
Corporate Strategy Vs Business Strategy
Corporate strategy and business strategy are two distinct but closely related concepts that are critical to the success of any organization.
Corporate strategy is the overarching plan that guides an entire organization and its various business units or subsidiaries. It defines the overall direction and scope of the company, including its goals, objectives, and the industries or markets in which it operates. It also outlines the company’s overall competitive positioning and how it will allocate resources to achieve its goals. For example, a company may decide to focus on expanding its market share in a particular industry or enter a new market through acquisition.
A business strategy, on the other hand, refers to the specific plans and actions that a business unit or subsidiary takes to achieve its goals within the context of the overall corporate strategy. It focuses on how a business unit will compete in a specific market or industry and may include elements such as product development, marketing, and distribution. For example, a business unit may decide to target a specific customer segment or to differentiate its products through superior quality or innovation.
One of the most well-known corporate strategy examples is that of Amazon, which started as an online bookseller but diversified into other areas such as consumer electronics, clothing, and grocery delivery. Through its corporate strategy, Amazon has positioned itself as a leader in the e-commerce industry and has expanded into various other markets. A business strategy example from Amazon would be the development and launch of Amazon Prime, which provides customers with free 2-day shipping and access to streaming services, and has been a significant driver of customer loyalty and revenue growth for the company.
Another example is GE, which transformed its corporate strategy from being a traditional manufacturing company to a digital industrial company through the use of data and analytics to improve efficiency and productivity across its operations. GE’s business unit, GE Power, took a specific approach to its business strategy by focusing on increasing the efficiency and output of its power generation equipment through the use of digital technologies such as sensors and data analytics.
In conclusion, corporate strategy and business strategy are both essential components of any organization’s success. The corporate strategy provides the overall direction and scope for the company, while the business strategy focuses on how specific business units or subsidiaries will compete and succeed within that overall direction. Effective implementation of both corporate and business strategies can lead to increased market share, revenue growth, and customer loyalty.
In a Survey by PMI, the coveted body for Project Management, only 41% of the Leaders believe that they have competent people to frame strategic initiatives
PMI Report on Why Good Strategies Fail
Who is responsible for creating corporate strategy?
Corporate strategy and business strategy are typically developed and implemented by a company’s top management team, which may include the CEO, CFO, and other C-level executives. The process of creating and implementing corporate and business strategy is often a collaborative effort that involves input and participation from various departments and stakeholders within the organization.
The CEO or top management team is typically responsible for setting the overall direction and goals of the company through the development of corporate strategy. They will consider factors such as the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, as well as its current market position and future growth prospects. Once the corporate strategy is established, it is then the responsibility of the business unit managers or subsidiary leaders to develop and implement specific business strategies that align with the overall corporate strategy.
In some larger companies, there may be a dedicated corporate strategy or business development department responsible for facilitating the strategy development process and working closely with top management and other departments to ensure alignment and implementation. In smaller companies, the responsibility for creating and implementing corporate and business strategies may fall more heavily on the CEO and other top executives.
It’s also important to note that the process of creating and implementing corporate and business strategy is not a one-time event, but an ongoing process that requires regular review and adjustment in response to changing market conditions and internal developments.
67% of Projects Fail Due to poor Execution
Cascade.app
Who is responsible for creating a business strategy?
Business strategy is typically developed and implemented by the business unit managers or subsidiary leaders within an organization. These individuals are responsible for managing the day-to-day operations of a specific business unit or subsidiary and are best equipped to understand the unique challenges and opportunities facing that unit.
The process of creating a business strategy typically begins with a thorough analysis of the business unit’s current market position, including factors such as its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The business unit manager or leader will also consider the overall corporate strategy and goals set by top management, as well as any relevant industry trends or changes.
