decisions and operations, while in a decentralized organization, decision-making power is distributed among different levels of management and employees.

centralization in an Organization – Advantages
One of the main benefits is that it allows for efficient decision-making, as the top management has access to all the necessary information and resources to make informed decisions. This can lead to quicker decision-making and a faster response to changes in the market or industry.
Centralization also allows for better coordination and control of the organization’s resources, as the top management can make decisions that align with the overall goals and strategies of the organization. This can lead to increased efficiency and productivity.
Centralization In An Organization – Disadvantages
However, there are also several disadvantages of centralization in an organization. One of the main disadvantages is that it can lead to a lack of innovation and creativity, as the lower levels of management and employees may not have the opportunity to contribute their ideas and insights. This can result in a lack of diversity in the decision-making process and may lead to missed opportunities or suboptimal solutions.
Another disadvantage of centralization is that it can create communication problems and slow down the decision-making process. As the top management makes most of the decisions, there may be a lack of communication and consultation with the lower levels of management and employees, which can lead to a lack of buy-in and commitment to the decisions.
Centralization In An Organization – Examples
There are several examples of organizations that have adopted a centralized structure. One example is the military, where the top commanders have complete control over the operations and decisions of the organization. Another example is a large corporation, where the CEO and top executives make most of the important decisions for the organization.
On the other hand, there are also examples of organizations that have adopted a decentralized structure. One example is a cooperative, where the decision-making power is distributed among the members of the organization. Another example is a federal government, where the power is divided among different levels of government, such as the national government, state governments, and local governments.
In conclusion, centralization in an organization refers to the concentration of decision-making power at the top levels of management. While it has several benefits, such as efficient decision-making and better coordination and control of resources, it also has several disadvantages, such as a lack of innovation and creativity, and communication problems. The degree of centralization will depend on the specific needs and goals of the organization.
What are various types of Centralized Organizations?
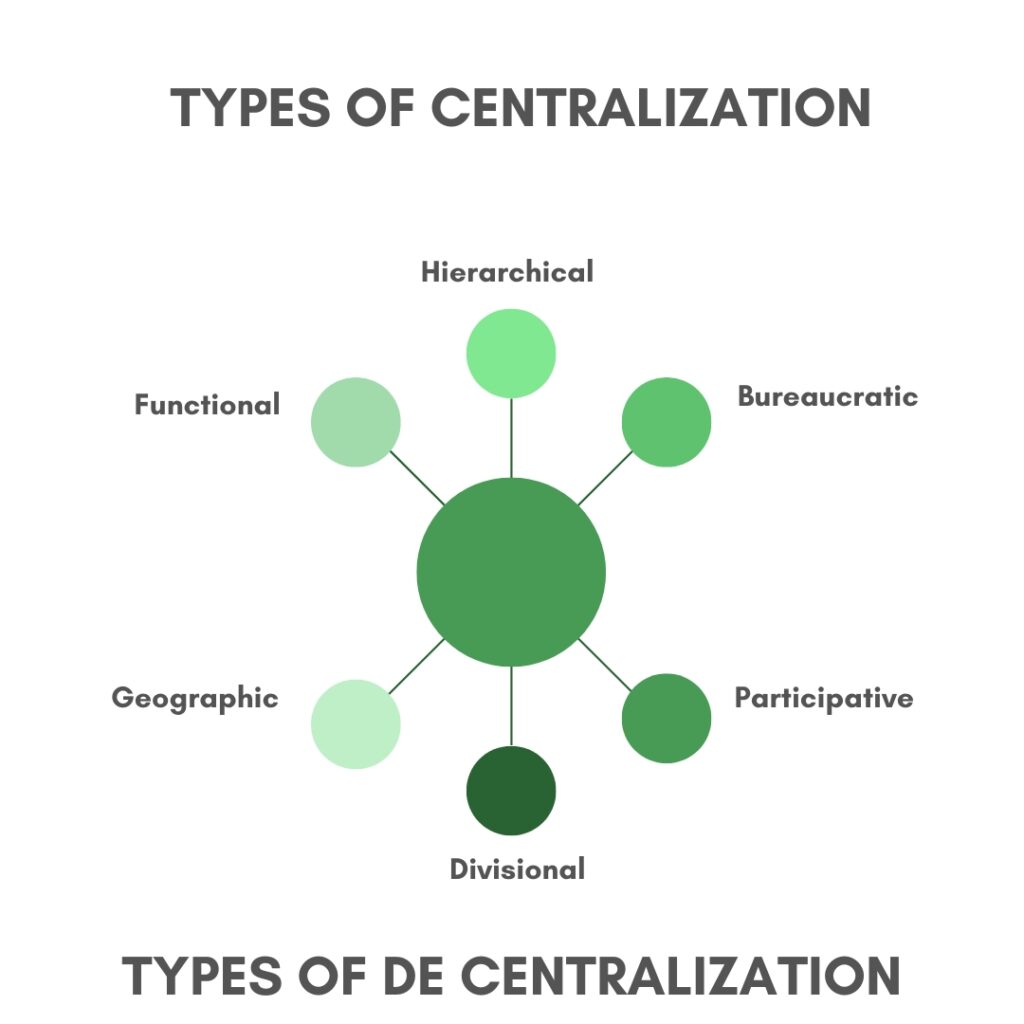
Centralized organizations can be divided into the following categories:
- Hierarchical centralization: This type of centralization is characterized by a tall organizational structure, where the top management has complete control over the decisions and operations of the organization. This type of centralization is commonly found in large corporations and military organizations.
- Bureaucratic centralization: This type of centralization is characterized by a formalized organizational structure with strict rules and procedures for decision-making and communication. This centralization is commonly found in government agencies and large non-profit organizations.
- Functional centralization: This type of centralization is characterized by the concentration of decision-making power in specific functional areas of the organization, such as marketing or finance. This type of centralization is commonly found in organizations with a narrow focus or specialization.
What are the core Leadership skills of a centralized organization?
There are several personal traits that are commonly associated with leaders of centralized organizations. These traits may include:
- Strong decision-making skills: Leaders of centralized organizations are responsible for making important decisions that impact the operations and direction of the organization. As such, they should have strong decision-making skills and the ability to analyze information and make informed decisions.
- Excellent communication skills: Leaders of centralized organizations need to be able to effectively communicate their decisions and expectations to the lower levels of management and employees. They should have excellent verbal and written communication skills and be able to clearly articulate their ideas and vision for the organization.
- Strong leadership skills: Leaders of centralized organizations should be able to inspire and motivate their team members to work towards the goals and objectives of the organization. They should be able to build trust and credibility with their team and create a positive and productive work environment.
- Strong organizational skills: Leaders of centralized organizations need to be able to effectively manage and coordinate the resources of the organization. This includes the ability to plan and prioritize tasks, delegate responsibilities, and track progress toward goals.
- Strategic thinking: Leaders of centralized organizations should be able to think strategically and have a long-term perspective. They should be able to anticipate and respond to changes in the market or industry and make decisions that align with the overall goals and strategy of the organization.
In conclusion, leaders of centralized organizations should possess strong decision-making skills, excellent communication skills, strong leadership skills, strong organizational skills, and strategic thinking. These traits will enable them to effectively lead and manage the organization and make informed decisions that align with its goals and objectives.
What are the various types of decentralized organizations?
- Geographic decentralization: This type of decentralization is characterized by the distribution of decision-making power among different geographic locations or regions. This type of decentralization is commonly found in multinational corporations and federal governments.
- Divisional decentralization: This type of decentralization is characterized by creating separate divisions or units within the organization, each with its own decision-making authority. This type of decentralization is commonly found in large corporations with diverse product or service offerings.
- Participative decentralization: This type of decentralization is characterized by the involvement of employees and lower levels of management in the decision-making process. This type of decentralization is commonly found in cooperatives and organizations with a flat organizational structure.
What are the core Leadership skills of a decentralized organization?
- Collaborative decision-making: Leaders in decentralized organizations should be able to effectively involve and collaborate with lower levels of management and employees in the decision-making process. This may involve seeking input and feedback from team members and incorporating their ideas and insights into the decision-making process.
- Empowerment: Leaders in decentralized organizations should be able to empower their team members by providing them with the resources, support, and autonomy they need to succeed. This may involve delegating tasks and responsibilities and allowing team members to make decisions within their areas of expertise.
- Adaptability: Leaders in decentralized organizations should be adaptable and able to respond to changing circumstances and environments. This may involve being open to new ideas and approaches and being able to quickly adapt to changes in the market or industry.
- Communication: Leaders in decentralized organizations should have strong communication skills and be able to effectively communicate with team members at all levels of the organization. This may involve using a variety of communication methods, such as in-person meetings, email, and video conferencing, to ensure that all team members are informed and involved in the decision-making process.
- Trust: Leaders in decentralized organizations should be able to build trust and credibility with their team members by being open, honest, and transparent in their communication and decision-making. This can help to foster a positive and productive work environment.

