
What is Engel’s Law?
Engel’s law is one of the cornerstones of macroeconomic and income studies. Ernst Engel first observed the pattern now known as Engel’s Law in the Prussian census of 1817-1818. He noticed that as incomes increased, households spent a smaller portion of their income on food consumption than those with lower incomes. It states that every family must spend money on necessities such as education, health, clothing, housing rent, electricity and fuel, and entertainment. A list of a family’s expenditures on each of these items is known as the “Family Budget.“
Earnest Engel (1857) conducted a study of family budgets. For this purpose, he examined three groups of people: the poor, the middle class, and the wealthy. He drew the following conclusions from his research, which are known as ” Engel’s Law on Family Expenditures.”
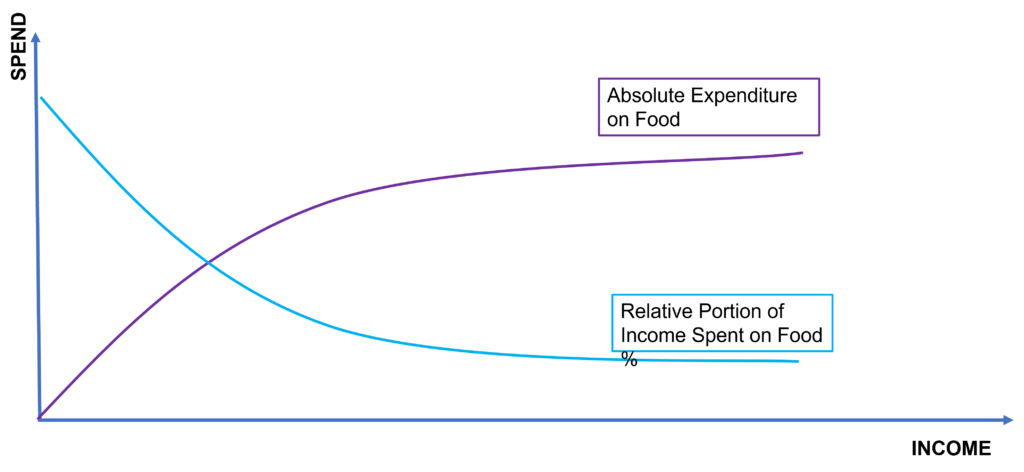
1) As a family’s income increases, the proportion of income spent on food decreases, while the actual amount spent on food increases.
2) Regardless of income level, the proportion of expenditures on clothing, housing rent, electricity, and fuel remains constant.
3) The proportion of a family’s income spent on education, health, and recreation rises with each increment of income.
Historical Background of Engel’s Law?
Earnest Engel (1857) conducted a study of family budgets. For this purpose, he examined three groups of people: the poor, the middle class, and the wealthy. He drew the following conclusions from his research, which are known as ” Engel’s Law on Family Expenditures.”
The law was later formalized by other economists, such as Alfred Marshall, who published a paper on the subject in 1890. The law has since been used extensively in economics, including in the study of consumer behavior and public policy.
Implications of Engel’s Law?
- Poor people may find it difficult to spend money on health, education, and recreation facilities because they must spend so much on food and other necessities.
- Because the poor must spend more on food expenditures, any increase in food prices or taxes would have a greater impact on the poor than on the wealthy.
Importance of the Family Budget
- Family budget studies help us determine the consumption patterns of individuals in various nations.
- We are able to comprehend the trends in people’s cost of living.
- The government can design its policies on the prices, subsidies, and taxes of various commodities in consideration of the national standard of living.
What Is an Engel Curve?
An Engel Curve is a graphical representation of Engel’s Law. It is a curve that shows the relationship between household income and the proportion of income spent on food (income elasticity). The curve is usually steep at the lower end of the income spectrum and flattens out at the higher end. This suggests that as income increases, the proportion of income spent on food decreases.
What Is the Engel’s Coefficient?
Engel’s Coefficient is a measure of the relationship between household income and the proportion of income spent on food. It is calculated by dividing the amount of money spent on food by the total household income. The higher the coefficient, the greater the proportion of the income spent on food.
It is widely used in determining the line of poverty in many countries or to depict the standard of living for a country.
Examples of Engel’s Law
Engel’s Law can be seen in many different countries and cultures around the world. For example, in the United States, the proportion of income spent on food decreases as household incomes increase. This can be seen in data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, which shows that households in the highest income brackets spend a smaller proportion of their income on food than those in the lowest income brackets.
In developing countries, the law is even more pronounced. In countries such as India, the poorest households spend up to half of their total income on food, while wealthier households spend only a small portion of their income on food.
Limitations of Engel’s Law
Engel’s Law is not an exact science and there are some limitations to its use. For example, the law does not take into account the cost of food in different regions or the cost of different types of food spending. It also does not take into account the cost of other goods and services that households may purchase.
Another limitation of Engel’s Law is that it assumes that all households have the same level of income. This is not always the case, as households can have different levels of income due to factors such as employment, investment, and inheritance.
Finally, Engel’s Law does not consider other factors that may affect consumer spendings, such as cultural norms and preferences.
How Is Engel’s Law Used Today?
Engel’s Law is still used today in a number of different fields. In economics, it is used to analyze consumer behavior and to make predictions about how people will spend their money. It is also used in public policy to assess the impact of various economic policies on households.
In marketing, Engel’s Law can be used to target different groups of consumers. For example, a company may use the law to target households with higher incomes, as they are more likely to have more disposable income to spend on other goods and services.
How to Use Engel’s Law for Marketing
Engel’s Law can be used to make better marketing decisions. For example, businesses can use the law to target different groups of consumers. By targeting households with higher incomes, businesses can increase their sales by focusing on customers who are more likely to have more disposable income to spend on other goods and services.
Businesses can also use the law to assess the impact of different economic policies. For example, businesses can look at how a policy change may affect the proportion of income households spend on food and make decisions accordingly.
Engel’s Law and Inequality
Engel’s Law is also relevant to the discussion of inequality. The law suggests that households with higher incomes tend to spend a smaller proportion of their income on food than those with lower incomes. This means that households with lower incomes are more likely to spend a larger portion of their income on food than those with higher incomes.
This suggests that inequality can be exacerbated by differences in the proportion of income spent on food. This can be seen in developed countries such as the United States, where the poorest households spend a larger portion of their income on food than the wealthiest households.
Practical Implications of Engel’s Law
Engel’s Law has practical implications for both businesses and policymakers. For businesses, it can be used to make better marketing decisions and assess the impact of different economic policies. For policymakers, it can provide useful insight into how different economic policies may affect households and the economy as a whole. Engel’s Law found prominence during COVID-19 when there were mass job cuts which resulted in higher proportions of food expenditure.
Engel’s Law can also be used to examine the impact of inequality. The law suggests that households with lower incomes are more likely to spend a larger portion of their income on food than those with higher incomes. This suggests that inequality can be exacerbated by differences in the proportion of income spent on food.
In conclusion, Engel’s Law is a powerful concept in economics that can provide useful insight into consumer behavior and the impact of different economic policies. It can be used by businesses to make better decisions and by policymakers to assess the impact of different policies. It is also relevant to the discussion of inequality, as it suggests that households with lower incomes are more likely to spend a larger portion of their income rises on food than those with higher incomes.
Follow our Page, Basics of Management, for more incisive insights on basic management and economics theories
Follow our Marketing Archives for more insightful articles
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page