Once the analysis is complete, the business unit manager or leader will develop a specific plan for how the business unit will compete and succeed in the market. This plan will include elements such as product development, marketing, and distribution, as well as specific goals and objectives for the business unit. The business unit manager or leader is also responsible for implementing the strategy, which may involve working closely with other departments within the organization such as finance, marketing, and operations.
It’s also important to note that the process of creating and implementing a business strategy is not a one-time event, but an ongoing process that requires regular review and adjustment in response to changing market conditions and internal developments. Business unit managers and leaders must continuously monitor the performance of their unit and make adjustments to their strategy as needed to ensure they are aligned with the company’s overall corporate strategy and continue to meet their goals and objectives.
How do corporate strategy and business strategy get aligned?
Corporate strategy and business strategy are closely related, and it is essential that they are aligned to ensure the overall success of the organization. There are several ways in which corporate strategy and business strategy can be aligned:
- Top-down approach: This approach involves the development of corporate strategy by top management, which is then communicated and implemented by business unit managers and subsidiary leaders. Top management sets the overall direction and goals for the organization, and business unit managers and leaders develop specific strategies that align with the corporate strategy and support the organization’s overall goals.
- Bottom-up approach: This approach involves business unit managers and subsidiary leaders developing their own strategies, which are then reviewed and aligned with the overall corporate strategy by top management. This approach allows for a more localized focus on specific business units or subsidiaries, while still ensuring alignment with the overall corporate strategy.
- Collaborative approach: This approach involves a collaborative process between top management, business unit managers, and subsidiary leaders in developing both corporate and business strategies. This approach allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the organization’s overall direction, goals, and opportunities and allows for a more effective alignment of corporate and business strategies.
- Regular review and alignment: Once the corporate and business strategies are developed, it is essential to have a regular review process to ensure they are still aligned and are still achieving the desired results. This process allows for the adaptation of strategies to changing market conditions and internal developments and ensures that the company stays on course.
In summary, aligning corporate strategy and business strategy is a continuous process that requires regular communication and collaboration between top management, business unit managers, and subsidiary leaders. By ensuring alignment, organizations can ensure that all efforts and resources are directed toward achieving the overall goals and objectives of the company.
Differentiate corporate strategy and business strategy
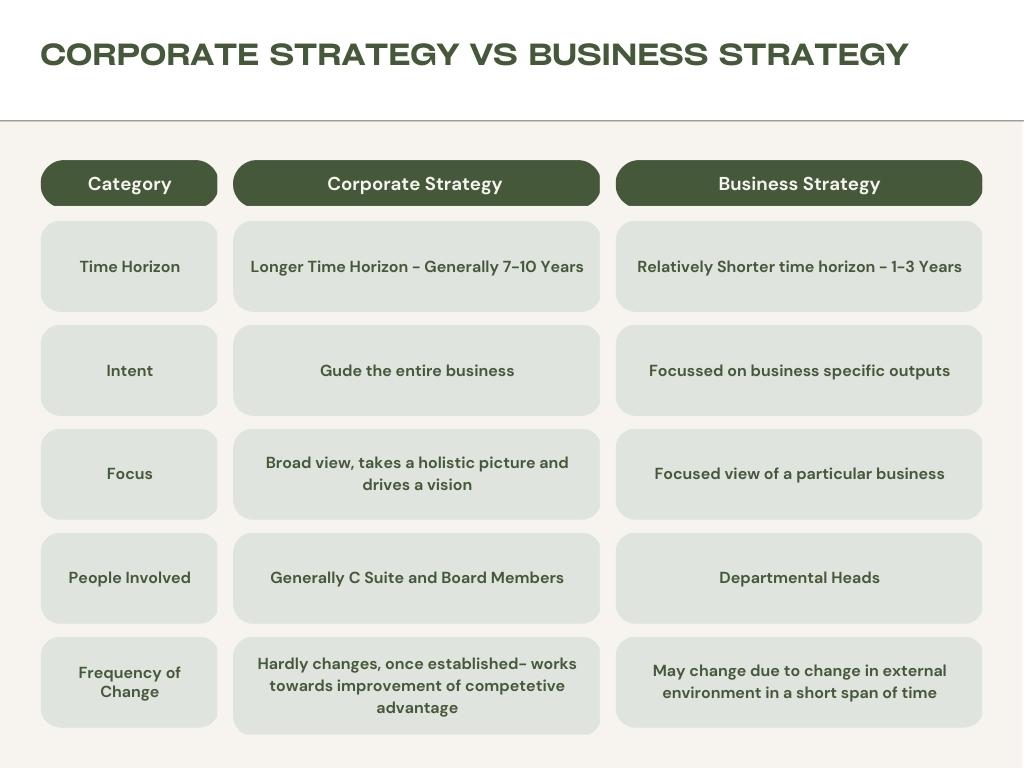
Corporate strategy and business strategy are both important aspects of organizational management, but they have some key differences in terms of time horizon, intent, focus, and the people involved.