In conclusion, leaders in decentralized organizations should possess collaborative decision-making skills, the ability to empower their team members, adaptability, strong communication skills, and the ability to build trust. These traits will enable them to effectively lead and manage the organization and involve team members in the decision-making process.
Comparisons between centralized and decentralized organizations?

There have been several studies comparing centralized and decentralized organizations in terms of various factors such as efficiency, innovation, and decision-making. These studies have generally found that centralized organizations tend to be more efficient and effective at achieving their goals, as the top management has complete control over the operations and decisions of the organization. This can allow for quicker decision-making and a faster response to changes in the market or industry.
On the other hand, decentralized organizations tend to be more innovative and adaptable, as lower levels of management and employees have the opportunity to contribute their ideas and insights and make decisions within their areas of expertise. This can lead to a more diverse and creative decision-making process and a greater ability to respond to changing circumstances and environments.
However, it is important to note that the appropriate structure for an organization will depend on its specific needs and goals. A centralized structure may be more effective for organizations that require a high degree of control and coordination, while a decentralized structure may be more effective for organizations that value innovation and adaptability.
In conclusion, centralized and decentralized organizations have different strengths and weaknesses, and the appropriate structure for an organization will depend on its specific needs and goals. Centralized organizations tend to be more efficient and effective, while decentralized organizations tend to be more innovative and adaptable.
Can an organization take a mixed approach of centralization and decentralization?
Yes, companies can take a mixed approach, also known as a hybrid approach, to centralization and decentralization. This means that the organization combines elements of both centralized and decentralized structures in its operations and decision-making processes.
A hybrid approach allows an organization to take advantage of the benefits of both centralization and decentralization. For example, the organization may have a centralized structure for strategic decision-making, while allowing for decentralized decision-making at the operational level. This can allow for efficient decision-making at the top levels of management, while also allowing for local flexibility and adaptability.
A hybrid approach can also allow for a balance between efficiency and innovation. By centralizing certain decisions and operations, the organization can achieve efficiency, while also allowing for decentralization at other levels to encourage creativity and innovation.
However, it is important for an organization to carefully consider the appropriate balance between centralization and decentralization based on its specific needs and goals. If the balance is not properly managed, it can lead to confusion and conflict within the organization.
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page