Time Horizon: Corporate strategy generally has a longer time horizon, often looking ahead several years or even decades. It sets the overall direction and goals for the organization and guides decision-making for the long term. A business strategy, on the other hand, typically has a shorter time horizon, focusing on specific goals and objectives for the next one to three years.
Intent: The intent of the corporate strategy is to guide the overall direction and scope of the organization, including its goals, objectives, and the industries or markets in which it operates. It outlines the company’s overall competitive positioning and how it will allocate resources to achieve its goals. A business strategy, on the other hand, focuses on the specific plans and actions that a business unit or subsidiary takes to achieve its goals within the context of the overall corporate strategy.
Focus: Corporate strategy is a broad, overall plan that guides the entire organization, taking into account the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It also considers the company’s market position and future growth prospects. A business strategy, on the other hand, is more specific, focusing on how a business unit or subsidiary will compete in a specific market or industry and may include elements such as product development, marketing, and distribution.
People Involved: Corporate strategy is typically developed and implemented by a company’s top management team, which may include the CEO, CFO, and other C-level executives. Business strategy is developed and implemented by the business unit managers or subsidiary leaders within an organization. They are responsible for managing the day-to-day operations of a specific business unit or subsidiary and are best equipped to understand the unique challenges and opportunities facing that unit.
In summary, corporate strategy is a broad, overall plan that guides the entire organization, while business strategy is more specific, focusing on the plans and actions of a specific business unit or subsidiary. Corporate strategy has a longer time horizon, and its intent is to guide the overall direction and scope of the organization, while business strategy is shorter and its intent is to achieve specific goals and objectives within the context of the overall corporate strategy. Both are developed and implemented by different people, Corporate strategy by the top management team and business strategy by the business unit managers or subsidiary leaders.
corporate strategy vs business strategy example
Here are a few examples of corporate strategy and business strategy in real-life scenarios:
Corporate Strategy:
- A retail company decides to expand its operations into online sales and delivery to reach a wider customer base and increase revenue. This is an example of a diversification corporate strategy.
- A manufacturing company decides to shift its focus from fossil fuel-based energy to renewable energy sources. This is an example of a corporate strategy that is focused on sustainability.
- A technology company decides to acquire several smaller companies in the same industry to increase its market share and expand its product offerings. This is an example of a corporate strategy focused on growth through acquisition.
Business Strategy:
- A business unit within a retail company decides to target a specific customer segment, such as millennial parents, with its marketing efforts and product offerings. This is an example of a business strategy focused on segmentation.
- A business unit within a manufacturing company decides to differentiate its products through superior quality and innovation, in order to charge a premium price. This is an example of a business strategy focused on differentiation.
- A business unit within a technology company decides to expand its service offerings to include consulting and training services to increase revenue and customer loyalty. This is an example of a business strategy focused on expanding into related industries.
It’s important to note that the examples provided are general in nature and the strategies may be more complex in real-life scenarios.
What are various types of corporate strategy?
Corporate strategy is the overarching plan that guides an entire organization and its various business units or subsidiaries. There are several types of corporate strategies that companies can adopt to achieve their goals and objectives. Some of the most common types of the corporate strategy include:
- Growth strategy: This type of corporate strategy focuses on expanding the company’s market share, revenue, or customer base. This may be achieved through a variety of methods such as expanding into new markets, launching new products or services, or acquiring other companies.
- Diversification strategy: This type of corporate strategy involves expanding the company’s operations into new industries or markets that are not related to its current business. This can be achieved through organic growth or acquisition.
- Stability strategy: This type of corporate strategy focuses on maintaining the company’s current market position and operations. It may involve cost-cutting measures, efficiency improvements, or other tactics to preserve the company’s current revenue and profitability.
- Retrenchment strategy: This type of corporate strategy involves reducing the company’s operations, often in response to a decline in revenue or profitability. It may involve divesting non-core business units, reducing staff, or closing unprofitable operations.
- Turnaround strategy: This type of corporate strategy is implemented when a company is facing financial difficulties, and it is intended to restore the company to profitability. This strategy usually involves a combination of cost-cutting measures, operational changes, and sometimes, the replacement of management.
- Sustainability strategy: This type of corporate strategy is focused on addressing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues and integrating them into the company’s decision-making process. It aims to reduce the company’s negative impact on the environment, improve its social and governance performance, and to create long-term value for all stakeholders.
It’s important to note that companies may adopt multiple types of corporate strategy simultaneously or may shift between them depending on the market conditions and internal developments. The best strategy depends on the company’s goals, resources, and the industry it operates in.
What is the importance of a corporate strategy?
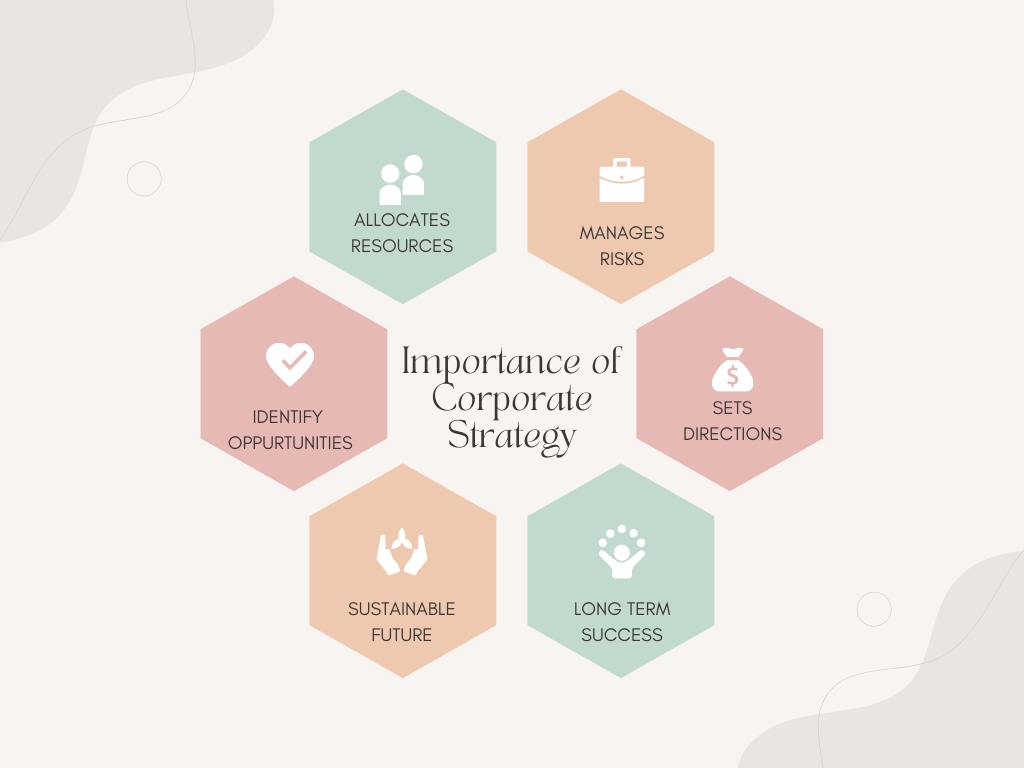
A corporate strategy is important for several reasons. Some of the key reasons include:
- Setting direction: A corporate strategy provides the overall direction and scope for the organization, including its goals and objectives. It helps to align the efforts of all stakeholders, including employees, shareholders, and customers, towards a common vision and mission.
- Allocating resources: A corporate strategy also helps to guide the allocation of resources to achieve the organization’s goals and objectives. This can include financial resources, human resources, and technology resources.
- Identifying growth opportunities: A corporate strategy helps organizations to identify new growth opportunities and to make informed decisions about entering new markets or developing new products or services.
- Managing risks: A corporate strategy also helps organizations to manage and mitigate risks associated with their operations. It can help organizations identify and prepare for potential threats, such as changes in the market, economic downturns, or disruptions caused by new technologies.
- Achieving long-term success: By setting clear goals and objectives, and by aligning the efforts of all stakeholders, a corporate strategy can help organizations to achieve long-term success. It can also help organizations to adapt to changing market conditions and to stay competitive in an ever-changing business environment.
- Meeting stakeholders’ expectations: A corporate strategy helps organizations to meet the expectations of their stakeholders, including shareholders, customers, employees, and other stakeholders. It also helps to create a culture of transparency and accountability, which helps to build trust between the company and its stakeholders.
- Creating a sustainable future: A corporate strategy that includes sustainability considerations allows organizations to create a sustainable future for their business and its stakeholders by addressing environmental, social, and governance issues.
In summary, a corporate strategy is crucial for setting direction, allocating resources, identifying growth opportunities, managing risks, achieving long-term success, meeting stakeholders’ expectations, and creating a sustainable future. It helps organizations to make informed decisions that will enable them to achieve their goals and stay competitive in the long term.
What makes a good corporate strategy?
A good corporate strategy should have several key characteristics to make it effective:
- Clear and measurable goals: A good corporate strategy should have clear and measurable goals that align with the overall vision and mission of the organization. These goals should be specific, achievable, realistic, and time-bound, and they should be communicated clearly to all stakeholders.
- Alignment with the company’s strengths: A good corporate strategy should take into account the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, and should be aligned with the company’s core competencies. This will help to ensure that the company is well-positioned to succeed in the marketplace.
- Flexibility: A good corporate strategy should be flexible and adaptable to changing market conditions and internal developments. It should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
- Communicated and understood: A good corporate strategy should be communicated clearly and understood by all stakeholders, including employees, shareholders, and customers. This will help to ensure that everyone is aligned and working towards the same goals.
- Actionable: A good corporate strategy should include specific actions and plans that can be implemented to achieve the company’s goals. It should be actionable and should outline how the company will allocate its resources to achieve its objectives.
- Sustainability considerations: A good corporate strategy should take into account the environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues that can affect the company’s future. It should provide a framework for addressing these issues and integrating them in the company’s decision-making process.
- Aligned with business strategy: A good corporate strategy should be aligned with the business strategies of the company’s units and subsidiaries. This will help
What are the corporate strategies of Nike, Zara, and Walmart?
Nike, Zara, and Walmart are all large, global companies with different corporate strategies, which I’ll describe below.
Nike: Nike has a growth strategy as a key element of its corporate strategy. Nike focuses on expanding its market share and revenue by introducing new products, expanding into new markets, and increasing its online presence. Nike is also focusing on sustainability as a corporate strategy, which includes reducing the environmental impact of its operations and promoting fair labor practices.
Zara: Zara has a corporate strategy focused on fast fashion, which involves quickly producing trendy clothing styles at a low cost. This strategy allows Zara to respond quickly to changing fashion trends, which helps to differentiate the company from competitors. Zara also has a diversification strategy, it’s expanding its product line to include accessories and home goods, and it’s also expanding its market to include online and offline retail, wholesale, and franchise.
Walmart: Walmart’s corporate strategy is focused on cost leadership, which involves keeping costs low to offer low prices to customers. This strategy is achieved through a combination of buying in bulk, using efficient supply chain management and technology, and keeping overhead costs low. Walmart is also focused on expanding its e-commerce capabilities and increasing its online presence to better compete with other online retailers like Amazon. Additionally, Walmart is also focused on sustainability as a corporate strategy, which includes reducing the environmental impact of its operations, promoting fair labor practices, and investing in renewable energy.
It’s worth noting that these are general descriptions of the corporate strategies of these companies, and their strategies may evolve over time. Additionally, companies may have multiple strategies in place, and they may shift between them depending on market conditions and internal developments.
Does having a corporate strategy actually matter?
Having a corporate strategy can be important for companies, as it provides direction and guides decision-making, aligns the efforts of all stakeholders, and helps to allocate resources. A well-designed corporate strategy can also help companies to identify new growth opportunities, manage risks, and achieve long-term success.
However, it’s worth noting that having a corporate strategy does not guarantee success. A company may have a well-designed corporate strategy, but if it’s not executed well or if the external environment changes, the company may not achieve its goals. Additionally, in some cases, companies may be able to achieve success without a formal corporate strategy, for example, if they are able to react quickly to changes in the market or if they have a strong culture of innovation.
An example of a company that succeeded without a formal corporate strategy is Amazon. In the beginning, the company had a very clear goal of providing the best customer experience, but they didn’t have a formal corporate strategy. Amazon’s success was driven by its ability to quickly adapt to changes in the market and to take advantage of new technologies. The company has grown rapidly by diversifying into new markets, such as consumer electronics, clothing, and grocery delivery, and by investing in new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and cloud computing.
On the other hand, Blockbuster is an example of a company that failed with a corporate strategy. Blockbuster was once the dominant player in the video rental market, but it was slow to adapt to the changing market conditions and the emergence of new technologies. The company had a corporate strategy that focused on maintaining its existing business model and expanding its physical footprint, instead of investing in new.
what is the difference between corporate strategy and finance strategy?
Corporate strategy and finance strategy are two distinct but closely related concepts that are critical to the success of any organization.
Corporate strategy is the overarching plan that guides an entire organization and its various business units or subsidiaries. It defines the overall direction and scope of the company, including its goals, objectives, and the industries or markets in which it operates. It also outlines the company’s overall competitive positioning and how it will allocate resources to achieve its goals. Corporate strategy is not limited to just a financial perspective but takes a holistic approach toward the company’s overall vision, mission and objectives.
Finance strategy, on the other hand, is a sub-part of corporate strategy, and it is more specific to the financial aspects of the company. It deals with the management of financial resources, investment decisions, and financing strategies. It focuses on how the company will generate revenue, manage costs, and maximize shareholder value. The finance strategy includes budgeting, forecasting, financial analysis, financial planning, and risk management. It also deals with investment decisions and financing strategies such as debt or equity financing, mergers and acquisitions, and divestitures.
In summary, corporate strategy is a broad, overall plan that guides the entire organization, while finance strategy is a specific aspect of corporate strategy that deals with the management of financial resources and investment decisions. Both are critical to the success of an organization, but the focus of each is different. The corporate strategy provides the overall direction and scope for the company, while the finance strategy focuses on how the company will generate revenue, manage costs, and maximize shareholder value.
Samrat is a Delhi-based MBA from the Indian Institute of Management. He is a Strategy, AI, and Marketing Enthusiast and passionately writes about core and emerging topics in Management studies. Reach out to his LinkedIn for a discussion or follow his Quora Page
